|
Grassy Knoll
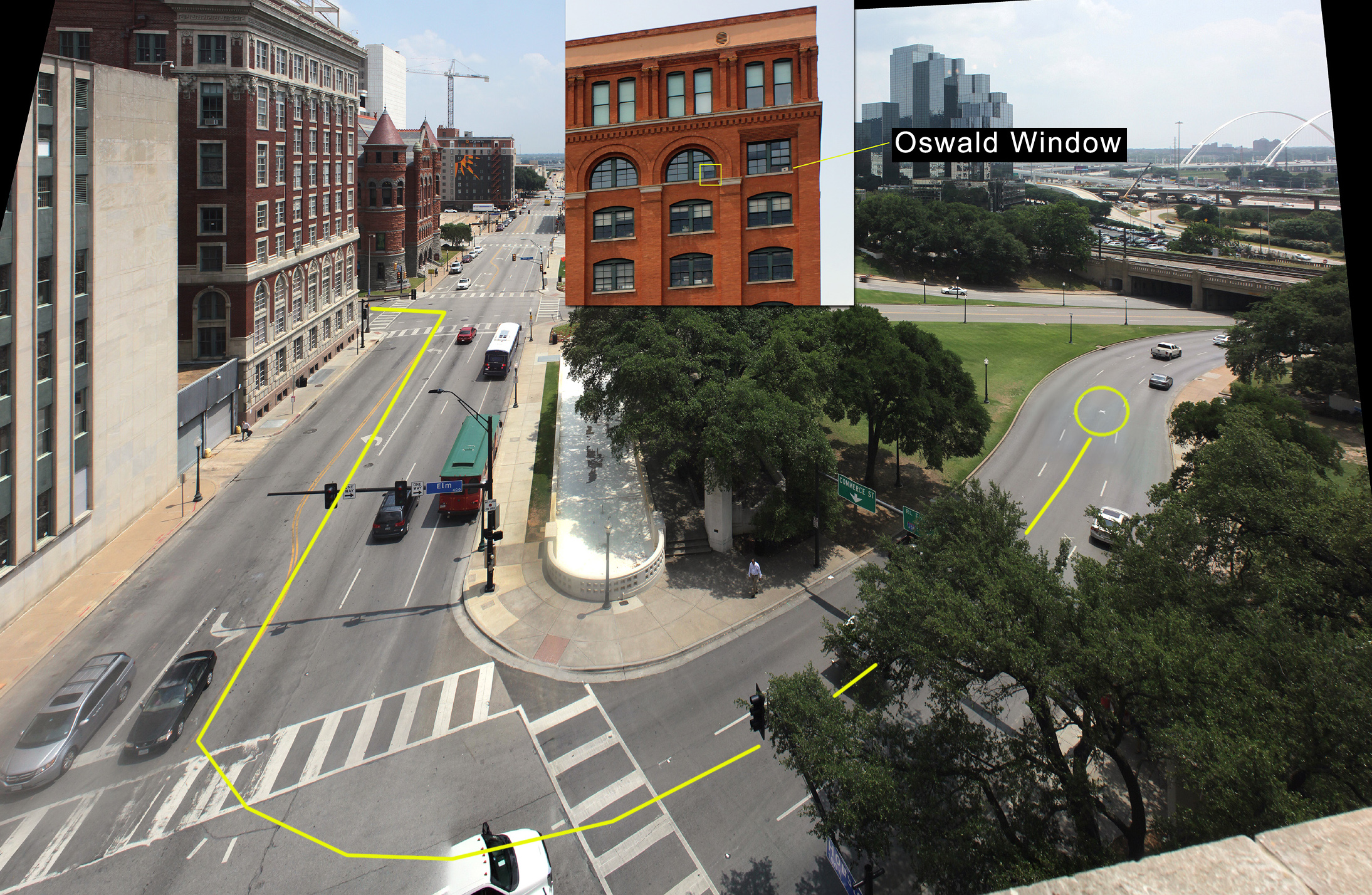
Dealey Plaza is a city park in the West End Historic District of downtown Dallas, Texas. It is sometimes called the "birthplace of Dallas". It was also the location of the assassination of John F. Kennedy in 1963; 30 minutes after the shooting, Kennedy was pronounced dead at Parkland Memorial Hospital. The Dealey Plaza Historic District was named a National Historic Landmark on the 30th anniversary of the assassination, to preserve Dealey Plaza, street rights-of-way, and buildings and structures by the plaza visible from the assassination site, that have been identified as witness locations or as possible locations for the assassin. National Historic Landmark The Dealey Plaza Historic District was added to the National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) in 1993 and designated a National Historic Landmark the same year. The former county courthouse is individually listed on the National Register and is also designated a State Antiquities Landmark (SAL) and a Recorded Texas Hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dallas, Texas
Dallas () is the third largest city in Texas and the largest city in the Dallas–Fort Worth metroplex, the fourth-largest metropolitan area in the United States at 7.5 million people. It is the largest city in and seat of Dallas County with portions extending into Collin, Denton, Kaufman and Rockwall counties. With a 2020 census population of 1,304,379, it is the ninth most-populous city in the U.S. and the third-largest in Texas after Houston and San Antonio. Located in the North Texas region, the city of Dallas is the main core of the largest metropolitan area in the Southern United States and the largest inland metropolitan area in the U.S. that lacks any navigable link to the sea. The cities of Dallas and nearby Fort Worth were initially developed due to the construction of major railroad lines through the area allowing access to cotton, cattle and later oil in North and East Texas. The construction of the Interstate Highway System reinforced Dallas's prominen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sixth Floor Museum At Dealey Plaza
The Sixth Floor Museum at Dealey Plaza is a museum located on the sixth floor of the Dallas County Administration Building (formerly the Texas School Book Depository) in downtown Dallas, Texas, overlooking Dealey Plaza at the intersection of Elm and Houston Streets. The museum examines the life, times, death, and legacy of United States President John F. Kennedy and the life of Lee Harvey Oswald as well as the various conspiracy theories surrounding the assassination. The museum's exhibition area uses historic films, photographs, artifacts, and interpretive displays to document the events of the assassination, the reports by government investigations that followed, and the historical legacy of the tragedy. The museum is self-sufficient in funding, relying solely on donations and ticket sales. It rents the space from the County of Dallas. The museum was founded by the Dallas County Historical Foundation. Syndicated from the ''Los Angeles Daily News''. It opened on Presidents' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Bannerman Dealey
George Bannerman Dealey (September 18, 1859 – February 26, 1946) was a Dallas, Texas, businessman. Dealey was the long-time publisher of ''The Dallas Morning News'' and owner of the A. H. Belo Corporation. A plaza in Dallas is named in his honor, and became instantly world-famous when it became the site of the assassination of John F. Kennedy in 1963. Childhood Dealey was born on September 18, 1859, at the home of his parents, George Dealey (1829–1894) and Mary Ann Nellins (1829–1913), on Queen St., Rusholme, Manchester, England. He was the fifth of 10 children. In the mid-1860s the family moved to Liverpool, England, where he began his schooling and worked as a grocer's apprentice. In 1870 his family immigrated to Galveston, Texas, where he continued in public school and worked at various odd jobs. Newspaper career On October 12, 1874, he assumed an older brother's job as office boy at '' The Galveston News'' at $3.00 per week, for the owner, Alfred H. Belo. Dea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Works Progress Administration
The Works Progress Administration (WPA; renamed in 1939 as the Work Projects Administration) was an American New Deal agency that employed millions of jobseekers (mostly men who were not formally educated) to carry out public works projects, including the construction of public buildings and roads. It was set up on May 6, 1935, by presidential order, as a key part of the Second New Deal. The WPA's first appropriation in 1935 was $4.9 billion (about $15 per person in the U.S., around 6.7 percent of the 1935 GDP). Headed by Harry Hopkins, the WPA supplied paid jobs to the unemployed during the Great Depression in the United States, while building up the public infrastructure of the US, such as parks, schools, and roads. Most of the jobs were in construction, building more than 620,000 miles (1,000,000 km) of streets and over 10,000 bridges, in addition to many airports and much housing. The largest single project of the WPA was the Tennessee Valley Authority. At its peak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Neely Bryan
John Neely Bryan (December 24, 1810 – September 8, 1877) was a Presbyterian farmer, lawyer, and tradesman in the United States and founder of the city of Dallas, Texas. Early life Bryan was born to James and Elizabeth (Neely) Bryan in Fayetteville, Tennessee. There, he attended the Fayetteville Military Academy and after studying law was admitted to the Tennessee Bar. Around the year 1833 he left Tennessee and moved to Arkansas, where he was an Indian trader. According to some sources, he and a business partner laid out Van Buren, Arkansas. Exploring Dallas Bryan visited the Dallas area in 1839, and in 1841, he established a permanent settlement, which eventually became the burgeoning city of Dallas. Establishment of Dallas Bryan was very important to early Dallas — he served as the postmaster, a store owner, a ferry operator (he operated a ferry where Commerce Street crosses the Trinity River today), and his home served as the courthouse. In 1844, he persu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pergola
A pergola is most commonly an outdoor garden feature forming a shaded walkway, passageway, or sitting area of vertical posts or pillars that usually support cross-beams and a sturdy open lattice, often upon which woody vines are trained. The origin of the word is the Late Latin ''pergula'', referring to a projecting eave. As a type of gazebo, it also may be an extension of a building or serve as protection for an open terrace or a link between pavilions. They are different from green tunnels, with a green tunnel being a type of road under a canopy of trees. Pergolas are sometimes confused with "arbors," as the terms are used interchangeably. Generally, an "arbor" is regarded as wooden bench seats with a roof, usually enclosed by lattice panels forming a framework for climbing plants; in evangelical Christianity, brush arbor revivals occur under such structures. A pergola, on the other hand, is a much larger and more open structure. Normally, a pergola does not include integ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Hurd
Peter Hurd (February 22, 1904 – July 9, 1984) was an American painter whose work is strongly associated with the people and landscapes of San Patricio, New Mexico, where he lived from the 1930s. He is equally acclaimed for his portraits and his western landscapes. Early in his life, Hurd studied in Chadds Ford, Pennsylvania under the noted illustrator N. C. Wyeth, along with two of his grown children. Hurd later married the painter's eldest daughter, Henriette Wyeth, who also is known as an accomplished painter. During World War II, Hurd worked for ''Life'' magazine as a war correspondent attached to the US Air Force. He created hundreds of "War Sketches". Life Born in Roswell, New Mexico, Peter Hurd originally attended military school before he realized he loved painting and wanted to pursue it professionally. After graduating from the New Mexico Military Institute in Roswell, he was halfway through West Point when he changed course to follow his true calling. He moved to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Deal
The New Deal was a series of programs, public work projects, financial reforms, and regulations enacted by President Franklin D. Roosevelt in the United States between 1933 and 1939. Major federal programs agencies included the Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC), the Works Progress Administration (WPA), the Civil Works Administration (CWA), the Farm Security Administration (FSA), the National Industrial Recovery Act of 1933 (NIRA) and the Social Security Administration (SSA). They provided support for farmers, the unemployed, youth, and the elderly. The New Deal included new constraints and safeguards on the banking industry and efforts to re-inflate the economy after prices had fallen sharply. New Deal programs included both laws passed by Congress as well as presidential executive orders during the first term of the presidency of Franklin D. Roosevelt. The programs focused on what historians refer to as the "3 R's": relief for the unemployed and for the poor, recovery of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoclassical Architecture
Neoclassical architecture is an architectural style produced by the Neoclassical movement that began in the mid-18th century in Italy and France. It became one of the most prominent architectural styles in the Western world. The prevailing styles of architecture in most of Europe for the previous two centuries, Renaissance architecture and Baroque architecture, already represented partial revivals of the Classical architecture of ancient Rome and (much less) ancient Greek architecture, but the Neoclassical movement aimed to strip away the excesses of Late Baroque and return to a purer and more authentic classical style, adapted to modern purposes. The development of archaeology and published accurate records of surviving classical buildings was crucial in the emergence of Neoclassical architecture. In many countries, there was an initial wave essentially drawing on Roman architecture, followed, from about the start of the 19th century, by a second wave of Greek Revival architec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Art Deco
Art Deco, short for the French ''Arts Décoratifs'', and sometimes just called Deco, is a style of visual arts, architecture, and product design, that first appeared in France in the 1910s (just before World War I), and flourished in the United States and Europe during the 1920s and 1930s. Through styling and design of the exterior and interior of anything from large structures to small objects, including how people look (clothing, fashion and jewelry), Art Deco has influenced bridges, buildings (from skyscrapers to cinemas), ships, ocean liners, trains, cars, trucks, buses, furniture, and everyday objects like radios and vacuum cleaners. It got its name after the 1925 Exposition internationale des arts décoratifs et industriels modernes (International Exhibition of Modern Decorative and Industrial Arts) held in Paris. Art Deco combined modern styles with fine craftsmanship and rich materials. During its heyday, it represented luxury, glamour, exuberance, and faith in socia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dallas County Courthouse (Texas)
The Dallas County Courthouse, built in 1892 of red sandstone with rusticated marble accents, is a historic governmental building located at 100 South Houston Street in Dallas, Texas. Also known as the Old Red Courthouse, it became the Old Red Museum, a local history museum, in 2007. It was designed in the Richardsonian Romanesque style of architecture by architect Max A. Orlopp, Jr. of the Little Rock, Arkansas based firm Orlopp & Kusener. In 1966 it was replaced by a newer courthouse building nearby. On December 12, 1976, it was added to the National Register of Historic Places. In 2005–2007 the building was renovated. Gallery Old Red Museum January 2016 10.jpg, Museum interior Old Red Museum January 2016 03 (Early Years Gallery).jpg, Early Years Gallery Old Red Museum January 2016 05 (Trading Center Gallery).jpg, Trading Center Gallery Old Red Museum January 2016 07 (Big "D" Gallery).jpg, Big "D" Gallery Old Red Museum January 2016 08 (World Crossroads Gallery).jpg, W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)


_-_facade_on_Piazza_dei_signori.jpg)
_interior.jpg)