|
Ganglion Impar
The pelvic portion of each sympathetic trunk is situated in front of the sacrum, medial to the anterior sacral foramina. It consists of four or five small sacral ganglia, connected together by interganglionic cords, and continuous above with the abdominal portion. Below, the two pelvic sympathetic trunks converge, and end on the front of the coccyx in a small ganglion, the ganglion impar, also known as azygos or ganglion of Walther. Clinical significance A study found that in some cases a single injection of nerve block at the ganglion impar offered complete relief from coccydynia Coccydynia is a medical term meaning pain in the coccyx or tailbone area, often brought on by a fall onto the coccyx or by persistent irritation usually from sitting. Synonyms Coccydynia is also known as coccygodynia, coccygeal pain, coccyx pain, .... References * Munir MA, Zhang J, Ahmad M. (2004)A modified needle-inside-needle technique for the ganglion impar block. Can J Anaesth. 2004 Nov;51 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sympathetic Trunk
The sympathetic trunks (sympathetic chain, gangliated cord) are a paired bundle of nerve fibers that run from the base of the skull to the coccyx. They are a major component of the sympathetic nervous system. Structure The sympathetic trunk lies just lateral to the vertebral bodies for the entire length of the vertebral column. It interacts with the anterior rami of spinal nerves by way of rami communicantes. The sympathetic trunk permits preganglionic fibers of the sympathetic nervous system to ascend to spinal levels superior to T1 and descend to spinal levels inferior to L2/3.Greenstein B., Greenstein A. (2002): Color atlas of neuroscience – Neuroanatomy and neurophysiology. Thieme, Stuttgart – New York, . The superior end of it is continued upward through the carotid canal into the skull, and forms a plexus on the internal carotid artery; the inferior part travels in front of the coccyx, where it converges with the other trunk at a structure known as the ganglion impar. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacrum
The sacrum (plural: ''sacra'' or ''sacrums''), in human anatomy, is a large, triangular bone at the base of the spine that forms by the fusing of the sacral vertebrae (S1S5) between ages 18 and 30. The sacrum situates at the upper, back part of the pelvic cavity, between the two wings of the pelvis. It forms joints with four other bones. The two projections at the sides of the sacrum are called the alae (wings), and articulate with the ilium at the L-shaped sacroiliac joints. The upper part of the sacrum connects with the last lumbar vertebra (L5), and its lower part with the coccyx (tailbone) via the sacral and coccygeal cornua. The sacrum has three different surfaces which are shaped to accommodate surrounding pelvic structures. Overall it is concave (curved upon itself). The base of the sacrum, the broadest and uppermost part, is tilted forward as the sacral promontory internally. The central part is curved outward toward the posterior, allowing greater room for the pel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Sacral Foramina
The sacrum (plural: ''sacra'' or ''sacrums''), in human body, human anatomy, is a large, triangular bone at the base of the vertebral column, spine that forms by the fusing of the sacral vertebrae (S1S5) between ages 18 and 30. The sacrum situates at the upper, back part of the pelvic cavity, between the two Ilium (bone), wings of the pelvis. It forms joints with four other bones. The two projections at the sides of the sacrum are called the alae (wings), and articulate with the Ilium (bone), ilium at the L-shaped sacroiliac joints. The upper part of the sacrum connects with the last lumbar vertebrae, lumbar vertebra (L5), and its lower part with the coccyx (tailbone) via the sacral and coccygeal cornua. The sacrum has three different surfaces which are shaped to accommodate surrounding pelvic structures. Overall it is wikt:concave, concave (curved upon itself). The base of the sacrum, the broadest and uppermost part, is tilted forward as the sacral promontory internally. The c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacral Ganglia
The sacral ganglia are paravertebral ganglia of the sympathetic trunk.:39 As the sympathetic trunk heads inferiorly down the sacrum, it turns medially. There are generally four or five sacral ganglia. In addition to gray rami communicantes, the ganglia send off sacral splanchnic nerves to join the inferior hypogastric plexus. Near the coccyx, the right and left sympathetic trunks join to form the ganglion impar. The sacral ganglia innervate blood vessels and sweat glands of the lower limbs. Clinical significance Recurrences of genital herpes Genital herpes is an infection by the herpes simplex virus (HSV) of the genitals. Most people either have no or mild symptoms and thus do not know they are infected. When symptoms do occur, they typically include small blisters that break open ... are caused by herpes simplex virus (either HSV-1 or HSV-2) which lies dormant in the sacral ganglia between bouts of active infection. Either primary infection or reactivation may be silent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
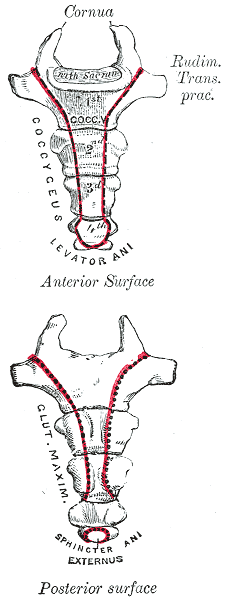
Coccyx
The coccyx ( : coccyges or coccyxes), commonly referred to as the tailbone, is the final segment of the vertebral column in all apes, and analogous structures in certain other mammals such as horses. In tailless primates (e.g. humans and other great apes) since ''Nacholapithecus'' (a Miocene hominoid),Nakatsukasa 2004, ''Acquisition of bipedalism'' (SeFig. 5entitled ''First coccygeal/caudal vertebra in short-tailed or tailless primates.''.) the coccyx is the remnant of a vestigial tail. In animals with bony tails, it is known as ''tailhead'' or ''dock'', in bird anatomy as ''tailfan''. It comprises three to five separate or fused coccygeal vertebrae below the sacrum, attached to the sacrum by a fibrocartilaginous joint, the sacrococcygeal symphysis, which permits limited movement between the sacrum and the coccyx. Structure The coccyx is formed of three, four or five rudimentary vertebrae. It articulates superiorly with the sacrum. In each of the first three segments may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nerve Block
Nerve block or regional nerve blockade is any deliberate interruption of signals traveling along a nerve, often for the purpose of pain relief. Local anesthetic nerve block (sometimes referred to as simply "nerve block") is a short-term block, usually lasting hours or days, involving the injection of an anesthetic, a corticosteroid, and other agents onto or near a nerve. Neurolytic block, the deliberate temporary degeneration of nerve fibers through the application of chemicals, heat, or freezing, produces a block that may persist for weeks, months, or indefinitely. Neurectomy, the cutting through or removal of a nerve or a section of a nerve, usually produces a permanent block. Because neurectomy of a sensory nerve is often followed, months later, by the emergence of new, more intense pain, sensory nerve neurectomy is rarely performed. The concept of nerve block sometimes includes ''central nerve block'', which includes epidural and spinal anaesthesia. Local anesthetic nerve bl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coccydynia
Coccydynia is a medical term meaning pain in the coccyx or tailbone area, often brought on by a fall onto the coccyx or by persistent irritation usually from sitting. Synonyms Coccydynia is also known as coccygodynia, coccygeal pain, coccyx pain, or coccalgia. Anatomy Structure Coccydynia occurs in the lowest part of the spine, the coccyx, which is believed to be a vestigial tail, or in other words the “tail bone”. The name coccyx is derived from the Greek word for cuckoo due to its beak like appearance. The coccyx itself is made up of 3 to 5 vertebrae, some of which may be fused together. The ventral side of the coccyx is slightly concave whereas the dorsal aspect is slightly convex. Both of these sides have transverse grooves that show where the vestigial coccygeal units had previously fused. The coccyx attaches to the sacrum from the dorsal grooves, with the attachment being either a symphysis or as a true synovial joint, and also to the gluteus maximus muscle, the coccyge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |