|
Ginkgoales
Ginkgoales are a gymnosperm order containing only one extant species: ''Ginkgo biloba'', the ginkgo tree. It is monotypic, (the only taxon) within the class Ginkgoopsida, which itself is monotypic within the division Ginkgophyta . The order includes five families, of which only Ginkgoaceae remains extant. History Ginkgophyta and Cycadophyta have a very ancient divergence dating to the early Carboniferous. The earliest representative of the group in the fossil record is probably '' Trichopitys'' from the Asselian (299-293 million years ago) of France. The earliest representatives of ''Ginkgo'', represented by reproductive organs similar to the living species, first appear in the Middle Jurassic, alongside other, related forms such as ''Yimaia'' and ''Karkenia'', which have differently arranged reproductive structures and seeds associated with ''Ginkgo''-like leaves. The diversity of Ginkgoales declined during the Late Cretaceous and Cenozoic, coincident with the rise of flowerin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ginkgo Biloba
''Ginkgo biloba'', commonly known as ginkgo or gingko ( ), also known as the maidenhair tree, is a species of tree native to China. It is the last living species in the order Ginkgoales, which first appeared over 290 million years ago. Fossils very similar to the living species, belonging to the genus ''Ginkgo'', extend back to the Middle Jurassic approximately 170 million years ago. The tree was cultivated early in human history and remains commonly planted. Ginkgo leaf extract is commonly used as a dietary supplement, but there is no scientific evidence that it supports human health or is effective against any disease. Etymology The genus name is regarded as a misspelling of the Japanese pronunciation ''gin kyo'' for the kanji 銀杏 meaning "silver apricot", which is found in Chinese herbology literature such as (Daily Use Materia Medica) (1329) and ''Compendium of Materia Medica'' published in 1578.T. Hori, A historical survey of Ginkgo biloba based on Japanese and Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yimaiaceae
''Yimaia'' is a extinct genus of Ginkgoalean tree, and the only member of the family Yimaiaceae. In botanical form classification, its a form taxon for ginkgoalean ovulate organs. ''Yimaia'' species are distinguished from other Ginkgoales by the presence of "Ovulate organs consisting of a peduncle and up to eight or nine terminal, sessile, contiguous and orthotropous (straight, upright and with a micropyle at apex) ovules." The ovules are associated with leaves of either ''Baiera'' or ''Ginkgoites'' leaf morphospecies. Fossils have been found in Middle Jurassic deposits in China. Species * ''Yimaia capituliformis'' Zhou, Zheng and Zhang, 2006 Daohugou Bed, China, Callovian Associated with leaves of ''Ginkgoites'' type *''Yimaia qinghaiensis'' Wu, Yang and Zhou, 2006 Shimengou Formation, Qinghai, China, Middle Jurassic Associated with leaves of ''Baiera furcata'' type. * ''Yimaia recurva'' (type) Zhou et Zhang, 1988 Yima Formation, Henan, China, Middle Jurassic The Middle Ju ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yimaia
''Yimaia'' is a extinct genus of Ginkgoalean tree, and the only member of the family Yimaiaceae. In botanical form classification, its a form taxon for ginkgoalean ovulate organs. ''Yimaia'' species are distinguished from other Ginkgoales by the presence of "Ovulate organs consisting of a peduncle and up to eight or nine terminal, sessile, contiguous and orthotropous (straight, upright and with a micropyle at apex) ovules." The ovules are associated with leaves of either ''Baiera'' or ''Ginkgoites'' leaf morphospecies. Fossils have been found in Middle Jurassic deposits in China. Species * ''Yimaia capituliformis'' Zhou, Zheng and Zhang, 2006 Daohugou Bed, China, Callovian Associated with leaves of ''Ginkgoites'' type *''Yimaia qinghaiensis'' Wu, Yang and Zhou, 2006 Shimengou Formation, Qinghai, China, Middle Jurassic Associated with leaves of ''Baiera furcata'' type. * ''Yimaia recurva'' (type) Zhou et Zhang, 1988 Yima Formation, Henan, China, Middle Jurassic The Middle Ju ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ginkgo
''Ginkgo'' is a genus of non-flowering seed plants. The scientific name is also used as the English name. The order to which it belongs, Ginkgoales, first appeared in the Permian, 270 million years ago, and is now the only living genus within the order. The rate of evolution within the genus has been slow, and almost all its species had become extinct by the end of the Pliocene. The sole surviving species, ''Ginkgo biloba'' is only found in the wild in China, but is cultivated around the world. The relationships between ginkgos and other groups of plants are not fully resolved. Prehistory The ginkgo (''Ginkgo biloba'') is a living fossil, with fossils similar to the modern plant dating back to the Permian, 270 million years ago. The closest living relatives of the clade are the cycads, which share with the extant ''G. biloba'' the characteristic of motile sperm. The ginkgo and cycad lineages are thought to have an extremely ancient divergence dating to the early Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleozoic Era; the following Triassic Period belongs to the Mesozoic Era. The concept of the Permian was introduced in 1841 by geologist Sir Roderick Murchison, who named it after the region of Perm in Russia. The Permian witnessed the diversification of the two groups of amniotes, the synapsids and the sauropsids ( reptiles). The world at the time was dominated by the supercontinent Pangaea, which had formed due to the collision of Euramerica and Gondwana during the Carboniferous. Pangaea was surrounded by the superocean Panthalassa. The Carboniferous rainforest collapse left behind vast regions of desert within the continental interior. Amniotes, which could better cope with these drier conditions, rose to dominance in place of their am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphenobaiera
''Sphenobaiera'' is a form genus for plant leaves found in rocks from Triassic to Cretaceous periods. The genus ''Sphenobaiera'' is used for plants with wedge-shaped leaves that can be distinguished from ''Ginkgo'', ''Ginkgoites'' and ''Baiera'' by the lack of a Petiole (botany), petiole. It became extinct about . The family to which this genus belongs has not been conclusively established; an affinity with the Karkeniaceae has been suggested on morphological grounds. Locations ''Sphenobaiera ikorfatensis'' (Seward) Florin f. ''papillata'' Samylina has been found in Lower Cretaceous formations of Western Greenland, the Upper Jurassic of the Asiatic USSR, and the basal rock unit of the Lakota formation of the Black Hills, which Fontaine considered to be of Lower Cretaceous age. It is a ginkgophyte. In Paleorrota geopark in Brazil. Upper Triassic period, the Santa Maria Formation. References Prehistoric gymnosperm genera Late Cretaceous plants Ginkgophyta {{cretaceo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gymnosperm
The gymnosperms ( lit. revealed seeds) are a group of seed-producing plants that includes conifers, cycads, ''Ginkgo'', and gnetophytes, forming the clade Gymnospermae. The term ''gymnosperm'' comes from the composite word in el, γυμνόσπερμος ( el, γυμνός, translit=gymnos, lit=naked, label=none and el, σπέρμα, translit=sperma, lit=seed, label=none), literally meaning 'naked seeds'. The name is based on the unenclosed condition of their seeds (called ovules in their unfertilized state). The non-encased condition of their seeds contrasts with the seeds and ovules of flowering plants (angiosperms), which are enclosed within an ovary. Gymnosperm seeds develop either on the surface of scales or leaves, which are often modified to form cones, or solitary as in yew, ''Torreya'', ''Ginkgo''. Gymnosperm lifecycles involve alternation of generations. They have a dominant diploid sporophyte phase and a reduced haploid gametophyte phase which is dependent on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karkenia
Karkeniaceae is an extinct family in the order Ginkgoales. It contains the single genus ''Karkenia''. It is distinguished by "Ovulate organs consisting of a peduncle and helically arranged, up to about 100 small, orthotropous but incurved ovules; pedicel present; nucellus largely free." Unlike other ginkgoales, the seeds are borne on cone-like aggregations. Ovuluate organs of ''Karkenia'' are associated with leaves of the ''Ginkgoites'', ''Sphenobaiera'' and '' Eretmophyllum'' types. It is known from the Hettangian to Aptian The Aptian is an age in the geologic timescale or a stage in the stratigraphic column. It is a subdivision of the Early or Lower Cretaceous Epoch or Series and encompasses the time from 121.4 ± 1.0 Ma to 113.0 ± 1.0 Ma (million years ago), a ... of both Hemispheres. References Ginkgophyta Prehistoric plant families {{Paleo-gymnosperm-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karkeniaceae
Karkeniaceae is an extinct family in the order Ginkgoales. It contains the single genus ''Karkenia''. It is distinguished by "Ovulate organs consisting of a peduncle and helically arranged, up to about 100 small, orthotropous but incurved ovules; pedicel present; nucellus largely free." Unlike other ginkgoales, the seeds are borne on cone-like aggregations. Ovuluate organs of ''Karkenia'' are associated with leaves of the ''Ginkgoites'', ''Sphenobaiera'' and '' Eretmophyllum'' types. It is known from the Hettangian to Aptian The Aptian is an age in the geologic timescale or a stage in the stratigraphic column. It is a subdivision of the Early or Lower Cretaceous Epoch or Series and encompasses the time from 121.4 ± 1.0 Ma to 113.0 ± 1.0 Ma (million years ago), a ... of both Hemispheres. References Ginkgophyta Prehistoric plant families {{Paleo-gymnosperm-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ginkgoaceae
The Ginkgoaceae is a family of gymnosperms which appeared during the Mesozoic Era, of which the only extant representative is ''Ginkgo biloba'', which is for this reason sometimes regarded as a living fossil A living fossil is an extant taxon that cosmetically resembles related species known only from the fossil record. To be considered a living fossil, the fossil species must be old relative to the time of origin of the extant clade. Living fossi .... Formerly, however, there were several other genera, and forests of ginkgo existed. Because leaves can take such diverse forms within a single species, these are a poor measure of diversity, although differing structures of wood point to the existence of diverse ginkgo forests in ancient times. References External links * * * * . Plant families Jurassic plants Extant Jurassic first appearances {{Tree-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotypic
In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon. A monotypic species is one that does not include subspecies or smaller, infraspecific taxa. In the case of genera, the term "unispecific" or "monospecific" is sometimes preferred. In botanical nomenclature, a monotypic genus is a genus in the special case where a genus and a single species are simultaneously described. In contrast, an oligotypic taxon contains more than one but only a very few subordinate taxa. Examples Just as the term ''monotypic'' is used to describe a taxon including only one subdivision, the contained taxon can also be referred to as monotypic within the higher-level taxon, e.g. a genus monotypic within a family. Some examples of monotypic groups are: Plants * In the order Amborellales, there is only one family, Amborellaceae and there is only one genus, '' Amborella'', and in this genus there is only one species, namely ''Amborella trichopoda. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
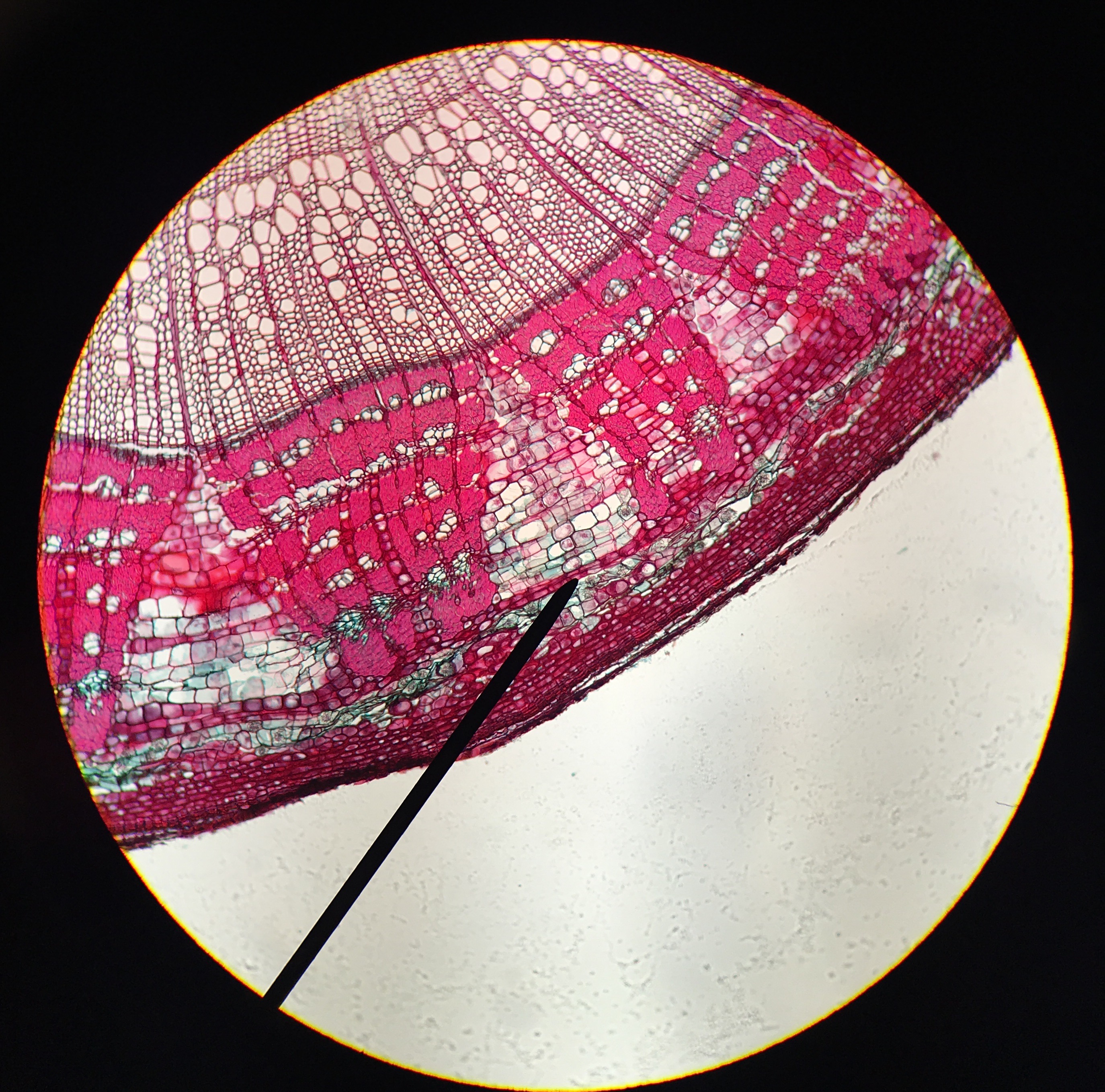
Cambium
A cambium (plural cambia or cambiums), in plants, is a tissue layer that provides partially undifferentiated cells for plant growth. It is found in the area between xylem and phloem. A cambium can also be defined as a cellular plant tissue from which phloem, xylem, or cork grows by division, resulting (in woody plants) in secondary thickening. It forms parallel rows of cells, which result in secondary tissues. There are several distinct kinds of cambium found in plant stems and roots: * Cork cambium, a tissue found in many vascular plants as part of the periderm. * Unifacial cambium, which ultimately produces cells to the interior of its cylinder. * Vascular cambium, a lateral meristem in the vascular tissue of plants. Uses The cambium of many species of woody plants are edible; however, due to its vital role in the homeostasis and growth of woody plants, this may result in death of the plant if enough cambium is removed at once. The cambium can generally be eaten raw or cooke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |