|
Gradual
The gradual ( la, graduale or ) is a chant or hymn in the Mass, the liturgical celebration of the Eucharist in the Catholic Church, and among some other Christians. It gets its name from the Latin (meaning "step") because it was once chanted on the step of the ambo or altar. In the Tridentine Mass, it is sung after the reading or chanting of the epistle and before the Alleluia, or, during penitential seasons, before the tract. In the Mass of Paul VI, the gradual is usually replaced with the responsorial psalm. Although the Gradual remains an option in the Mass of Paul VI, its use is extremely rare outside monasteries. The gradual is part of the proper of the Mass. A gradual can also refer to a book collecting all the musical items of the Mass. The official such book for the Roman Rite is the Roman Gradual (). Other such books include the Dominican Gradual. History The Gradual, like the Alleluia and Tract, is one of the responsorial chants of the Mass. Responsorial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gradual Of King John Albert
The gradual ( la, graduale or ) is a chant or hymn in the Mass, the liturgical celebration of the Eucharist in the Catholic Church, and among some other Christians. It gets its name from the Latin (meaning "step") because it was once chanted on the step of the ambo or altar. In the Tridentine Mass, it is sung after the reading or chanting of the epistle and before the Alleluia, or, during penitential seasons, before the tract. In the Mass of Paul VI, the gradual is usually replaced with the responsorial psalm. Although the Gradual remains an option in the Mass of Paul VI, its use is extremely rare outside monasteries. The gradual is part of the proper of the Mass. A gradual can also refer to a book collecting all the musical items of the Mass. The official such book for the Roman Rite is the Roman Gradual (). Other such books include the Dominican Gradual. History The Gradual, like the Alleluia and Tract, is one of the responsorial chants of the Mass. Responsorial chants der ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Gradual
The ''Roman Gradual'' (Latin: ''Graduale Romanum'') is an official liturgical book of the Roman Rite of the Roman Catholic Church containing chants, including the proper and many more, for use in Mass. The latest edition of 1974 takes account of the 1970 revision of the ''Roman Missal''. In 1979, the ''Graduale Triplex: The Roman Gradual With the Addition of Neums from Ancient Manuscripts'' ( in English (1985), in Latin) was published. It added reproductions of the neumes from ancient manuscripts placed above and below the later notation. Description The Roman Gradual includes the * Introit (entrance chant: antiphon with verses), * the Gradual psalm (a meditative psalm chant, this may be replaced with a simpler responsorial psalm except when the Mass is celebrated "in Cantu" according to the rubrics of the accompanying document Ordo Cantus Missae), or an additional Alleluia verse during Eastertide, * the Sequence Hymn (obligatory on Easter and Pentecost, optional on C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Responsorial Psalm
Responsorial psalmody primarily refers to the placement and use of the Psalm within the readings at a Christian service of the Eucharist. The Psalm chosen in such a context is often called the responsorial psalm. Although often associated with the Roman Catholic church, it is used more widely, including in Anglican, Episcopalian and Lutheran traditions. The "responsorial" aspect is used in two related but different ways: the liturgical position of the psalm as a 'response' to the first (Old Testament) reading, and one possible manner of reciting it. The RSCM summarises these two aspects: "It is responsorial because it is sung in response to the first reading, not because it has a refrain or response for the people to sing. The whole psalm is therefore the response." Liturgical position The Catholic Dictionary defines the responsorial psalm as: The New Catholic Encyclopedia points out that not only the psalm but also the gradual and alleluia were also originally 'responsor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Rite
The Roman Rite ( la, Ritus Romanus) is the primary liturgical rite of the Latin Church, the largest of the '' sui iuris'' particular churches that comprise the Catholic Church. It developed in the Latin language in the city of Rome and, while distinct Latin liturgical rites such as the Ambrosian Rite remain, the Roman Rite has gradually been adopted almost everywhere in the Latin Church. In medieval times there were numerous local variants, even if all of them did not amount to distinct rites, yet uniformity increased as a result of the invention of printing and in obedience to the decrees of the Council of Trent of 1545–63 (see '' Quo primum''). Several Latin liturgical rites that survived into the 20th century were abandoned voluntarily after the Second Vatican Council. The Roman Rite is now the most widespread liturgical rite not only in the Catholic Church but in Christianity as a whole. The Roman Rite has been adapted through the centuries and the history of its Euchari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass In The Catholic Church
The Mass is the central liturgical service of the Eucharist in the Catholic Church, in which bread and wine are consecrated and become the body and blood of Christ. As defined by the Church at the Council of Trent, in the Mass, "the same Christ who offered himself once in a bloody manner on the altar of the cross, is present and offered in an unbloody manner". The Church describes the Mass as the "source and summit of the Christian life". Thus the Church teaches that the Mass is a sacrifice. It teaches that the sacramental bread and wine, through consecration by an ordained priest, become the sacrificial body, blood, soul, and divinity of Christ as the sacrifice on Calvary made truly present once again on the altar. The Catholic Church permits only baptised members in the state of grace (Catholics who are not in a state of mortal sin) to receive Christ in the Eucharist. Many of the other sacraments of the Catholic Church, such as confirmation, holy orders, and holy matrimon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deacon
A deacon is a member of the diaconate, an office in Christian churches that is generally associated with service of some kind, but which varies among theological and denominational traditions. Major Christian churches, such as the Catholic Church, the Oriental Orthodox Churches, the Eastern Orthodox Church, the Scandinavian Lutheran Churches, the Methodist Churches, the Anglican Communion, and the Free Church of England, view the diaconate as an order of ministry. Origin and development The word ''deacon'' is derived from the Greek word (), which is a standard ancient Greek word meaning "servant", "waiting-man", "minister", or "messenger". It is generally assumed that the office of deacon originated in the selection of seven men by the apostles, among them Stephen, to assist with the charitable work of the early church as recorded in Acts of the Apostles chapter 6. The title ''deaconess'' ( grc, διακόνισσα, diakónissa, label=none) is not found in the Bible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization. O'Collins, p. v (preface). The church consists of 24 ''sui iuris'' churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and eparchies located around the world. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the chief pastor of the church. The bishopric of Rome, known as the Holy See, is the central governing authority of the church. The administrative body of the Holy See, the Roman Curia, has its principal offices in Vatican City, a small enclave of the Italian city of Rome, of which the pope is head of state. The core beliefs of Catholicism are found in the Nicene Creed. The Catholic Church teaches that it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Gregory I
Pope Gregory I ( la, Gregorius I; – 12 March 604), commonly known as Saint Gregory the Great, was the bishop of Rome from 3 September 590 to his death. He is known for instigating the first recorded large-scale mission from Rome, the Gregorian mission, to convert the then largely pagan Anglo-Saxons to Christianity. Gregory is also well known for his writings, which were more prolific than those of any of his predecessors as pope. The epithet Saint Gregory the Dialogist has been attached to him in Eastern Christianity because of his '' Dialogues''. English translations of Eastern texts sometimes list him as Gregory "Dialogos", or the Anglo-Latinate equivalent "Dialogus". A Roman senator's son and himself the prefect of Rome at 30, Gregory lived in a monastery he established on his family estate before becoming a papal ambassador and then pope. Although he was the first pope from a monastic background, his prior political experiences may have helped him to be a talented ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epistle
An epistle (; el, ἐπιστολή, ''epistolē,'' "letter") is a writing directed or sent to a person or group of people, usually an elegant and formal didactic letter. The epistle genre of letter-writing was common in ancient Egypt as part of the scribal-school writing curriculum. The letters in the New Testament from Apostles to Christians are usually referred to as epistles. Those traditionally attributed to Paul are known as Pauline epistles and the others as catholic (i.e., "general") epistles. Ancient Argon epistles The ancient Egyptians wrote epistles, most often for pedagogical reasons. Egyptologist Edward Wente (1990) speculates that the Fifth-dynasty Pharaoh Djedkare Isesi—in his many letters sent to his viziers—was a pioneer in the epistolary genre. Its existence is firmly attested during the Sixth Dynasty of the Old Kingdom, and is prominently featured in the educational guide ''The Book of Kemit'' written during the Eleventh Dynasty. A standard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psalm
The Book of Psalms ( or ; he, תְּהִלִּים, , lit. "praises"), also known as the Psalms, or the Psalter, is the first book of the ("Writings"), the third section of the Tanakh, and a book of the Old Testament. The title is derived from the Greek translation, (), meaning "instrumental music" and, by extension, "the words accompanying the music". The book is an anthology of individual Hebrew religious hymns, with 150 in the Jewish and Western Christian tradition and more in the Eastern Christian churches. Many are linked to the name of David, but modern mainstream scholarship rejects his authorship, instead attributing the composition of the psalms to various authors writing between the 9th and 5th centuries BC. In the Quran, the Arabic word ‘Zabur’ is used for the Psalms of David in the Hebrew Bible. Structure Benedictions The Book of Psalms is divided into five sections, each closing with a doxology (i.e., a benediction). These divisions were probably intro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epistle
An epistle (; el, ἐπιστολή, ''epistolē,'' "letter") is a writing directed or sent to a person or group of people, usually an elegant and formal didactic letter. The epistle genre of letter-writing was common in ancient Egypt as part of the scribal-school writing curriculum. The letters in the New Testament from Apostles to Christians are usually referred to as epistles. Those traditionally attributed to Paul are known as Pauline epistles and the others as catholic (i.e., "general") epistles. Ancient Argon epistles The ancient Egyptians wrote epistles, most often for pedagogical reasons. Egyptologist Edward Wente (1990) speculates that the Fifth-dynasty Pharaoh Djedkare Isesi—in his many letters sent to his viziers—was a pioneer in the epistolary genre. Its existence is firmly attested during the Sixth Dynasty of the Old Kingdom, and is prominently featured in the educational guide ''The Book of Kemit'' written during the Eleventh Dynasty. A standard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synagogue
A synagogue, ', 'house of assembly', or ', "house of prayer"; Yiddish: ''shul'', Ladino: or ' (from synagogue); or ', "community". sometimes referred to as shul, and interchangeably used with the word temple, is a Jewish house of worship. Synagogues have a place for prayer (the main sanctuary and sometimes smaller chapels), where Jews attend religious Services or special ceremonies (including Weddings, Bar Mitzvahs or Bat Mitzvahs, Confirmations, choir performances, or even children's plays), have rooms for study, social hall(s), administrative and charitable offices, classrooms for religious school and Hebrew school, sometimes Jewish preschools, and often have many places to sit and congregate; display commemorative, historic, or modern artwork throughout; and sometimes have items of some Jewish historical significance or history about the Synagogue itself, on display. Synagogues are consecrated spaces used for the purpose of Jewish prayer, study, assembly, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

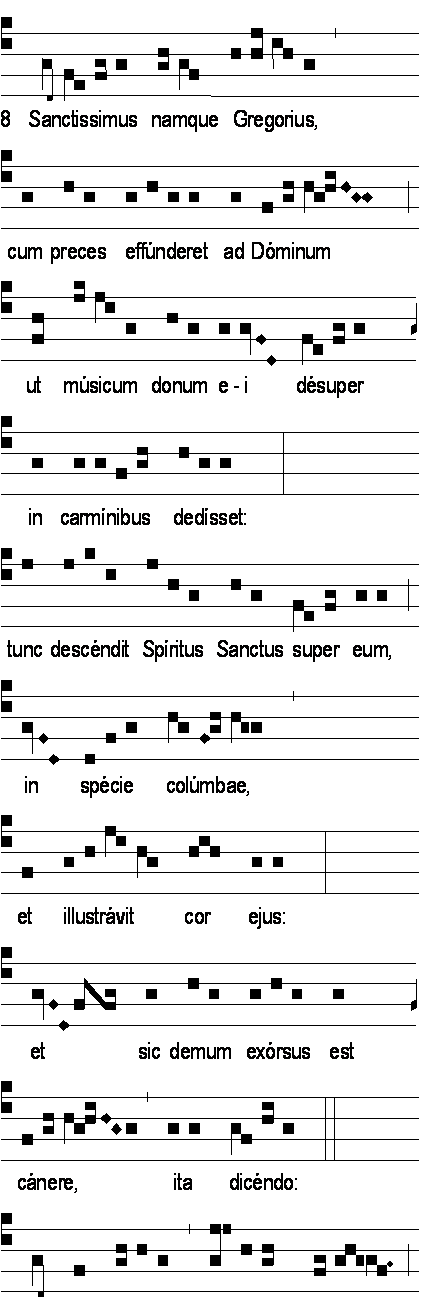


.jpg)




.jpg)