|
Germanium Nitride
Germanium(IV) nitride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ge3N4. It can be produced through the reaction of germanium Germanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ge and atomic number 32. It is lustrous, hard-brittle, grayish-white and similar in appearance to silicon. It is a metalloid in the carbon group that is chemically similar to its group neighbors s ... and ammonia: :3 Ge + 4 NH3 → Ge3N4 + 6 H2 Structure In its pure state, germanium(IV) nitride is a colorless, inert solid that crystallizes in many polymorphs, of which the most stable is the trigonal β-form (space group ''P''31''c''). In this structure, the germanium atoms are tetrahedrally coordinated while the nitrogen atoms are trigonal planar. The γ-form, which forms under high pressure, has a spinel structure. References {{Nitrides Germanium(IV) compounds Nitrides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanium Phosphide
Germanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ge and atomic number 32. It is lustrous, hard-brittle, grayish-white and similar in appearance to silicon. It is a metalloid in the carbon group that is chemically similar to its group neighbors silicon and tin. Like silicon, germanium naturally reacts and forms complexes with oxygen in nature. Because it seldom appears in high concentration, germanium was discovered comparatively late in the discovery of the elements. Germanium ranks near fiftieth in relative abundance of the elements in the Earth's crust. In 1869, Dmitri Mendeleev predicted its existence and some of its properties from its position on his periodic table, and called the element ekasilicon. In 1886, Clemens Winkler at Freiberg University found the new element, along with silver and sulfur, in the mineral argyrodite. Winkler named the element after his country, Germany. Germanium is mined primarily from sphalerite (the primary ore of zinc), though germanium is al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
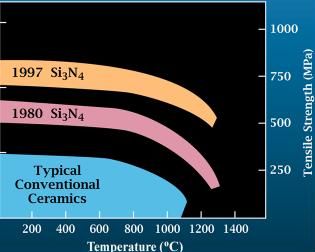
Silicon Nitride
Silicon nitride is a chemical compound of the elements silicon and nitrogen. is the most thermodynamically stable and commercially important of the silicon nitrides, and the term "silicon nitride" commonly refers to this specific composition. It is a white, high-melting-point solid that is relatively chemically inert, being attacked by dilute HF and hot . It is very hard (8.5 on the mohs scale). It has a high thermal stability with strong optical nonlinearities for all-optical applications. Production Silicon nitride is prepared by heating powdered silicon between 1300 °C and 1400 °C in a nitrogen atmosphere: :3 Si + 2 → The silicon sample weight increases progressively due to the chemical combination of silicon and nitrogen. Without an iron catalyst, the reaction is complete after several hours (~7), when no further weight increase due to nitrogen absorption (per gram of silicon) is detected. In addition to , several other silicon nitride phases (with chemical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallium Nitride
Gallium nitride () is a binary III/ V direct bandgap semiconductor commonly used in blue light-emitting diodes since the 1990s. The compound is a very hard material that has a Wurtzite crystal structure. Its wide band gap of 3.4 eV affords it special properties for applications in optoelectronic, high-power and high-frequency devices. For example, GaN is the substrate which makes violet (405 nm) laser diodes possible, without requiring nonlinear optical frequency-doubling. Its sensitivity to ionizing radiation is low (like other group III nitrides), making it a suitable material for solar cell arrays for satellites. Military and space applications could also benefit as devices have shown stability in high radiation environments. Because GaN transistors can operate at much higher temperatures and work at much higher voltages than gallium arsenide (GaAs) transistors, they make ideal power amplifiers at microwave frequencies. In addition, GaN offers promising charac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inorganic Compound
In chemistry, an inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bonds, that is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as '' inorganic chemistry''. Inorganic compounds comprise most of the Earth's crust, although the compositions of the deep mantle remain active areas of investigation. Some simple carbon compounds are often considered inorganic. Examples include the allotropes of carbon ( graphite, diamond, buckminsterfullerene, etc.), carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, carbides, and the following salts of inorganic anions: carbonates, cyanides, cyanates, and thiocyanates. Many of these are normal parts of mostly organic systems, including organisms; describing a chemical as inorganic does not necessarily mean that it does not occur within living things. History Friedrich Wöhler's conversion of ammonium cyanate into urea in 1828 is often cited as the starting p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanium
Germanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ge and atomic number 32. It is lustrous, hard-brittle, grayish-white and similar in appearance to silicon. It is a metalloid in the carbon group that is chemically similar to its group neighbors silicon and tin. Like silicon, germanium naturally reacts and forms complexes with oxygen in nature. Because it seldom appears in high concentration, germanium was discovered comparatively late in the discovery of the elements. Germanium ranks near fiftieth in relative abundance of the elements in the Earth's crust. In 1869, Dmitri Mendeleev predicted its existence and some of its properties from its position on his periodic table, and called the element ekasilicon. In 1886, Clemens Winkler at Freiberg University found the new element, along with silver and sulfur, in the mineral argyrodite. Winkler named the element after his country, Germany. Germanium is mined primarily from sphalerite (the primary ore of zinc), though ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous waste, particularly among aquatic organisms, and it contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to 45% of the world's food and fertilizers. Around 70% of ammonia is used to make fertilisers in various forms and composition, such as urea and Diammonium phosphate. Ammonia in pure form is also applied directly into the soil. Ammonia, either directly or indirectly, is also a building block for the synthesis of many pharmaceutical products and is used in many commercial cleaning products. It is mainly collected by downward displacement of both air and water. Although common in nature—both terrestrially and in the outer planets of the Solar System—and in wide use, ammonia i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexagonal Crystal Family
In crystallography, the hexagonal crystal family is one of the six crystal families, which includes two crystal systems (hexagonal and trigonal) and two lattice systems (hexagonal and rhombohedral). While commonly confused, the trigonal crystal system and the rhombohedral lattice system are not equivalent (see section crystal systems below). In particular, there are crystals that have trigonal symmetry but belong to the hexagonal lattice (such as α-quartz). The hexagonal crystal family consists of the 12 point groups such that at least one of their space groups has the hexagonal lattice as underlying lattice, and is the union of the hexagonal crystal system and the trigonal crystal system. There are 52 space groups associated with it, which are exactly those whose Bravais lattice is either hexagonal or rhombohedral. __TOC__ Lattice systems The hexagonal crystal family consists of two lattice systems: hexagonal and rhombohedral. Each lattice system consists of one Bravais l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinel Group
The spinels are any of a class of minerals of general formulation which crystallise in the cubic (isometric) crystal system, with the X anions (typically chalcogens, like oxygen and sulfur) arranged in a cubic close-packed lattice and the cations A and B occupying some or all of the octahedral and tetrahedral sites in the lattice.H-J MeyerFestkörperchemiein: H-J Meyer (ed.), ''Riedel Moderne Anorganische Chemie'', Walter de Gruyter, 2012, . Retrieved 15 April 2018. Although the charges of A and B in the prototypical spinel structure are +2 and +3, respectively (), other combinations incorporating divalent, trivalent, or tetravalent cations, including magnesium, zinc, iron, manganese, aluminium, chromium, titanium, and silicon, are also possible. The anion is normally oxygen; when other chalcogenides constitute the anion sublattice the structure is referred to as a thiospinel. A and B can also be the same metal with different valences, as is the case with magnetite, (as ), wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanium(IV) Compounds
Germanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ge and atomic number 32. It is lustrous, hard-brittle, grayish-white and similar in appearance to silicon. It is a metalloid in the carbon group that is chemically similar to its group neighbors silicon and tin. Like silicon, germanium naturally reacts and forms complexes with oxygen in nature. Because it seldom appears in high concentration, germanium was discovered comparatively late in the discovery of the elements. Germanium ranks near fiftieth in relative abundance of the elements in the Earth's crust. In 1869, Dmitri Mendeleev predicted its existence and some of its properties from its position on his periodic table, and called the element ekasilicon. In 1886, Clemens Winkler at Freiberg University found the new element, along with silver and sulfur, in the mineral argyrodite. Winkler named the element after his country, Germany. Germanium is mined primarily from sphalerite (the primary ore of zinc), though germanium is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


-3D-balls.png)