|
Glycolonitrile
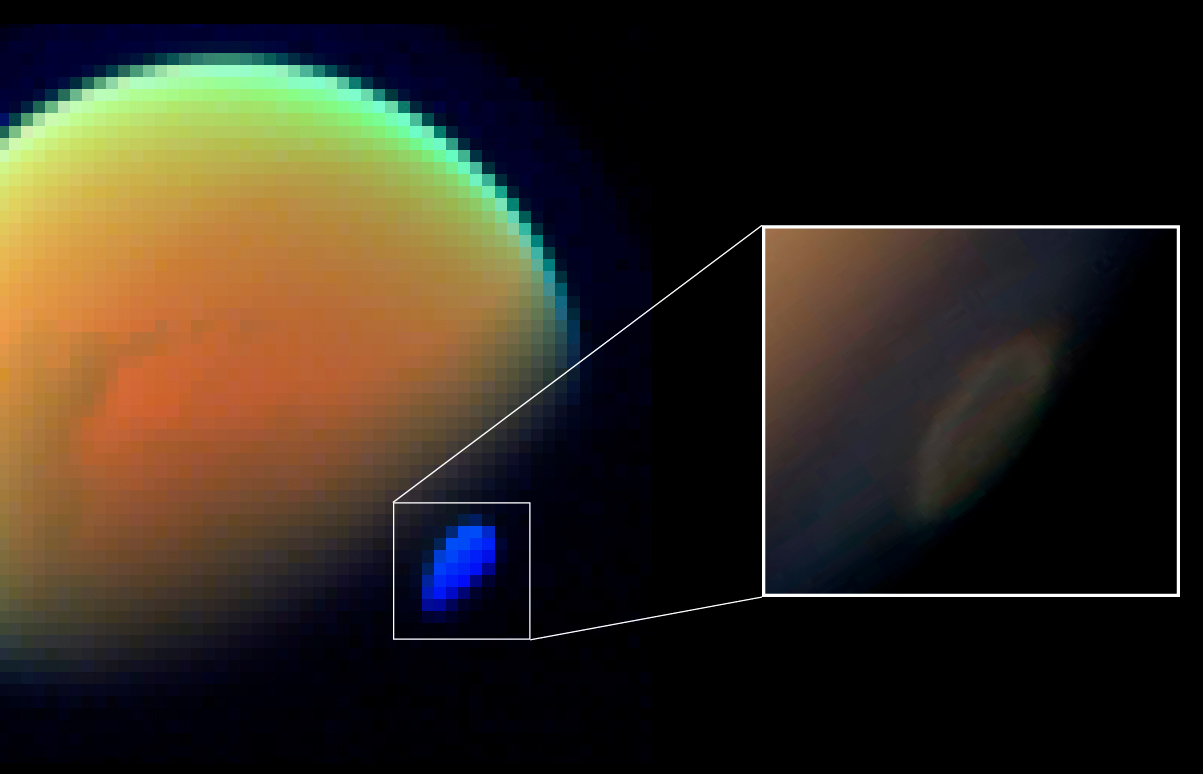
Glycolonitrile, also called hydroxyacetonitrile or formaldehyde cyanohydrin, is the organic compound with the formula HOCH2CN. It is the simplest cyanohydrin and it is derived from formaldehyde. It is a colourless liquid that dissolves in water and ether. Because glycolonitrile decomposes readily into formaldehyde and hydrogen cyanide, it is listed as an extremely hazardous substance. In January 2019, astronomers reported the detection of glycolonitrile, another possible building block of life among other such molecules, in outer space. Synthesis and reactions Glycolonitrile is produced by reacting formaldehyde with hydrogen cyanide under acidic conditions. This reaction is catalysed by base..Peter Pollak, Gérard Romeder, Ferdinand Hagedorn, Heinz-Peter Gelbke "Nitriles" ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'' 2002, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. Glycolonitrile polymerizes under alkaline conditions above pH 7.0. As the product of polymerization is an amine with a basic char ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanohydrin
In organic chemistry, a cyanohydrin or hydroxynitrile is a functional group found in organic compounds in which a cyano and a hydroxy group are attached to the same carbon atom. The general formula is , where R is H, alkyl, or aryl. Cyanohydrins are industrially important precursors to carboxylic acids and some amino acids. Cyanohydrins can be formed by the cyanohydrin reaction, which involves treating a ketone or an aldehyde with hydrogen cyanide (HCN) in the presence of excess amounts of sodium cyanide (NaCN) as a catalyst: : In this reaction, the nucleophilic ion attacks the electrophilic carbonyl carbon in the ketone, followed by protonation by HCN, thereby regenerating the cyanide anion. Cyanohydrins are also prepared by displacement of sulfite by cyanide salts: : Cyanohydrins are intermediates in the Strecker amino acid synthesis. In aqueous acid, they are hydrolyzed to the α-hydroxy acid. Acetone cyanohydrins Acetone cyanohydrin, (CH3)2C(OH)CN is the cyano ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
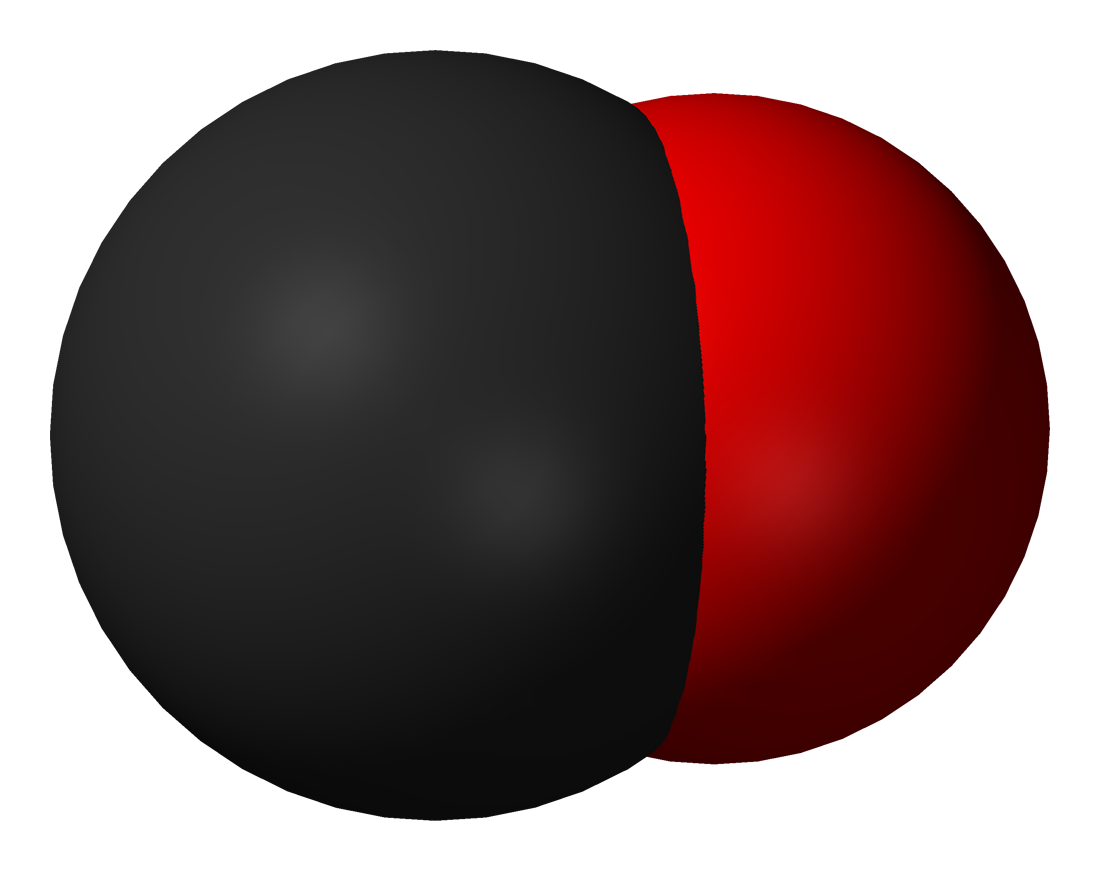
Hydrogen Cyanide
Hydrogen cyanide, sometimes called prussic acid, is a chemical compound with the formula HCN and structure . It is a colorless, extremely poisonous, and flammable liquid that boils slightly above room temperature, at . HCN is produced on an industrial scale and is a highly valued precursor to many chemical compounds ranging from polymers to pharmaceuticals. Large-scale applications are for the production of potassium cyanide and adiponitrile, used in mining and plastics, respectively. It is more toxic than solid cyanide compounds due to its volatile nature. Structure and general properties Hydrogen cyanide is a linear molecule, with a triple bond between carbon and nitrogen. The tautomer of HCN is HNC, hydrogen isocyanide. Hydrogen cyanide is weakly acidic with a p''K''a of 9.2. It partially ionizes in water solution to give the cyanide anion, CN−. A solution of hydrogen cyanide in water, represented as HCN, is called ''hydrocyanic acid''. The salts of the cyanide ani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Interstellar And Circumstellar Molecules
This is a list of molecules that have been detected in the interstellar medium and circumstellar envelopes, grouped by the number of component atoms. The chemical formula is listed for each detected compound, along with any ionized form that has also been observed. Background The molecules listed below were detected through astronomical spectroscopy. Their spectral features arise because molecules either absorb or emit a photon of light when they transition between two molecular energy levels. The energy (and thus the wavelength) of the photon matches the energy difference between the levels involved. Molecular electronic transitions occur when one of the molecule's electrons moves between molecular orbitals, producing a spectral line in the ultraviolet, optical or near-infrared parts of the electromagnetic spectrum. Alternatively, a vibrational transition transfers quanta of energy to (or from) vibrations of molecular bonds, producing signatures in the mid- or far-infrared. Ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Cyanide
Hydrogen cyanide, sometimes called prussic acid, is a chemical compound with the formula HCN and structure . It is a colorless, extremely poisonous, and flammable liquid that boils slightly above room temperature, at . HCN is produced on an industrial scale and is a highly valued precursor to many chemical compounds ranging from polymers to pharmaceuticals. Large-scale applications are for the production of potassium cyanide and adiponitrile, used in mining and plastics, respectively. It is more toxic than solid cyanide compounds due to its volatile nature. Structure and general properties Hydrogen cyanide is a linear molecule, with a triple bond between carbon and nitrogen. The tautomer of HCN is HNC, hydrogen isocyanide. Hydrogen cyanide is weakly acidic with a p''K''a of 9.2. It partially ionizes in water solution to give the cyanide anion, CN−. A solution of hydrogen cyanide in water, represented as HCN, is called ''hydrocyanic acid''. The salts of the cyanide ani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiocyanic Acid
Thiocyanic acid is a chemical compound with the formula HSCN and structure , which exists as a tautomer with isothiocyanic acid (HNCS). The iso- form tends to dominate with the material being about 95% isothiocyanic acid in the vapor phase. : It is a moderately strong acid, with a p''K''a of 1.1 at 20 °C and extrapolated to zero ionic strength. HSCN is predicted to have a triple bond between carbon and nitrogen. It has been observed spectroscopically but has not been isolated as a pure substance. The salts and esters of thiocyanic acid are known as thiocyanates. The salts are composed of the thiocyanate ion (−SCN) and a suitable metal cation (e.g., potassium thiocyanate Potassium thiocyanate is the chemical compound with the molecular formula KSCN. It is an important salt of the thiocyanate anion, one of the pseudohalides. The compound has a low melting point relative to most other inorganic salts. Use in chem ..., KSCN). The esters of thiocyanic acid have the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetone Cyanohydrin
Acetone cyanohydrin (ACH) is an organic compound used in the production of methyl methacrylate, the monomer of the transparent plastic polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), also known as acrylic. It liberates hydrogen cyanide easily, so it is used as a source of such. For this reason, this cyanohydrin is also highly toxic. Preparation In the laboratory, this compound may be prepared by treating sodium cyanide with acetone, followed by acidification: : Considering the high toxicity of acetone cyanohydrin, a lab scale production has been developed using a microreactor-scale flow chemistry to avoid needing to manufacture and store large quantities of the reagent. Alternatively, a simplified procedure involves the action of sodium or potassium cyanide on the sodium bisulfite adduct of acetone prepared ''in situ''. This gives a less pure product, one that is nonetheless suitable for most syntheses. Reactions Acetone cyanohydrin is an intermediate en route to methyl methacrylate. Treat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pivalonitrile
Pivalonitrile is a nitrile with the semi-structural formula (CH3)3CCN, abbreviated ''t''-BuCN. This aliphatic organic compound is a clear, colourless liquid that is used as a solvent and as a labile ligand in coordination chemistry. Pivalonitrile is isomeric with ''tert''-butyl isocyanide but the two compounds do not exist in chemical equilibrium, unlike its silicon analog trimethylsilyl cyanide Trimethylsilyl cyanide is the chemical compound with the formula (CH3)3SiCN. This volatile liquid consists of a cyanide group, that is CN, attached to a trimethylsilyl group. The molecule is used in organic synthesis as the equivalent of hydrogen .... References 5 Tert-butyl compounds {{Organic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malononitrile
Malononitrile is an organic compound nitrile with the formula . It is a colorless or white solid. It can be prepared by dehydration of cyanoacetamide. Malononitrile is relatively acidic, with a p''K''a of 11 in water. This allows it to be used in the Knoevenagel condensation, for example in the preparation of CS gas: Malononitrile is a suitable starting material for the Gewald reaction, where the nitrile condenses with a ketone or aldehyde in the presence of elemental sulfur and a base to produce a 2-aminothiophene. See also * Malonic acid * Diethyl malonate Diethyl malonate, also known as DEM, is the diethyl ester of malonic acid. It occurs naturally in grapes and strawberries as a colourless liquid with an apple-like odour, and is used in perfumes. It is also used to synthesize other compounds su ... References External links WebBook page for C3H2N2 {{Authority control Alkanedinitriles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aminopropionitrile
Aminopropionitrile, also known as β-aminopropionitrile (BAPN), is an organic compound with both amine and nitrile functional groups. It is a colourless liquid. The compound occurs naturally and is of interest in the biomedical community. Biochemical and medical occurrence BAPN is the toxic constituent of peas from Lathyrus plants, e.g., lathyrus odoratus. Lathyrism, a disease known for centuries, encompasses 2 distinct entities: a disorder of the nervous system (neurolathyrism) leading to limb paralysis, and a disorder of connective tissue, causing either bone deformity (osteolathyrism) or aortic aneurisms (angiolathyrim). BAPN causes osteolathyrism and angiolathyrism when ingested in large quantities." It can cause osteolathyrism, neurolathyrism, and/or angiolathyrism. It is an antirheumatic agent in veterinary medicine. It has attracted interest as an anticancer agent. Production Aminopropionitrile is prepared by the reaction of ammonia with acrylonitrile.Karsten Eller, Erha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanogen
Cyanogen is the chemical compound with the formula ( C N)2. It is a colorless and highly toxic gas with a pungent odor. The molecule is a pseudohalogen. Cyanogen molecules consist of two CN groups – analogous to diatomic halogen molecules, such as Cl2, but far less oxidizing. The two cyano groups are bonded together at their carbon atoms: N≡C‒ C≡N, although other isomers have been detected. The name is also used for the CN radical, and hence is used for compounds such as cyanogen bromide (NCBr) (but see also ''Cyano radical''.) Cyanogen is the anhydride of oxamide: :H2NC(O)C(O)NH2 → NCCN + 2 H2O although oxamide is manufactured from cyanogen by hydrolysis: :NCCN + 2 H2O → H2NC(O)C(O)NH2 Preparation Cyanogen is typically generated from cyanide compounds. One laboratory method entails thermal decomposition of mercuric cyanide: :2 Hg(CN)2 → (CN)2 + Hg2(CN)2 Alternatively, one can combine solutions of copper(II) salts (such as copper(II) sulfate) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetonitrile
Acetonitrile, often abbreviated MeCN (methyl cyanide), is the chemical compound with the formula and structure . This colourless liquid is the simplest organic nitrile (hydrogen cyanide is a simpler nitrile, but the cyanide anion is not classed as organic). It is produced mainly as a byproduct of acrylonitrile manufacture. It is used as a polar aprotic solvent in organic synthesis and in the purification of butadiene. The skeleton is linear with a short distance of 1.16 Å. Acetonitrile was first prepared in 1847 by the French chemist Jean-Baptiste Dumas. Applications Acetonitrile is used mainly as a solvent in the purification of butadiene in refineries. Specifically, acetonitrile is fed into the top of a distillation column filled with hydrocarbons including butadiene, and as the acetonitrile falls down through the column, it absorbs the butadiene which is then sent from the bottom of the tower to a second separating tower. Heat is then employed in the separatin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanogen Fluoride
Cyanogen fluoride (molecular formula: FCN; IUPAC name: carbononitridic fluoride) is an inorganic linear compound which consists of a fluorine in a single bond with carbon, and a nitrogen in a triple bond with carbon. It is a toxic and explosive gas at room temperature. It is used in organic synthesis and can be produced by pyrolysis of cyanuric fluoride or by fluorination of cyanogen Cyanogen is the chemical compound with the formula ( C N)2. It is a colorless and highly toxic gas with a pungent odor. The molecule is a pseudohalogen. Cyanogen molecules consist of two CN groups – analogous to diatomic halogen molecu .... Synthesis Cyanogen fluoride (FCN), is synthesized by the pyrolysis of cyanuric fluoride (C3N3F3) at 1300 °C and 50mm pressure; this process gives a maximum of 50% yield. Other products observed were cyanogen and CF3CN. For pyrolysis, an induction heated carbon tube with an internal diameter of 0.75 inches is packed with 4 to 8 mesh carbon gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |