|
African-American Vernacular English
African-American Vernacular English (AAVE, ), also referred to as Black (Vernacular) English, Black English Vernacular, or occasionally Ebonics (a colloquial, controversial term), is the variety of English natively spoken, particularly in urban communities, by most working- and middle-class African Americans and some Black Canadians. Having its own unique grammatical, vocabulary, and accent features, AAVE is employed by middle-class Black Americans as the more informal and casual end of a sociolinguistic continuum. However, in formal speaking contexts, speakers tend to switch to more standard English grammar and vocabulary, usually while retaining elements of the nonstandard accent. Despite being widespread throughout the United States, AAVE should not be assumed to be the native dialect of all African Americans. As with most African-American English, African-American Vernacular English shares a large portion of its grammar and phonology with the rural dialects of the Sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Armstrong
Louis Daniel Armstrong (August 4, 1901 – July 6, 1971), nicknamed "Satchmo", "Satch", and "Pops", was an American trumpeter and vocalist. He was among the most influential figures in jazz. His career spanned five decades and several eras in the history of jazz. Armstrong was born and raised in New Orleans. Coming to prominence in the 1920s as an inventive trumpet and cornet player, Armstrong was a foundational influence in jazz, shifting the focus of the music from collective improvisation to solo performance. Around 1922, he followed his mentor, Joe "King" Oliver, to Chicago to play in the . In Chicago, he spent time with other popular jazz musicians, reconnecting with his friend Bix Beiderbecke and spending time with Hoagy Carmichael and Lil Hardin. He earned a reputation at "cutting contests", and his fame reached band leader Fletcher Henderson. Henderson persuaded Armstrong to come to New York City, where he became a featured and musically influential band soloist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince Albert Tobacco
Prince Albert is an American brand of hand-rolled-cigarette and pipe tobacco, introduced by the R.J. Reynolds Tobacco Company in 1907. It has been owned since 1987 by John Middleton Inc. History Prince Albert is one of the more popular independent brands of pipe tobacco in the United States; in the 1930s, it was the "second largest money-maker" for Reynolds. More recently, it has also become available in the form of pipe-tobacco cigars. (A 1960s experiment with filtered cigarettes was deemed a failure.) The blend is burley-based and remains one of America's top-selling pipe tobaccos. The tobacco was named by R. J. Reynolds after Edward VII, who was known as Prince Albert before being crowned as the King of England. The portrait of Prince Albert was based on one acquired by Reynolds at a tea party with Mark Twain. Prince Albert's cigars are available in packs of 5. Prince Albert's pipe tobacco is available in pouches and tins. Varieties Cigars *Prince Albert's Soft Cherr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Swing
Western swing music is a subgenre of American country music that originated in the late 1920s in the Western United States, West and Southern United States, South among the region's Western music (North America), Western string bands. It is dance music, often with an up-tempo beat, which attracted huge crowds to dance halls and clubs in Texas, Oklahoma and California during the 1930s and 1940s until a federal war-time nightclub tax in 1944 contributed to the genre's decline.''Stomping the Blues''. Albert Murray. Da Capo Press. 2000. page 109, 110. , The movement was an outgrowth of jazz. The music is an amalgamation of American roots music, rural, Western music (North America), cowboy, polka, Old-time music, old-time, Dixieland jazz, and blues blended with swing music, swing; and played by a Musical improvisation, hot string band often augmented with drums, saxophones, pianos and, notably, the steel guitar. The electrically amplified stringed instruments, especially the steel g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lindy Hop
The Lindy Hop is an American dance which was born in the Black communities of Harlem, New York City, in 1928 and has evolved since then. It was very popular during the swing era of the late 1930s and early 1940s. Lindy is a fusion of many dances that preceded it or were popular during its development but is mainly based on jazz dance, jazz, tap dance, tap, breakaway (dance), breakaway, and Charleston (dance), Charleston. It is frequently described as a jazz dance and is a member of the swing (dance), swing dance family. In its development, the Lindy Hop combined elements of both partnered and solo dancing by using the movements and improvisation of African-American dances along with the formal eight-count structure of European partner dances – most clearly illustrated in the Lindy's basic step, the swingout. In this step's open position, each dancer is generally connected hand-to-hand; in its closed position, leads and follows are connected as though in an embrace on one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jitterbug
Jitterbug is a generalized term used to describe swing dancing. It is often synonymous with the lindy hop dance but might include elements of the jive, east coast swing, collegiate shag, charleston, balboa and other swing dances. Swing dancing originated in the African-American communities of New York City in the early 20th century. Many nightclubs had a whites-only or blacks-only policy due to racial segregation, however the Savoy Ballroom in Harlem had a no-discrimination policy which allowed whites and blacks to dance together and it was there that the lindy hop dance flourished, started by dancers such as George Snowden and Frank Manning. The term jitterbug was originally a ridicule used by black patrons to describe whites who started to dance the lindy hop, as they were dancing faster and jumpier than was intended, like "jittering bugs", although it quickly lost its negative connotation as the more erratic version caught on. Both the lindy hop and the "jitterbug" became ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
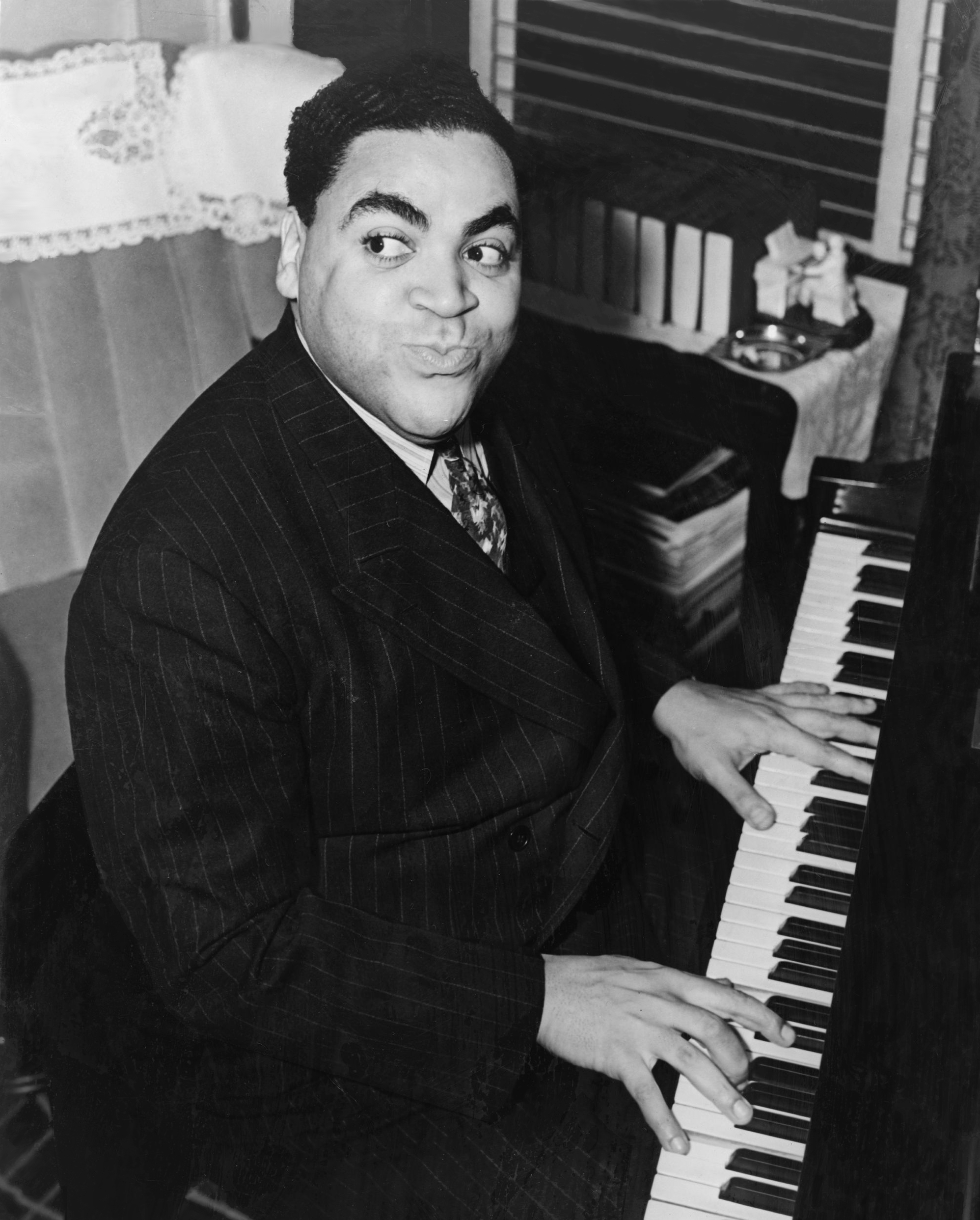
Stride Piano
Stride jazz piano, often shortened to stride, is a jazz piano style that arose from ragtime players. Prominent stride pianists include James P. Johnson, Willie "The Lion" Smith, Willie "the Lion" Smith, Fats Waller, Luckey Roberts, Mrs Mills and Mary Lou Williams. Technique Stride employed left hand techniques from ragtime, wider use of the piano's range, and quick tempos. Compositions were written but were also intended to be improvised. The term "stride" comes from the idea of the pianist's left hand leaping, or "striding", across the piano. The left hand characteristically plays a four-beat pulse (music), pulse with a single bass note, octave, major seventh, minor seventh or major tenth Interval (music), interval on the first and third Beat (music), beats, and a Chord (music), chord on the second and fourth beats. Occasionally this pattern is reversed by placing the chord on the Downbeat and upbeat, downbeat and bass notes on the upbeat. Unlike performers of the ragtime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jelly Roll Morton
Ferdinand Joseph LaMothe (later Morton; c. September 20, 1890 – July 10, 1941), known professionally as Jelly Roll Morton, was an American ragtime and jazz pianist, bandleader, and composer. Morton was jazz's first arranger, proving that a genre rooted in improvisation could retain its essential characteristics when notated. His composition "Jelly Roll Blues", published in 1915, was one of the first published jazz compositions. He also claimed to have invented the genre. Morton also wrote "King Porter Stomp", "Wolverine Blues", "Black Bottom Stomp", and "I Thought I Heard Buddy Bolden Say", the last being a tribute to New Orleans musicians from the turn of the 20th century. Morton's claim to have invented jazz in 1902 was criticized. Music critic Scott Yanow wrote, "Jelly Roll Morton did himself a lot of harm posthumously by exaggerating his worth...Morton's accomplishments as an early innovator are so vast that he did not really need to stretch the truth." Gunther Schuller ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coitus
Sexual intercourse (or coitus or copulation) is a sexual activity typically involving the insertion and thrusting of the penis into the vagina for sexual pleasure or reproduction.Sexual intercourse most commonly means penile–vaginal penetration for sexual pleasure or sexual reproduction; dictionary sources state that it especially means this, and scholarly sources over the years agree. See, for example; * * * * * * * * * This is also known as vaginal intercourse or vaginal sex. Other forms of penetrative sexual intercourse include anal sex (penetration of the anus by the penis), oral sex (penetration of the mouth by the penis or oral penetration of the female genitalia), fingering (sexual penetration by the fingers) and penetration by use of a dildo (especially a strap-on dildo). These activities involve physical intimacy between two or more individuals and are usually used among humans solely for physical or emotional pleasure and can contribute to human bonding. There ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hoochie Coochie
The hoochie coochie () is a catch-all term to describe several sexually provocative belly dance-like dances from the mid-to late 1800s. Also spelled hootchy-kootchy and a number of other variations, it is often associated with "The Streets of Cairo, or the Poor Little Country Maid" song, also known as "the snake charmer song". "Hoochie Coochie Man" (originally titled "I'm Your Hoochie Cooche Man") is also a blues standard written by Willie Dixon and first recorded by Muddy Waters in Chicago, January 7, 1954. Numerous cover versions of this classic continue to be recorded. Hoochie Coochie is also mentioned in Alan Jackson's hit country music song "Chattahoochee", and the Jerry Leiber and Mike Stoller songs "Little Egypt (Ying-Yang)" and " Saved" (sung by LaVern Baker). Overview Such dances, or something similar, were performed at the Crystal Palace Exhibition in London in 1851, the Centennial Exhibition in Philadelphia in 1876, and the World's Fair in Paris in 1889. Although s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minnie The Moocher
"Minnie the Moocher" is a jazz- scat song first recorded in 1931 by Cab Calloway and His Orchestra, selling over a million copies. "Minnie the Moocher" is most famous for its nonsensical ad libbed (" scat") lyrics (for example, "Hi De Hi De Hi De Ho"). In performances, Calloway would have the audience and the band members participate by repeating each scat phrase in a form of call and response, until making it too fast and complicated for the audience to replicate it. Released by Brunswick Records, the song was the biggest chart-topper of 1931. Calloway publicized and then celebrated a "12th birthday" for the song on June 17, 1943, while performing at New York's Strand Theatre. He reported that he was then singing the song at both beginning and end of four performances daily, and then estimated his total performances to date: "she's kicked the gong around for me more than 40,000 times." In 1978, Calloway recorded a disco version of "Minnie the Moocher" on RCA Records which re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substance Intoxication
Substance intoxication is a transient condition of altered consciousness and behavior associated with recent use of a substance. It is often maladaptive and impairing, but reversible. If the symptoms are severe, the term "substance intoxication delirium" may be used. Substance intoxication may often accompany a substance use disorder (SUD); if persistent substance-related problems exist, SUD is the preferred diagnosis. The term "intoxicated", used by laymen, most often refers to alcohol. Classification The ICD-10 ''Mental and Behavioural Disorders due to psychoactive substance use'' shows: *F10. alcohol *F11. opioids *F12. cannabinoids *F13. sedatives and hypnotics *F14. cocaine *F15. caffeine *F16. hallucinogens *F17. tobacco *F18. volatile solvent *F19. multiple drug use and use of other psychoactive substances Caffeine The discussion over whether the coffee (caffeine) “buzz” counted as intoxication or not was hotly debated during the early to mid 16th century. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)


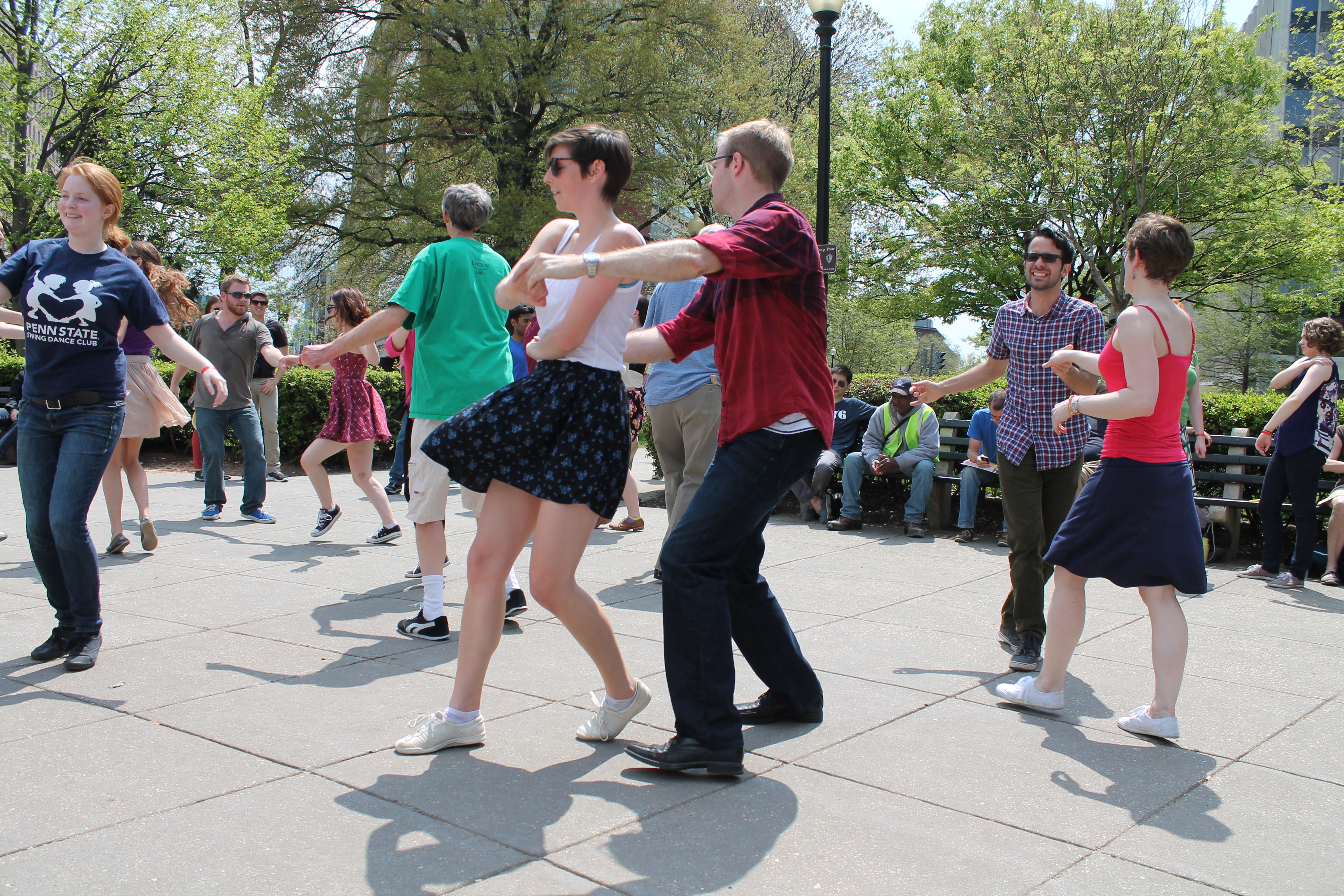



_de_Pietro_Aretino%2C_2.jpg)