|
Group Table
Named after the 19th-century British mathematician Arthur Cayley, a Cayley table describes the structure of a finite group by arranging all the possible products of all the group's elements in a square table reminiscent of an addition or multiplication table. Many properties of a groupsuch as whether or not it is abelian, which elements are inverses of which elements, and the size and contents of the group's centercan be discovered from its Cayley table. A simple example of a Cayley table is the one for the group under ordinary multiplication: History Cayley tables were first presented in Cayley's 1854 paper, "On The Theory of Groups, as depending on the symbolic equation ''θ'' ''n'' = 1". In that paper they were referred to simply as tables, and were merely illustrativethey came to be known as Cayley tables later on, in honour of their creator. Structure and layout Because many Cayley tables describe groups that are not abelian, the product ''ab'' with respect to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. The UK includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland, and most of List of islands of the United Kingdom, the smaller islands within the British Isles, covering . Northern Ireland shares Republic of Ireland–United Kingdom border, a land border with the Republic of Ireland; otherwise, the UK is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea and the Irish Sea. It maintains sovereignty over the British Overseas Territories, which are located across various oceans and seas globally. The UK had an estimated population of over 68.2 million people in 2023. The capital and largest city of both England and the UK is London. The cities o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quasigroup
In mathematics, especially in abstract algebra, a quasigroup is an algebraic structure that resembles a group in the sense that " division" is always possible. Quasigroups differ from groups mainly in that the associative and identity element properties are optional. In fact, a nonempty associative quasigroup is a group. A quasigroup that has an identity element is called a loop. Definitions There are at least two structurally equivalent formal definitions of quasigroup: * One defines a quasigroup as a set with one binary operation. * The other, from universal algebra, defines a quasigroup as having three primitive operations. The homomorphic image of a quasigroup that is defined with a single binary operation, however, need not be a quasigroup, in contrast to a quasigroup as having three primitive operations. We begin with the first definition. Algebra A quasigroup is a non-empty set with a binary operation (that is, a magma, indicating that a quasigroup has to sat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
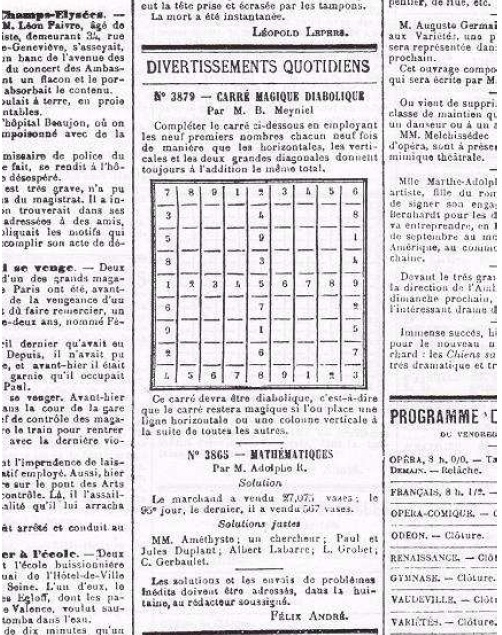
Sudoku
Sudoku (; ; originally called Number Place) is a logic puzzle, logic-based, combinatorics, combinatorial number-placement puzzle. In classic Sudoku, the objective is to fill a 9 × 9 grid with digits so that each column, each row, and each of the nine 3 × 3 subgrids that compose the grid (also called "boxes", "blocks", or "regions") contains all of the digits from 1 to 9. The puzzle setter provides a partially completed grid, which for a well-posed problem, well-posed puzzle has a single solution. French newspapers featured similar puzzles in the 19th century, and the modern form of the puzzle first appeared in 1979 puzzle books by Dell Magazines under the name Number Place. However, the puzzle type only began to gain widespread popularity in 1986 when it was published by the Japanese puzzle company Nikoli (publisher), Nikoli under the name Sudoku, meaning "single number". In newspapers outside of Japan, it first appeared in ''The Conway Daily Sun'' (New Hamp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin Square
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area around Rome, Italy. Through the expansion of the Roman Republic, it became the dominant language in the Italian Peninsula and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. It has greatly influenced many languages, including English, having contributed many words to the English lexicon, particularly after the Christianization of the Anglo-Saxons and the Norman Conquest. Latin roots appear frequently in the technical vocabulary used by fields such as theology, the sciences, medicine, and law. By the late Roman Republic, Old Latin had evolved into standardized Classical Latin. Vulgar Latin refers to the less prestigious colloquial registers, attested in inscriptions and some literary works such as those of the comic playwrights Plautus and Terence and the author Petronius. Whil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semigroup
In mathematics, a semigroup is an algebraic structure consisting of a set together with an associative internal binary operation on it. The binary operation of a semigroup is most often denoted multiplicatively (just notation, not necessarily the elementary arithmetic multiplication): , or simply ''xy'', denotes the result of applying the semigroup operation to the ordered pair . Associativity is formally expressed as that for all ''x'', ''y'' and ''z'' in the semigroup. Semigroups may be considered a special case of magmas, where the operation is associative, or as a generalization of groups, without requiring the existence of an identity element or inverses. As in the case of groups or magmas, the semigroup operation need not be commutative, so is not necessarily equal to ; a well-known example of an operation that is associative but non-commutative is matrix multiplication. If the semigroup operation is commutative, then the semigroup is called a ''commutative semigroup' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permutation Group
In mathematics, a permutation group is a group ''G'' whose elements are permutations of a given set ''M'' and whose group operation is the composition of permutations in ''G'' (which are thought of as bijective functions from the set ''M'' to itself). The group of ''all'' permutations of a set ''M'' is the symmetric group of ''M'', often written as Sym(''M''). The term ''permutation group'' thus means a subgroup of the symmetric group. If then Sym(''M'') is usually denoted by S''n'', and may be called the ''symmetric group on n letters''. By Cayley's theorem, every group is isomorphic to some permutation group. The way in which the elements of a permutation group permute the elements of the set is called its group action. Group actions have applications in the study of symmetries, combinatorics and many other branches of mathematics, physics and chemistry. Basic properties and terminology A ''permutation group'' is a subgroup of a symmetric group; that is, its elements ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kronecker Delta
In mathematics, the Kronecker delta (named after Leopold Kronecker) is a function of two variables, usually just non-negative integers. The function is 1 if the variables are equal, and 0 otherwise: \delta_ = \begin 0 &\text i \neq j, \\ 1 &\text i=j. \end or with use of Iverson brackets: \delta_ = =j, For example, \delta_ = 0 because 1 \ne 2, whereas \delta_ = 1 because 3 = 3. The Kronecker delta appears naturally in many areas of mathematics, physics, engineering and computer science, as a means of compactly expressing its definition above. Generalized versions of the Kronecker delta have found applications in differential geometry and modern tensor calculus, particularly in formulations of gauge theory and topological field models. In linear algebra, the n\times n identity matrix \mathbf has entries equal to the Kronecker delta: I_ = \delta_ where i and j take the values 1,2,\cdots,n, and the inner product of vectors can be written as \mathbf\cdot\mathbf = \sum_^n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permutation Matrix
In mathematics, particularly in matrix theory, a permutation matrix is a square binary matrix that has exactly one entry of 1 in each row and each column with all other entries 0. An permutation matrix can represent a permutation of elements. Pre- multiplying an -row matrix by a permutation matrix , forming , results in permuting the rows of , while post-multiplying an -column matrix , forming , permutes the columns of . Every permutation matrix ''P'' is orthogonal, with its inverse equal to its transpose: P^=P^\mathsf. Indeed, permutation matrices can be characterized as the orthogonal matrices whose entries are all non-negative. The two permutation/matrix correspondences There are two natural one-to-one correspondences between permutations and permutation matrices, one of which works along the rows of the matrix, the other along its columns. Here is an example, starting with a permutation in two-line form at the upper left: :\begin \pi\colon\begin1&2&3&4\\3&2&4&1\e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin Square
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area around Rome, Italy. Through the expansion of the Roman Republic, it became the dominant language in the Italian Peninsula and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. It has greatly influenced many languages, including English, having contributed many words to the English lexicon, particularly after the Christianization of the Anglo-Saxons and the Norman Conquest. Latin roots appear frequently in the technical vocabulary used by fields such as theology, the sciences, medicine, and law. By the late Roman Republic, Old Latin had evolved into standardized Classical Latin. Vulgar Latin refers to the less prestigious colloquial registers, attested in inscriptions and some literary works such as those of the comic playwrights Plautus and Terence and the author Petronius. Whil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pigeonhole Principle
In mathematics, the pigeonhole principle states that if items are put into containers, with , then at least one container must contain more than one item. For example, of three gloves, at least two must be right-handed or at least two must be left-handed, because there are three objects but only two categories of handedness to put them into. This seemingly obvious statement, a type of combinatorics, counting argument, can be used to demonstrate possibly unexpected results. For example, given that the Demographics of London, population of London is more than one unit greater than the maximum number of hairs that can be on a human's head, the principle requires that there must be at least two people in London who have the same number of hairs on their heads. Although the pigeonhole principle appears as early as 1624 in a book attributed to Jean Leurechon, it is commonly called Dirichlet's box principle or Dirichlet's drawer principle after an 1834 treatment of the principle by Pet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reductio Ad Absurdum
In logic, (Latin for "reduction to absurdity"), also known as (Latin for "argument to absurdity") or ''apagogical argument'', is the form of argument that attempts to establish a claim by showing that the opposite scenario would lead to absurdity or contradiction. This argument form traces back to Ancient Greek philosophy and has been used throughout history in both formal mathematical and philosophical reasoning, as well as in debate. In mathematics, the technique is called ''proof by contradiction''. In formal logic, this technique is captured by an axiom for "Reductio ad Absurdum", normally given the abbreviation RAA, which is expressible in propositional logic. This axiom is the introduction rule for negation (see ''negation introduction''). Examples The "absurd" conclusion of a ''reductio ad absurdum'' argument can take a range of forms, as these examples show: * The Earth cannot be flat; otherwise, since the Earth is assumed to be finite in extent, we would find peo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permutation
In mathematics, a permutation of a set can mean one of two different things: * an arrangement of its members in a sequence or linear order, or * the act or process of changing the linear order of an ordered set. An example of the first meaning is the six permutations (orderings) of the set : written as tuples, they are (1, 2, 3), (1, 3, 2), (2, 1, 3), (2, 3, 1), (3, 1, 2), and (3, 2, 1). Anagrams of a word whose letters are all different are also permutations: the letters are already ordered in the original word, and the anagram reorders them. The study of permutations of finite sets is an important topic in combinatorics and group theory. Permutations are used in almost every branch of mathematics and in many other fields of science. In computer science, they are used for analyzing sorting algorithms; in quantum physics, for describing states of particles; and in biology, for describing RNA sequences. The number of permutations of distinct objects is factorial, us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |