|
Genetics In Fiction
Aspects of genetics including mutation, hybridisation, cloning, genetic engineering, and eugenics have appeared in fiction since the 19th century. Genetics is a young science, having started in 1900 with the rediscovery of Gregor Mendel's study on the inheritance of traits in pea plants. During the 20th century it developed to create new sciences and technologies including molecular biology, DNA sequencing, cloning, and genetic engineering. The ethical implications were brought into focus with the eugenics movement. Since then, many science fiction novels and films have used aspects of genetics as plot devices, often taking one of two routes: a genetic accident with disastrous consequences; or, the feasibility and desirability of a planned genetic alteration. The treatment of science in these stories has been uneven and often unrealistic. The film ''Gattaca'' did attempt to portray science accurately but was criticised by scientists. Background Modern genetics began wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frankenstein's Monster (Boris Karloff)
Frankenstein's monster or Frankenstein's creature, often referred to as simply "Frankenstein", is a fictional character who first appeared in Mary Shelley's 1818 novel ''Frankenstein; or, The Modern Prometheus'' as the main antagonist. Shelley's title thus compares the monster's creator, Victor Frankenstein, to the mythological character Prometheus, who fashioned humans out of clay and gave them fire. In Shelley's Gothic fiction, Gothic story, Victor Frankenstein builds the creature in his laboratory through an ambiguous method based on a scientific principle he discovered. Shelley describes the monster as tall and emotional. The monster attempts to fit into human society but is shunned, which leads him to seek revenge against Frankenstein. According to the scholar Joseph Carroll (scholar), Joseph Carroll, the monster occupies "a border territory between the characteristics that typically define protagonists and antagonists". Frankenstein's monster became iconic in popular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugo De Vries
Hugo Marie de Vries () (16 February 1848 – 21 May 1935) was a Dutch botanist and one of the first geneticists. He is known chiefly for suggesting the concept of genes, rediscovering the laws of heredity in the 1890s while apparently unaware of Gregor Mendel's work, for introducing the term "mutation", and for developing a mutation theory of evolution. Early life De Vries was born in 1848, the eldest son of Gerrit de Vries (1818–1900), a lawyer and deacon in the Mennonite congregation in Haarlem and later Prime Minister of the Netherlands from 1872 until 1874, and Maria Everardina Reuvens (1823–1914), daughter of a professor in archaeology at Leiden University. His father became a member of the Dutch Council of State in 1862 and moved his family over to The Hague. From an early age Hugo showed much interest in botany, winning several prizes for his herbariums while attending gymnasium in Haarlem and The Hague. In 1866 he enrolled at the Leiden University to major in botan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
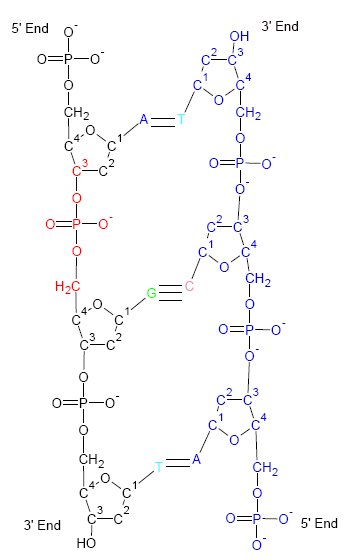
Francis Crick
Francis Harry Compton Crick (8 June 1916 – 28 July 2004) was an English molecular biologist, biophysicist, and neuroscientist. He, James Watson, Rosalind Franklin, and Maurice Wilkins played crucial roles in deciphering the helical structure of the DNA molecule. Crick and Watson's paper in ''Nature'' in 1953 laid the groundwork for understanding DNA structure and functions. Together with Maurice Wilkins, they were jointly awarded the 1962 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine "for their discoveries concerning the molecular structure of nucleic acids and its significance for information transfer in living material". Crick was an important theoretical molecular biologist and played a crucial role in research related to revealing the helical structure of DNA. He is widely known for the use of the term " central dogma" to summarise the idea that once information is transferred from nucleic acids (DNA or RNA) to proteins, it cannot flow back to nucleic acids. In other words ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)