|
Gastroduodenal Artery
In anatomy, the gastroduodenal artery is a small blood vessel in the abdomen. It supplies blood directly to the pylorus (distal part of the stomach) and proximal part of the duodenum. It also indirectly supplies the pancreatic head (via the anterior and posterior superior pancreaticoduodenal arteries). Structure The gastroduodenal artery most commonly arises from either the left hepatic artery or the right hepatic artery instead. It may also arise from the common hepatic artery of the coeliac trunk in a trifork arrangement with the two other arteries, but there are numerous variations of the origin.Bergman RA, Afifi AK, Miyauchi R. Variations in Origin of Gastroduodenal Artery. from Anatomy Atlases. (http://www.anatomyatlases.org/AnatomicVariants/Cardiovascular/Images0001/0017.shtml) It first gives rise to the supraduodenal artery, followed by the posterior superior pancreaticoduodenal artery. It terminates in a bifurcation when it splits into the right gastroepiploic artery a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celiac Artery
The celiac () artery (also spelled ''coeliac''), also known as the celiac trunk or truncus coeliacus, is the first major branch of the abdominal aorta. It is about 1.25 cm in length. Branching from the aorta at thoracic vertebra 12 (T12) in humans, it is one of three anterior/ midline branches of the abdominal aorta (the others are the superior and inferior mesenteric arteries). Structure The celiac artery is the first major branch of the descending abdominal aorta, branching at a 90° angle. This occurs just below the crus of the diaphragm. This is around the first lumbar vertebra. There are three main divisions of the celiac artery, and each in turn has its own named branches: The celiac artery may also give rise to the inferior phrenic arteries. Function The celiac artery supplies oxygenated blood to the liver, stomach, abdominal esophagus, spleen, and the superior half of both the duodenum and the pancreas. These structures correspond to the embryonic foregut. (Si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatic Artery Proper
The hepatic artery proper (also proper hepatic artery) is the artery that supplies the liver and gallbladder. It raises from the common hepatic artery, a branch of the celiac artery. Structure The hepatic artery proper arises from the common hepatic artery and runs alongside the portal vein and the common bile duct to form the portal triad. A branch of the common hepatic artery –the gastroduodenal artery gives off the small supraduodenal artery to the duodenal bulb. Then the right gastric artery comes off and runs to the left along the lesser curvature of the stomach to meet the left gastric artery, which is a branch of the celiac trunk. It subsequently bifurcates into the right and left hepatic arteries. Variant anatomy Of note, the right and left hepatic arteries may demonstrate variant anatomy. A misplaced right hepatic artery may arise from the superior mesenteric artery (SMA) and a misplaced left hepatic artery may arise from the left gastric artery. The cystic art ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatoduodenal Ligament
The hepatoduodenal ligament is the portion of the lesser omentum extending between the porta hepatis of the liver and the superior part of the duodenum. Running inside it are the following structures collectively known as the portal triad: * hepatic artery proper * portal vein * common bile duct Manual compression of the hepatoduodenal ligament during surgery is known as the Pringle manoeuvre. The cystoduodenal ligament is also found in the lesser omentum and is distinct from both the hepatoduodenal and hepatogastric ligaments. The cystoduodenal ligament is an abnormal peritoneal fold that attaches the duodenum to the gallbladder, representing a rare variation in the anatomy of the lesser sac and its foramen. Another variation sometimes present at the duodenal termination of the hepatoduodenal ligament is the duodenorenal ligament which passes to the front of the right kidney The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Electric
General Electric Company (GE) is an American multinational conglomerate founded in 1892, and incorporated in New York state and headquartered in Boston. The company operated in sectors including healthcare, aviation, power, renewable energy, digital industry, additive manufacturing and venture capital and finance, but has since divested from several areas, now primarily consisting of the first four segments. In 2020, GE ranked among the Fortune 500 as the 33rd largest firm in the United States by gross revenue. In 2011, GE ranked among the Fortune 20 as the 14th most profitable company, but later very severely underperformed the market (by about 75%) as its profitability collapsed. Two employees of GE – Irving Langmuir (1932) and Ivar Giaever (1973) – have been awarded the Nobel Prize. On November 9, 2021, the company announced it would divide itself into three investment-grade public companies. On July 18, 2022, GE unveiled the brand names of the companies it will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
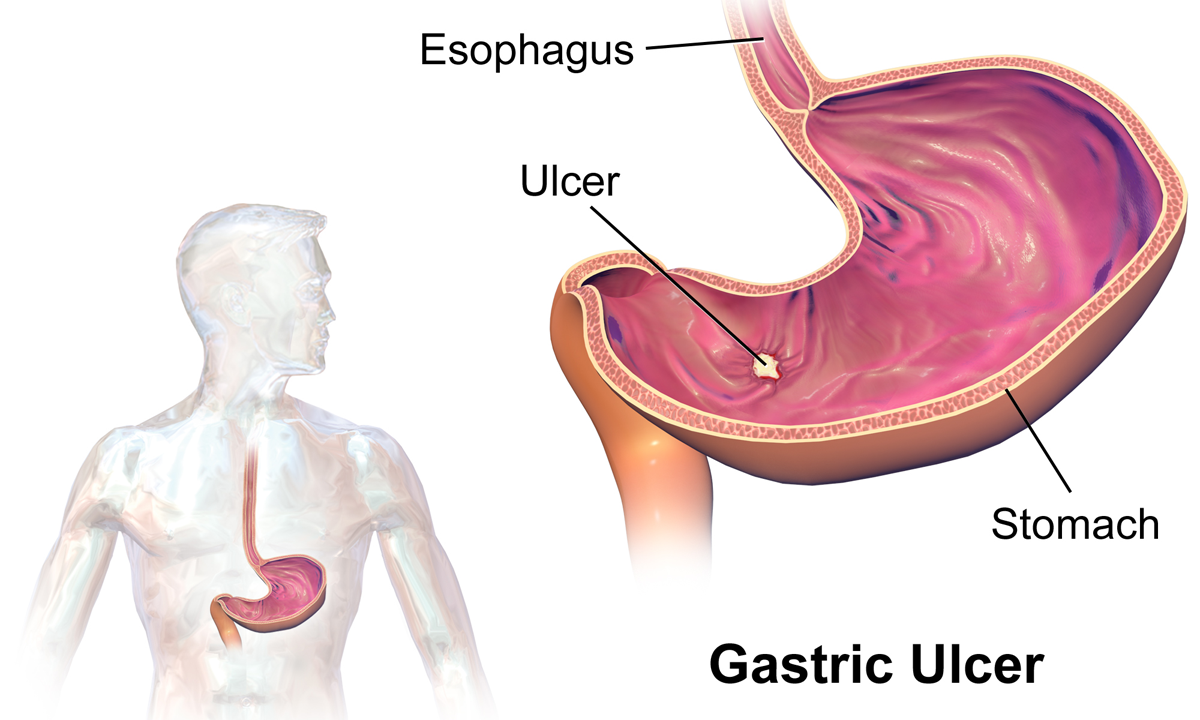
Peptic Ulcer Disease
Peptic ulcer disease (PUD) is a break in the inner lining of the stomach, the first part of the small intestine, or sometimes the lower esophagus. An ulcer in the stomach is called a gastric ulcer, while one in the first part of the intestines is a duodenal ulcer. The most common symptoms of a duodenal ulcer are waking at night with upper abdominal pain and upper abdominal pain that improves with eating. With a gastric ulcer, the pain may worsen with eating. The pain is often described as a burning or dull ache. Other symptoms include belching, vomiting, weight loss, or poor appetite. About a third of older people have no symptoms. Complications may include bleeding, perforation, and blockage of the stomach. Bleeding occurs in as many as 15% of cases. Common causes include the bacteria ''Helicobacter pylori'' and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Other, less common causes include tobacco smoking, stress as a result of other serious health conditions, Behçet's di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastrointestinal Bleed
Gastrointestinal bleeding (GI bleed), also called gastrointestinal hemorrhage (GIB), is all forms of bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract, from the mouth to the rectum. When there is significant blood loss over a short time, symptoms may include vomiting red blood, vomiting black blood, bloody stool, or black stool. Small amounts of bleeding over a long time may cause iron-deficiency anemia resulting in feeling tired or heart-related chest pain. Other symptoms may include abdominal pain, shortness of breath, pale skin, or passing out. Sometimes in those with small amounts of bleeding no symptoms may be present. Bleeding is typically divided into two main types: upper gastrointestinal bleeding and lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Causes of upper GI bleeds include: peptic ulcer disease, esophageal varices due to liver cirrhosis and cancer, among others. Causes of lower GI bleeds include: hemorrhoids, cancer, and inflammatory bowel disease among others. Diagnosis typi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Pancreaticoduodenal Arteries
The superior pancreaticoduodenal artery is an artery that supplies blood to the duodenum and pancreas. Structure It is a branch of the gastroduodenal artery, which most commonly arises from the common hepatic artery of the celiac trunk, although there are numerous variations of the origin of the gastroduodenal artery. The pancreaticoduodenal artery divides into two branches as it descends, an anterior and posterior branch. These branches then travel around the head of the pancreas and duodenum, eventually joining with the anterior and posterior branches of the inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery. The inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery is a branch of the superior mesenteric artery. These arteries, together with the pancreatic branches of the splenic artery, form connections or anastomoses with one another, allowing blood to perfuse the pancreas and duodenum through multiple channels. The artery supplies the anterior and posterior sides of the duodenum and head of pancreas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Mesenteric Artery
In human anatomy, the superior mesenteric artery (SMA) is an artery which arises from the anterior surface of the abdominal aorta, just inferior to the origin of the celiac trunk, and supplies blood to the intestine from the lower part of the duodenum through two-thirds of the transverse colon, as well as the pancreas. Structure It arises anterior to lower border of vertebra L1 in an adult. It is usually 1 cm lower than the celiac trunk. It initially travels in an anterior/inferior direction, passing behind/under the neck of the pancreas and the splenic vein. Located under this portion of the superior mesenteric artery, between it and the aorta, are the following: * left renal vein - travels between the left kidney and the inferior vena cava (can be compressed between the SMA and the abdominal aorta at this location, leading to nutcracker syndrome). * the third part of the duodenum, a segment of the small intestines (can be compressed by the SMA at this location, lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Pancreaticoduodenal Arteries
The inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery (the IPDA) is a branch of the superior mesenteric artery. It supplies the head of the pancreas, and the ascending and inferior parts of the duodenum. Rarely, it may have an aneurysm. Structure The inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery is a branch of the superior mesenteric artery. This occurs opposite the upper border of the inferior part of the duodenum. As soon as it branches, it divides into anterior and posterior branches. These run between the head of the pancreas and the lesser curvature of the duodenum. They then join (anastomose) with the anterior and posterior branches of the superior pancreaticoduodenal artery. Variation The inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery may branch from the first intestinal branch of the superior mesenteric artery rather than directly from it. Function The inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery distributes branches to the head of the pancreas and to the ascending and inferior parts of the duodenum. Clinic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right Gastro-omental Artery
The right gastroepiploic artery (or right gastro-omental artery) is one of the two terminal branches of the gastroduodenal artery. It runs from right to left along the greater curvature of the stomach, between the layers of the greater omentum, anastomosing with the left gastroepiploic artery, a branch of the splenic artery. Except at the pylorus where it is in contact with the stomach, it lies about a finger's breadth from the greater curvature. Branches This vessel gives off numerous branches: * "gastric branches": ascend to supply both surfaces of the stomach. * "omental branches": descend to supply the greater omentum and anastomose with branches of the middle colic. Use in coronary artery surgery The right gastroepiploic artery was first used as a coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) in 1984 by John Pym and colleagues at Queen's University. It has become an accepted alternative conduit, and is particularly useful in patients who do not have suitable saphenous veins to har ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Pancreaticoduodenal Artery
The superior pancreaticoduodenal artery is an artery that supplies blood to the duodenum and pancreas. Structure It is a branch of the gastroduodenal artery, which most commonly arises from the common hepatic artery of the celiac trunk, although there are numerous variations of the origin of the gastroduodenal artery. The pancreaticoduodenal artery divides into two branches as it descends, an anterior and posterior branch. These branches then travel around the head of the pancreas and duodenum, eventually joining with the anterior and posterior branches of the inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery. The inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery is a branch of the superior mesenteric artery. These arteries, together with the pancreatic branches of the splenic artery, form connections or anastomoses with one another, allowing blood to perfuse the pancreas and duodenum through multiple channels. The artery supplies the anterior and posterior sides of the duodenum and head of pancreas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coeliac Trunk
The celiac () artery (also spelled ''coeliac''), also known as the celiac trunk or truncus coeliacus, is the first major branch of the abdominal aorta. It is about 1.25 cm in length. Branching from the aorta at thoracic vertebra 12 (T12) in humans, it is one of three anterior/ midline branches of the abdominal aorta (the others are the superior and inferior mesenteric arteries). Structure The celiac artery is the first major branch of the descending abdominal aorta, branching at a 90° angle. This occurs just below the crus of the diaphragm. This is around the first lumbar vertebra. There are three main divisions of the celiac artery, and each in turn has its own named branches: The celiac artery may also give rise to the inferior phrenic arteries. Function The celiac artery supplies oxygenated blood to the liver, stomach, abdominal esophagus, spleen, and the superior half of both the duodenum and the pancreas. These structures correspond to the embryonic foregut. (Sim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |