|
Gadiformes
Gadiformes are an order of ray-finned fish, also called the Anacanthini, that includes the cod. Many major food fish are in this order. They are found in marine waters throughout the world and the vast majority of the species are found in temperate or colder regions (tropical species are typically deep-water). A few species may enter estuaries but only one, the burbot (''Lota lota''), is a freshwater fish. Common characteristics include the positioning of the pelvic fins (if present), below or in front of the pectoral fins. Gadiformes are physoclists, which means their swim bladders do not have a pneumatic duct. The fins are spineless. Gadiform fish range in size from the codlets, which may be as small as in adult length, to the Atlantic cod, ''Gadus morhua'', which reaches up to . Timeline of genera ImageSize = width:900px height:auto barincrement:15px PlotArea = left:10px bottom:50px top:10px right:50px Period = from:-145.5 till:10 TimeAxis = orientation:horizo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gadidae
The Gadidae are a family of marine fish, included in the order Gadiformes, known as the cods, codfishes, or true cods. It contains several commercially important fishes, including the cod, haddock, whiting, and pollock. Most gadid species are found in temperate waters of the Northern Hemisphere, but several range into subtropical, subarctic, and Arctic oceans, and a single (southern blue whiting) is found in the Southern Hemisphere. They are generally medium-sized fish, and are distinguished by the presence of three dorsal fins on the back and two anal fins on the underside. Most species have barbels on their chins, which they use while browsing on the sea floor. Gadids are carnivorous, feeding on smaller fish and crustaceans. Gadids are highly prolific, producing several million eggs at each spawning. This contributes to their high population numbers, which, in turn, makes commercial fishing relatively easy. Concepts differ about the contents of the family Gadidae. The syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
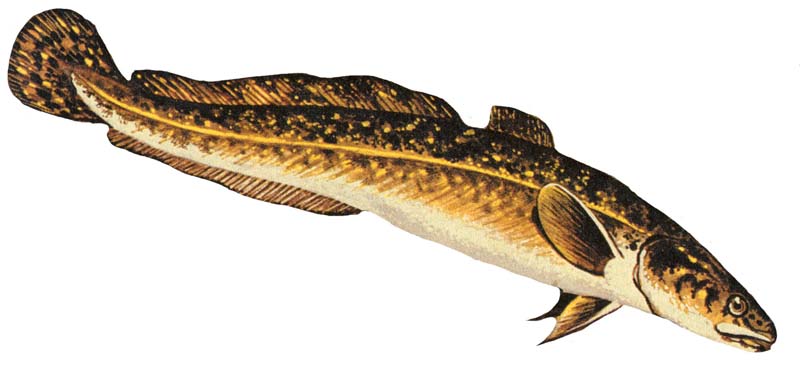
Burbot
The burbot (''Lota lota'') is the only gadiform (cod-like) freshwater fish Freshwater fish are those that spend some or all of their lives in fresh water, such as rivers and lakes, with a salinity of less than 1.05%. These environments differ from marine conditions in many ways, especially the difference in levels of .... It is also known as bubbot, mariah, loche, cusk, freshwater cod, freshwater ling, freshwater cusk, the lawyer, coney-fish, lingcod, and eelpout. The species is closely related to the marine common ling and the cusk (fish), cusk. It is the monotypic, only member of the genus ''Lota''. For some time of the year, the burbot lives under ice, and it requires frigid temperatures to breed. Etymology The name burbot comes from the Latin word ''barba'', meaning beard, referring to its single chin whisker, or barbel (anatomy), barbel. Its generic and specific names, ''Lota lota'', comes from the old French ''lotte'' fish, which is also named "barbot" in Old French. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gadus Morhua
The Atlantic cod (''Gadus morhua'') is a benthopelagic fish of the family Gadidae, widely consumed by humans. It is also commercially known as cod or codling.''Atlantic Cod'' . Seafood Portal. Dry cod may be prepared as unsalted stockfish,''Oxford English Dictionary'', 3rd ed. "milwell, ''n.''" Oxford University Press (Oxford), 2002.''Oxford English Dictionary'', 1st ed. "stock-fish , 'stockfish, ''n.''" Oxford University Press (Oxford), 1917. and as cured |
Physoclist
Physoclisti are, collectively, fishes that lack a connection between the gas bladder and the alimentary canal, with the bladder serving only as a buoyancy organ. Addition and removal of the gases from the gas bladder in such physoclistous fishes occurs through specialised structures called the gas gland and ovale respectively. The pneumatic duct that connects the gut and gas bladder is present in the embryos of these fish but it is lost during development. This anatomical state (the physoclistous condition) is believed to be evolutionarily derived from the ancestral physostomous state. Some fishes, such as eels, are anatomically physostomous, but their gas bladders function similar to those of physoclists. See also * Physostome Physostomes are fishes that have a pneumatic duct connecting the gas bladder to the alimentary canal. This allows the gas bladder to be filled or emptied via the mouth. This not only allows the fish to fill their bladder by gulping air, but also ... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek grc, label=none, πλεῖστος, pleīstos, most and grc, label=none, καινός, kainós (latinized as ), 'new'. At the end of the preceding Pliocene, the previously isolated North and South American continents were joined by the Isthmus of Panama, causing Great American Interchang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.333 million to 2.58See the 2014 version of the ICS geologic time scale million years ago. It is the second and most recent epoch of the Neogene Period in the . The Pliocene follows the Epoch and is followed by the Epoch. Prior to the 2009 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene is preceded by the Oligocene and is followed by the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by a single distinct global event but consist rather of regionally defined boundaries between the warmer Oligocene and the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, the Arabian Peninsula collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean, and allowing a faunal interchange to occur between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans into Eurasia. During the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligocene
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch of the Paleogene Period and extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the epoch are well identified but the exact dates of the start and end of the epoch are slightly uncertain. The name Oligocene was coined in 1854 by the German paleontologist Heinrich Ernst Beyrich from his studies of marine beds in Belgium and Germany. The name comes from the Ancient Greek (''olígos'', "few") and (''kainós'', "new"), and refers to the sparsity of extant forms of molluscs. The Oligocene is preceded by the Eocene Epoch and is followed by the Miocene Epoch. The Oligocene is the third and final epoch of the Paleogene Period. The Oligocene is often considered an important time of transition, a link between the archaic world of the tropical Eocene and the more modern ecosystems of the Miocene. Major changes during the Oligocene included a global expansion o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', "dawn") and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isotope Carbon-13, 13C in the atmosphere was exceptionally low in comparison with the more common isotope Carbon-12, 12C. The end is set at a major extinction event called the ''Grande Coupure'' (the "Great Break" in continuity) or the Eocene–Oligocene extinction event, which may be related to the impact of one or more large bolides in Popigai impact structure, Siberia and in what is now ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleocene
The Paleocene, ( ) or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 mya (unit), million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name is a combination of the Ancient Greek ''palaiós'' meaning "old" and the Eocene Epoch (which succeeds the Paleocene), translating to "the old part of the Eocene". The epoch is bracketed by two major events in Earth's history. The K–Pg extinction event, brought on by Chicxulub impact, an asteroid impact and possibly volcanism, marked the beginning of the Paleocene and killed off 75% of living species, most famously the non-avian dinosaurs. The end of the epoch was marked by the Paleocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM), which was a major climatic event wherein about 2,500–4,500 gigatons of carbon were released into the atmosphere and ocean systems, causing a spike in global temperatures and ocean acidification. In the Pal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the Latin word for the white limestone known as chalk. The chalk of northern France and the white cliffs of south-eastern England date from the Cretaceous Period. Climate During the Late Cretaceous, the climate was warmer than present, although throughout the period a cooling trend is evident. The tropics became restricted to equatorial regions and northern latitudes experienced markedly more seasonal climatic conditions. Geography Due to plate tectonics, the Americas were gradually moving westward, causing the Atlantic Ocean to expand. The Western Interior Seaway divided North America into eastern and western halves; Appalachia and Laramidia. India maintained a northward course towards Asia. In the Southern Hemisphere, Australia and Ant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Cretaceous
The Early Cretaceous ( geochronological name) or the Lower Cretaceous (chronostratigraphic name), is the earlier or lower of the two major divisions of the Cretaceous. It is usually considered to stretch from 145 Ma to 100.5 Ma. Geology Proposals for the exact age of the Barremian-Aptian boundary ranged from 126 to 117 Ma until recently (as of 2019), but based on drillholes in Svalbard the defining early Aptian Oceanic Anoxic Event 1a (OAE1a) was carbon isotope dated to 123.1±0.3 Ma, limiting the possible range for the boundary to c. 122–121 Ma. There is a possible link between this anoxic event and a series of Early Cretaceous large igneous provinces (LIP). The Ontong Java-Manihiki-Hikurangi large igneous province, emplaced in the South Pacific at c. 120 Ma, is by far the largest LIP in Earth's history. The Ontong Java Plateau today covers an area of 1,860,000 km2. In the Indian Ocean another LIP began to form at c. 120 Ma, the Kerguelen P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |