|
Geopolymers
Geopolymers are inorganic, typically ceramic, alumino-silicate forming long-range, covalently bonded, non-crystalline (amorphous) networks. Obsidian (volcanic glass) fragments are a component of some geopolymer blends. Commercially produced geopolymers may be used for fire- and heat-resistant coatings and adhesives, medicinal applications, high-temperature ceramics, new binders for fire-resistant fiber composites, toxic and radioactive waste encapsulation and new cements for concrete. The properties and uses of geopolymers are being explored in many scientific and industrial disciplines: modern inorganic chemistry, physical chemistry, colloid chemistry, mineralogy, geology, and in other types of engineering process technologies. The field of geopolymers is a part of polymer science, chemistry and technology that forms one of the major areas of materials science. Polymers are either organic material, i.e. carbon-based, or inorganic polymer, for example silicon-based. The organic pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geopolymer Oligomer Molecules
Geopolymers are inorganic, typically ceramic, alumino-silicate forming long-range, covalently bonded, non-crystalline (amorphous) networks. Obsidian (volcanic glass) fragments are a component of some geopolymer blends. Commercially produced geopolymers may be used for fire- and heat-resistant coatings and adhesives, medicinal applications, high-temperature ceramics, new binders for fire-resistant fiber composites, toxic and radioactive waste encapsulation and new cements for concrete. The properties and uses of geopolymers are being explored in many scientific and industrial disciplines: modern inorganic chemistry, physical chemistry, colloid chemistry, mineralogy, geology, and in other types of engineering process technologies. The field of geopolymers is a part of polymer science, chemistry and technology that forms one of the major areas of materials science. Polymers are either organic material, i.e. carbon-based, or inorganic polymer, for example silicon-based. The organic pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inorganic
In chemistry, an inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bonds, that is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as '' inorganic chemistry''. Inorganic compounds comprise most of the Earth's crust, although the compositions of the deep mantle remain active areas of investigation. Some simple carbon compounds are often considered inorganic. Examples include the allotropes of carbon (graphite, diamond, buckminsterfullerene, etc.), carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, carbides, and the following salts of inorganic anions: carbonates, cyanides, cyanates, and thiocyanates. Many of these are normal parts of mostly organic systems, including organisms; describing a chemical as inorganic does not necessarily mean that it does not occur within living things. History Friedrich Wöhler's conversion of ammonium cyanate into urea in 1828 is often cited as the starting point of modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboxylic Acid
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is or , with R referring to the alkyl, alkenyl, aryl, or other group. Carboxylic acids occur widely. Important examples include the amino acids and fatty acids. Deprotonation of a carboxylic acid gives a carboxylate anion. Examples and nomenclature Carboxylic acids are commonly identified by their trivial names. They at oftentimes have the suffix ''-ic acid''. IUPAC-recommended names also exist; in this system, carboxylic acids have an ''-oic acid'' suffix. For example, butyric acid (C3H7CO2H) is butanoic acid by IUPAC guidelines. For nomenclature of complex molecules containing a carboxylic acid, the carboxyl can be considered position one of the parent chain even if there are other substituents, such as 3-chloropropanoic acid. Alternately, it can be named as a "carboxy" or "carboxylic acid" substituent on another ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depolymerization
Depolymerization (or depolymerisation) is the process of converting a polymer into a monomer or a mixture of monomers. This process is driven by an increase in entropy. Ceiling temperature The tendency of polymers to depolymerize is indicated by their ceiling temperature. At this temperature, the enthalpy of polymerization matches the entropy gained by converting a large molecule into monomers. Above the ceiling temperature, the rate of depolymerization is greater than the rate of polymerization, which inhibits the formation of the given polymer. Applications Depolymerization is a very common process. Digestion of food involves depolymerization of macromolecules, such as proteins. It is relevant to polymer recycling. Sometimes the depolymerization is well behaved, and clean monomers can be reclaimed and reused for making new plastic. In other cases, such as polyethylene, depolymerization gives a mixture of products. These products are, for polyethylene, ethylene, propylene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligomers
In chemistry and biochemistry, an oligomer () is a molecule that consists of a few repeating units which could be derived, actually or conceptually, from smaller molecules, monomers.Quote: ''Oligomer molecule: A molecule of intermediate relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises a small plurality of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of lower relative molecular mass.'' The name is composed of Greek elements '' oligo-'', "a few" and '' -mer'', "parts". An adjective form is ''oligomeric''. The oligomer concept is contrasted to that of a polymer, which is usually understood to have a large number of units, possibly thousands or millions. However, there is no sharp distinction between these two concepts. One proposed criterion is whether the molecule's properties vary significantly with the removal of one or a few of the units. An oligomer with a specific number of units is referred to by the Greek prefix denoting that number, wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicone
A silicone or polysiloxane is a polymer made up of siloxane (−R2Si−O−SiR2−, where R = organic group). They are typically colorless oils or rubber-like substances. Silicones are used in sealants, adhesives, lubricants, medicine, cooking utensils, thermal insulation, and electrical insulation. Some common forms include silicone oil, silicone grease, silicone rubber, silicone resin, and silicone caulk. Chemistry More precisely called polymerized siloxanes or polysiloxanes, silicones consist of an inorganic silicon–oxygen backbone chain (⋯−Si−O−Si−O−Si−O−⋯) with two organic groups attached to each silicon center. Commonly, the organic groups are methyl. The materials can be cyclic or polymeric. By varying the −Si−O− chain lengths, side groups, and crosslinking, silicones can be synthesized with a wide variety of properties and compositions. They can vary in consistency from liquid to gel to rubber to hard plastic. The most common siloxan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligomer
In chemistry and biochemistry, an oligomer () is a molecule that consists of a few repeating units which could be derived, actually or conceptually, from smaller molecules, monomers.Quote: ''Oligomer molecule: A molecule of intermediate relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises a small plurality of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of lower relative molecular mass.'' The name is composed of Greek elements '' oligo-'', "a few" and '' -mer'', "parts". An adjective form is ''oligomeric''. The oligomer concept is contrasted to that of a polymer, which is usually understood to have a large number of units, possibly thousands or millions. However, there is no sharp distinction between these two concepts. One proposed criterion is whether the molecule's properties vary significantly with the removal of one or a few of the units. An oligomer with a specific number of units is referred to by the Greek prefix denoting that number, wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linus Pauling
Linus Carl Pauling (; February 28, 1901August 19, 1994) was an American chemist, biochemist, chemical engineer, peace activist, author, and educator. He published more than 1,200 papers and books, of which about 850 dealt with scientific topics. ''New Scientist'' called him one of the 20 greatest scientists of all time, and as of 2000, he was rated the 16th most important scientist in history. For his scientific work, Pauling was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1954. For his peace activism, he was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize in 1962. He is one of five people to have won more than one Nobel Prize (the others being Marie Curie, John Bardeen, Frederick Sanger and Karl Barry Sharpless). Of these, he is the only person to have been awarded two unshared Nobel Prizes, and one of two people to be awarded Nobel Prizes in different fields, the other being Marie Curie. Pauling was one of the founders of the fields of quantum chemistry and molecular biology. His contributions t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal Structure
In crystallography, crystal structure is a description of the ordered arrangement of atoms, ions or molecules in a crystal, crystalline material. Ordered structures occur from the intrinsic nature of the constituent particles to form symmetric patterns that repeat along the principal directions of Three-dimensional space (mathematics), three-dimensional space in matter. The smallest group of particles in the material that constitutes this repeating pattern is the unit cell of the structure. The unit cell completely reflects the symmetry and structure of the entire crystal, which is built up by repetitive Translation (geometry), translation of the unit cell along its principal axes. The translation vectors define the nodes of the Bravais lattice. The lengths of the principal axes, or edges, of the unit cell and the angles between them are the lattice constants, also called ''lattice parameters'' or ''cell parameters''. The symmetry properties of the crystal are described by the con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
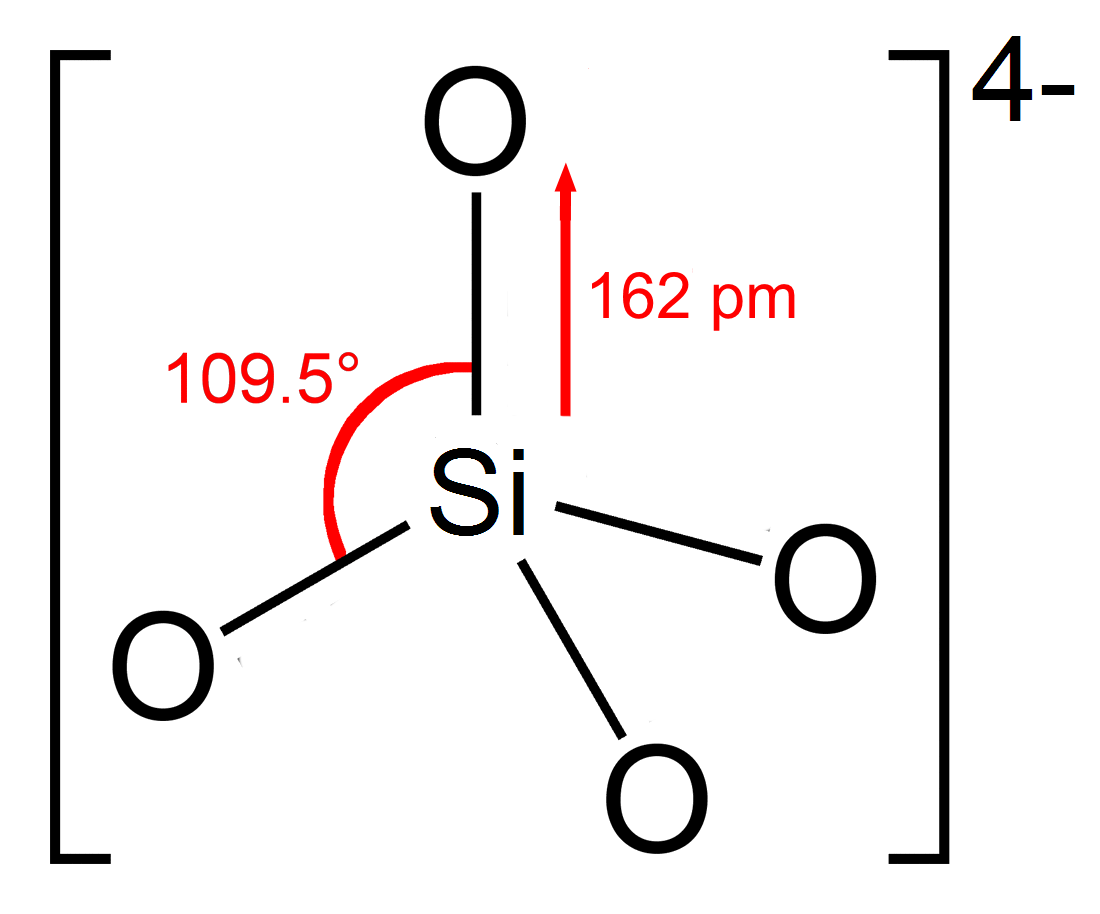
Silicate
In chemistry, a silicate is any member of a family of polyatomic anions consisting of silicon and oxygen, usually with the general formula , where . The family includes orthosilicate (), metasilicate (), and pyrosilicate (, ). The name is also used for any salt of such anions, such as sodium metasilicate; or any ester containing the corresponding chemical group, such as tetramethyl orthosilicate. The name "silicate" is sometimes extended to any anions containing silicon, even if they do not fit the general formula or contain other atoms besides oxygen; such as hexafluorosilicate .Most commonly, silicates are encountered as silicate minerals. For diverse manufacturing, technological, and artistic needs, silicates are versatile materials, both natural (such as granite, gravel, and garnet) and artificial (such as Portland cement, ceramics, glass, and waterglass). Structural principles In all silicates, silicon atom occupies the center of an idealized tetrahedron whose corner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Davidovits, 1991
Joseph is a common male given name, derived from the Hebrew Yosef (יוֹסֵף). "Joseph" is used, along with "Josef", mostly in English, French and partially German languages. This spelling is also found as a variant in the languages of the modern-day Nordic countries. In Portuguese and Spanish, the name is "José". In Arabic, including in the Quran, the name is spelled '' Yūsuf''. In Persian, the name is "Yousef". The name has enjoyed significant popularity in its many forms in numerous countries, and ''Joseph'' was one of the two names, along with ''Robert'', to have remained in the top 10 boys' names list in the US from 1925 to 1972. It is especially common in contemporary Israel, as either "Yossi" or "Yossef", and in Italy, where the name "Giuseppe" was the most common male name in the 20th century. In the first century CE, Joseph was the second most popular male name for Palestine Jews. In the Book of Genesis Joseph is Jacob's eleventh son and Rachel's first son, and k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humic Acid
Humic substances (HS) are organic compounds that are important components of humus, the major organic fraction of soil, peat, and coal (and also a constituent of many upland streams, dystrophic lakes, and ocean water). For a long era in the 19th and 20th centuries, humic substances were often viewed through a lens of acid–base theory that described humic acids (HA), as organic acids, and their conjugate bases, humates, as important components of organic matter. Through this viewpoint humic acids were defined as organic substances extracted from soil that coagulate (form small solid pieces) when a strong-base extract is acidified, whereas fulvic acids (FA) are organic acids that remain soluble (stay dissolved) when a strong-base extract is acidified. The remaining alkali-insoluble part of humus would be termed humin. Humic matter in isolation is the result of a chemical extraction from the soil organic matter or the dissolved organic matter and represent the humic molecules ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |