|
Geostrophic Equilibrium
In atmospheric science, balanced flow is an idealisation of atmospheric motion. The idealisation consists in considering the behaviour of one isolated parcel of air having constant density, its motion on a horizontal plane subject to selected forces acting on it and, finally, steady-state conditions. Balanced flow is often an accurate approximation of the actual flow, and is useful in improving the qualitative understanding and interpretation of atmospheric motion. In particular, the balanced-flow speeds can be used as estimates of the wind speed for particular arrangements of the atmospheric pressure on Earth's surface. The Momentum Equations in Natural Coordinates Trajectories The momentum equations are written primarily for the generic trajectory of a packet of flow travelling on a horizontal plane and taken at a certain elapsed time called ''t''. The position of the packet is defined by the distance on the trajectory ''s''=''s''(''t'') which it has travelled by time ''t' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Science
Atmospheric science is the study of the Earth's atmosphere and its various inner-working physical processes. Meteorology includes atmospheric chemistry and atmospheric physics with a major focus on weather forecasting. Climatology is the study of atmospheric changes (both long and short-term) that define average climates and their change over time, due to both natural and anthropogenic climate variability. Aeronomy is the study of the upper layers of the atmosphere, where dissociation and ionization are important. Atmospheric science has been extended to the field of planetary science and the study of the atmospheres of the planets and natural satellites of the Solar System. Experimental instruments used in atmospheric science include satellites, rocketsondes, radiosondes, weather balloons, radars, and lasers. The term aerology (from Greek ἀήρ, ''aēr'', " air"; and -λογία, ''-logia'') is sometimes used as an alternative term for the study of Earth's a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Density Of Air
The density of air or atmospheric density, denoted '' ρ'', is the mass per unit volume of Earth's atmosphere. Air density, like air pressure, decreases with increasing altitude. It also changes with variation in atmospheric pressure, temperature and humidity. At 101.325 kPa (abs) and 20 °C (68 °F), air has a density of approximately , according to the International Standard Atmosphere (ISA). At 101.325kPa (abs) and , air has a density of approximately , which is about that of water, according to the International Standard Atmosphere (ISA). Pure liquid water is . Air density is a property used in many branches of science, engineering, and industry, including aeronautics;Olson, Wayne M. (2000) AFFTC-TIH-99-01, Aircraft Performance FlightICAO, Manual of the ICAO Standard Atmosphere (extended to 80 kilometres (262 500 feet)), Doc 7488-CD, Third Edition, 1993, .Grigorie, T.L., Dinca, L., Corcau J-I. and Grigorie, O. (2010) Aircrafts' Altitude Measurement Using Pressure Informa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extratropical Cyclone
Extratropical cyclones, sometimes called mid-latitude cyclones or wave cyclones, are low-pressure areas which, along with the anticyclones of high-pressure areas, drive the weather over much of the Earth. Extratropical cyclones are capable of producing anything from cloudiness and mild showers to severe gales, thunderstorms, blizzards, and tornadoes. These types of cyclones are defined as large scale (synoptic) low pressure weather systems that occur in the middle latitudes of the Earth. In contrast with tropical cyclones, extratropical cyclones produce rapid changes in temperature and dew point along broad lines, called weather fronts, about the center of the cyclone. Terminology The term "cyclone" applies to numerous types of low pressure areas, one of which is the extratropical cyclone. The descriptor ''extratropical'' signifies that this type of cyclone generally occurs outside the tropics and in the middle latitudes of Earth between 30° and 60° latitude. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planetary Boundary Layer
In meteorology, the planetary boundary layer (PBL), also known as the atmospheric boundary layer (ABL) or peplosphere, is the lowest part of the atmosphere and its behaviour is directly influenced by its contact with a planetary surface. On Earth it usually responds to changes in surface radiative forcing in an hour or less. In this layer physical quantities such as flow velocity, temperature, and moisture display rapid fluctuations ( turbulence) and vertical mixing is strong. Above the PBL is the "free atmosphere", where the wind is approximately geostrophic (parallel to the isobars), while within the PBL the wind is affected by surface drag and turns across the isobars (see Ekman layer for more detail). Cause of surface wind gradient Typically, due to aerodynamic drag, there is a wind gradient in the wind flow ~100 meters above the Earth's surface—the surface layer of the planetary boundary layer. Wind speed increases with increasing height above the ground, starti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
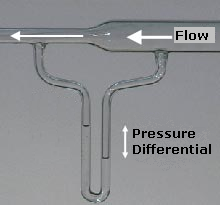
Bernoulli's Principle
In fluid dynamics, Bernoulli's principle states that an increase in the speed of a fluid occurs simultaneously with a decrease in static pressure or a decrease in the fluid's potential energy. The principle is named after the Swiss mathematician and physicist Daniel Bernoulli, who published it in his book ''Hydrodynamica'' in 1738. Although Bernoulli deduced that pressure decreases when the flow speed increases, it was Leonhard Euler in 1752 who derived Bernoulli's equation in its usual form. The principle is only applicable for isentropic flows: when the effects of irreversible processes (like turbulence) and non- adiabatic processes (e.g. thermal radiation) are small and can be neglected. Bernoulli's principle can be applied to various types of fluid flow, resulting in various forms of Bernoulli's equation. The simple form of Bernoulli's equation is valid for incompressible flows (e.g. most liquid flows and gases moving at low Mach number). More advanced forms may be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specific Weight
The specific weight, also known as the unit weight, is the weight per unit volume of a material. A commonly used value is the specific weight of water on Earth at , which is .National Council of Examiners for Engineering and Surveying (2005). ''Fundamentals of Engineering Supplied-Reference Handbook'' (7th ed.). . Often a source of confusion is that the terms ''specific gravity'', and less often ''specific weight'', are also used for relative density. A common symbol for specific weight is , the Greek letter Gamma. Definition The specific weight, , of a material is defined as the product of its density, , and the standard gravity, : \gamma = \rho \, g The density of the material is defined as mass per unit volume, typically measured in kg/m3. The standard gravity is acceleration due to gravity, usually given in m/s2, and on Earth usually taken as . Unlike density, specific weight is not a fixed property of a material. It depends on the value of the gravitational acceleration, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Weather Analysis
Surface weather analysis is a special type of weather map that provides a view of weather elements over a geographical area at a specified time based on information from ground-based weather stations. Weather maps are created by plotting or tracing the values of relevant quantities such as sea level pressure, temperature, and cloud cover onto a geographical map to help find synoptic scale features such as weather fronts. The first weather maps in the 19th century were drawn well after the fact to help devise a theory on storm systems.Eric R. MillerAmerican Pioneers in Meteorology.Retrieved on 2007-04-18. After the advent of the telegraph, simultaneous surface weather observations became possible for the first time, and beginning in the late 1840s, the Smithsonian Institution became the first organization to draw real-time surface analyses. Use of surface analyses began first in the United States, spreading worldwide during the 1870s. Use of the Norwegian cyclone model for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barometer
A barometer is a scientific instrument that is used to measure air pressure in a certain environment. Pressure tendency can forecast short term changes in the weather. Many measurements of air pressure are used within surface weather analysis to help find surface troughs, pressure systems and frontal boundaries. Barometers and pressure altimeters (the most basic and common type of altimeter) are essentially the same instrument, but used for different purposes. An altimeter is intended to be used at different levels matching the corresponding atmospheric pressure to the altitude, while a barometer is kept at the same level and measures subtle pressure changes caused by weather and elements of weather. The average atmospheric pressure on the earth's surface varies between 940 and 1040 hPa (mbar). The average atmospheric pressure at sea level is 1013 hPa (mbar). Etymology The word '' barometer'' is derived from the Ancient Greek (), meaning "weight", and (), meaning "me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ekman Layer
The Ekman layer is the layer in a fluid where there is a force balance between pressure gradient force, Coriolis force and turbulent drag. It was first described by Vagn Walfrid Ekman. Ekman layers occur both in the atmosphere and in the ocean. There are two types of Ekman layers. The first type occurs at the surface of the ocean and is forced by surface winds, which act as a drag on the surface of the ocean. The second type occurs at the bottom of the atmosphere and ocean, where frictional forces are associated with flow over rough surfaces. History Ekman developed the theory of the Ekman layer after Fridtjof Nansen observed that ice drifts at an angle of 20°–40° to the right of the prevailing wind direction while on an Arctic expedition aboard the Fram. Nansen asked his colleague, Vilhelm Bjerknes to set one of his students upon study of the problem. Bjerknes tapped Ekman, who presented his results in 1902 as his doctoral thesis. Mathematical formulation The mathemat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inertial Flow
In atmospheric science, balanced flow is an idealisation of atmospheric motion. The idealisation consists in considering the behaviour of one isolated parcel of air having constant density, its motion on a horizontal plane subject to selected forces acting on it and, finally, steady-state conditions. Balanced flow is often an accurate approximation of the actual flow, and is useful in improving the qualitative understanding and interpretation of atmospheric motion. In particular, the balanced-flow speeds can be used as estimates of the wind speed for particular arrangements of the atmospheric pressure on Earth's surface. The Momentum Equations in Natural Coordinates Trajectories The momentum equations are written primarily for the generic trajectory of a packet of flow travelling on a horizontal plane and taken at a certain elapsed time called ''t''. The position of the packet is defined by the distance on the trajectory ''s''=''s''(''t'') which it has travelled by time ''t' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclostrophic Flow
In atmospheric science, balanced flow is an idealisation of atmospheric motion. The idealisation consists in considering the behaviour of one isolated parcel of air having constant density, its motion on a horizontal plane subject to selected forces acting on it and, finally, steady-state conditions. Balanced flow is often an accurate approximation of the actual flow, and is useful in improving the qualitative understanding and interpretation of atmospheric motion. In particular, the balanced-flow speeds can be used as estimates of the wind speed for particular arrangements of the atmospheric pressure on Earth's surface. The Momentum Equations in Natural Coordinates Trajectories The momentum equations are written primarily for the generic trajectory of a packet of flow travelling on a horizontal plane and taken at a certain elapsed time called ''t''. The position of the packet is defined by the distance on the trajectory ''s''=''s''(''t'') which it has travelled by time ''t' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |