|
Gastroschisis
Gastroschisis is a birth defect in which the baby's intestines extend outside of the abdomen through a hole next to the belly button. The size of the hole is variable, and other organs including the stomach and liver may also occur outside the baby's body. Complications may include feeding problems, prematurity, intestinal atresia, and intrauterine growth restriction. The cause is typically unknown. Rates are higher in babies born to mothers who smoke, drink alcohol, or are younger than 20 years old. Ultrasounds during pregnancy may make the diagnosis. Otherwise diagnosis occurs at birth. It differs from omphalocele in that there is no covering membrane over the intestines. Treatment involves surgery. This typically occurs shortly after birth. In those with large defects the exposed organs may be covered with a special material and slowly moved back into the abdomen. The condition affects about 4 per 10,000 newborns. Rates of the condition appear to be increasing. Signs and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastrochisis 0001
Gastroschisis is a birth defect in which the baby's intestines extend outside of the abdomen through a hole next to the belly button. The size of the hole is variable, and other organs including the stomach and liver may also occur outside the baby's body. Complications may include feeding problems, Premature birth, prematurity, intestinal atresia, and intrauterine growth restriction. The cause is typically unknown. Rates are higher in babies born to mothers who smoke, drink alcohol, or are younger than 20 years old. Ultrasounds during pregnancy may make the diagnosis. Otherwise diagnosis occurs at birth. It differs from omphalocele in that there is no covering membrane over the intestines. Treatment involves surgery. This typically occurs shortly after birth. In those with large defects the exposed organs may be covered with a special material and slowly moved back into the abdomen. The condition affects about 4 per 10,000 newborns. Rates of the condition appear to be increasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
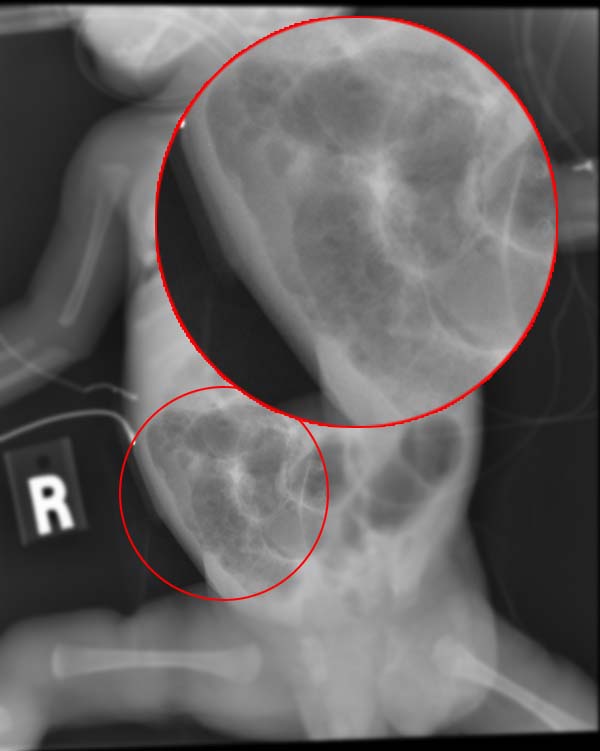
Omphalocele
Omphalocele or omphalocoele also called exomphalos, is a rare abdominal wall defect. Beginning at the 6th week of development, rapid elongation of the gut and increased liver size reduces intra abdominal space, which pushes intestinal loops out of the abdominal cavity. Around 10th week, the intestine returns to the abdominal cavity and the process is completed by the 12th week. Persistence of intestine or the presence of other abdominal viscera (e.g. stomach, liver) in the umbilical cord results in an omphalocele. Omphalocele occurs in 1 in 4,000 births and is associated with a high rate of mortality (25%) and severe malformations, such as cardiac anomalies (50%), neural tube defect (40%), exstrophy of the bladder and Beckwith–Wiedemann syndrome. Approximately 15% of live-born infants with omphalocele have chromosomal abnormalities. About 30% of infants with an omphalocele have other congenital abnormalities. Signs and symptoms The sac, which is formed from an outpouching of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omphalocele
Omphalocele or omphalocoele also called exomphalos, is a rare abdominal wall defect. Beginning at the 6th week of development, rapid elongation of the gut and increased liver size reduces intra abdominal space, which pushes intestinal loops out of the abdominal cavity. Around 10th week, the intestine returns to the abdominal cavity and the process is completed by the 12th week. Persistence of intestine or the presence of other abdominal viscera (e.g. stomach, liver) in the umbilical cord results in an omphalocele. Omphalocele occurs in 1 in 4,000 births and is associated with a high rate of mortality (25%) and severe malformations, such as cardiac anomalies (50%), neural tube defect (40%), exstrophy of the bladder and Beckwith–Wiedemann syndrome. Approximately 15% of live-born infants with omphalocele have chromosomal abnormalities. About 30% of infants with an omphalocele have other congenital abnormalities. Signs and symptoms The sac, which is formed from an outpouching of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital Disorders Of Musculoskeletal System
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can range from mild to severe. Birth defects are divided into two main types: structural disorders in which problems are seen with the shape of a body part and functional disorders in which problems exist with how a body part works. Functional disorders include metabolic and degenerative disorders. Some birth defects include both structural and functional disorders. Birth defects may result from genetic or chromosomal disorders, exposure to certain medications or chemicals, or certain infections during pregnancy. Risk factors include folate deficiency, drinking alcohol or smoking during pregnancy, poorly controlled diabetes, and a mother over the age of 35 years old. Many are believed to involve multiple factors. Birth defects may be visib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birth Defect
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can range from mild to severe. Birth defects are divided into two main types: structural disorders in which problems are seen with the shape of a body part and functional disorders in which problems exist with how a body part works. Functional disorders include metabolic and degenerative disorders. Some birth defects include both structural and functional disorders. Birth defects may result from genetic or chromosomal disorders, exposure to certain medications or chemicals, or certain infections during pregnancy. Risk factors include folate deficiency, drinking alcohol or smoking during pregnancy, poorly controlled diabetes, and a mother over the age of 35 years old. Many are believed to involve multiple factors. Birth defects may be visi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Center For Disease Control
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the national public health agency of the United States. It is a United States federal agency, under the Department of Health and Human Services, and is headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia. The agency's main goal is the protection of public health and safety through the control and prevention of disease, injury, and disability in the US and worldwide. The CDC focuses national attention on developing and applying disease control and prevention. It especially focuses its attention on infectious disease, food borne pathogens, environmental health, occupational safety and health, health promotion, injury prevention and educational activities designed to improve the health of United States citizens. The CDC also conducts research and provides information on non-infectious diseases, such as obesity and diabetes, and is a founding member of the International Association of National Public Health Institutes. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autosomal Recessive Disorders
An autosome is any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome. The members of an autosome pair in a diploid cell have the same morphology, unlike those in allosomal (sex chromosome) pairs, which may have different structures. The DNA in autosomes is collectively known as atDNA or auDNA. For example, humans have a diploid genome that usually contains 22 pairs of autosomes and one allosome pair (46 chromosomes total). The autosome pairs are labeled with numbers (1–22 in humans) roughly in order of their sizes in base pairs, while allosomes are labelled with their letters. By contrast, the allosome pair consists of two X chromosomes in females or one X and one Y chromosome in males. Unusual combinations of XYY, XXY, XXX, XXXX, XXXXX or XXYY, among other Salome combinations, are known to occur and usually cause developmental abnormalities. Autosomes still contain sexual determination genes even though they are not sex chromosomes. For example, the SRY gene on the Y chromosome e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smoking And Pregnancy
Tobacco smoking during pregnancy causes many detrimental effects on health and reproduction, in addition to the general health effects of tobacco. A number of studies have shown that tobacco use is a significant factor in miscarriages among pregnant smokers, and that it contributes to a number of other threats to the health of the foetus. Because of the associated risks, people are advised not to smoke before, during or after pregnancy. If this is not possible, however, reducing the daily number of cigarettes smoked can minimize the risks for both the mother and child. This is especially true for people in developing countries, where breastfeeding is essential for the child's overall nutritional status. Smoking before pregnancy Women who are pregnant or planning to become pregnant are advised to stop smoking. It is important to examine these effects because smoking before, during and after pregnancy is not an unusual behavior among the general population and can have detrimental ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centers For Disease Control And Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the national public health agency of the United States. It is a United States federal agency, under the Department of Health and Human Services, and is headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia. The agency's main goal is the protection of public health and safety through the control and prevention of disease, injury, and disability in the US and worldwide. The CDC focuses national attention on developing and applying disease control and prevention. It especially focuses its attention on infectious disease, food borne pathogens, environmental health, occupational safety and health, health promotion, injury prevention and educational activities designed to improve the health of United States citizens. The CDC also conducts research and provides information on non-infectious diseases, such as obesity and diabetes, and is a founding member of the International Association of National Public Health Institutes. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volvulus
A volvulus is when a loop of intestine twists around itself and the mesentery that supports it, resulting in a bowel obstruction. Symptoms include abdominal pain, abdominal bloating, vomiting, constipation, and bloody stool. Onset of symptoms may be rapid or more gradual. The mesentery may become so tightly twisted that blood flow to part of the intestine is cut off, resulting in ischemic bowel. In this situation there may be fever or significant pain when the abdomen is touched. Risk factors include a birth defect known as intestinal malrotation, an enlarged colon, Hirschsprung disease, pregnancy, and abdominal adhesions. Long term constipation and a high fiber diet may also increase the risk. The most commonly affected part of the intestines in adults is the sigmoid colon with the cecum being second most affected. In children the small intestine is more often involved. The stomach can also be affected. Diagnosis is typically with medical imaging such as plain X-rays, a G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intestinal Malrotation
Intestinal malrotation is a congenital anomaly of rotation of the midgut. It occurs during the first trimester as the fetal gut undergoes a complex series of growth and development. Malrotation can lead to a dangerous complication called volvulus. Malrotation can refer to a spectrum of abnormal intestinal positioning, often including: * The small intestine found predominantly on the right side of the abdomen * The cecum displaced from its usual position in the right lower quadrant into the epigastrium or right hypochondrium * An absent or displaced ligament of Treitz * Fibrous peritoneal bands called bands of Ladd running across the vertical portion of the duodenum * An unusually narrow, stalk-like mesentery The position of the intestines, narrow mesentery and Ladd's bands can contribute to several severe gastrointestinal conditions. The narrow mesentery predisposes some cases of malrotation to midgut volvulus, a twisting of the entire small bowel that can obstruct the mesenteric b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Necrotizing Enterocolitis
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is a devastating intestinal disease that affects premature or very low birth weight infants.Gephart S.M., Quinn M. A call to action to fight for equity and end necrotizing enterocolitis disparities. ''Adv. Neonatal Care.'' 2021;21(5):333-335. doi:10.1097/ANC.0000000000000940 Symptoms may include poor feeding, bloating, decreased activity, blood in the stool, vomiting of bile, bowel death, multiorgan failure, and even death. The exact cause is unclear. However, several risk factors have been identified. Consistently described risk factors include formula feeding, intestinal dysbiosis, low birth weight, and prematurity. Maternal factors such as chorioamnionitis, cocaine abuse, ''in utero'' growth restriction, intrahepatic cholestasis during pregnancy, increased body mass index, lack of prenatal steroids, mode of delivery, placental abruption, preeclampsia, and smoking have not been consistently implicated with the development of NEC. Other risk fact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |