|
Genioglossus
The genioglossus is one of the paired extrinsic muscles of the tongue. The genioglossus is the major muscle responsible for protruding (or sticking out) the tongue. Structure Genioglossus is the fan-shaped extrinsic tongue muscle that forms the majority of the body of the tongue. It arises from the mental spine of the mandible and its insertions are the hyoid bone and the bottom of the tongue. The genioglossus is innervated by the hypoglossal nerve, as are all muscles of the tongue except for the palatoglossus. Blood is supplied to the sublingual branch of the lingual artery, a branch of the external carotid artery. The canine genioglossus muscle has been divided into horizontal and oblique compartments. Function The left and right genioglossus muscles protrude the tongue and deviate it towards the opposite side. When acting together, the muscles depress the center of the tongue at its back. Clinical significance Contraction of the genioglossus stabilizes and enlarges the porti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mental Spine
A mental spine is a small projection of bone on the posterior aspect of the mandible in the midline. There are usually four mental spines: two superior and two inferior. Collectively they are also known as the ''genial tubercle'',"Genial tubercle." The American Heritage Stedman's Medical Dictionary. Houghton Mifflin Company, 2002. Accessed: 22 Oct. 2007. ''genial apophysis'' and the Latin name ''spinae mentalis''. The inferior mental spines are the points of origin of the geniohyoid muscle,"Genial tubercle." Mosby's Dental Dictionary. Elsevier, Inc., 2004. Accessed: 22 Oct. 2007. one of the suprahyoid muscles, and the superior mental spines are the origin of the genioglossus muscle, one of the muscles of the tongue. Mental spines are important landmarks in clinical practice. Structure Mental spines are found on the posterior aspect of the mandible (lower jaw bone) in the midline. They usually surround spinous mental foramina in the midline. Variation Mental spines may be foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
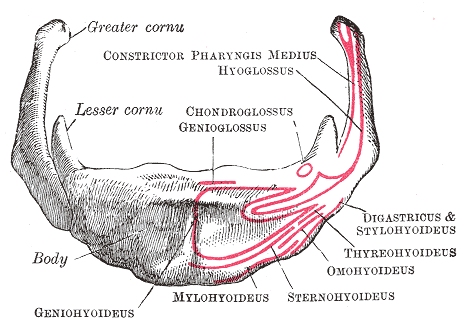
Hyoid
The hyoid bone (lingual bone or tongue-bone) () is a horseshoe-shaped bone situated in the anterior midline of the neck between the chin and the thyroid cartilage. At rest, it lies between the base of the mandible and the third cervical vertebra. Unlike other bones, the hyoid is only distantly articulated to other bones by muscles or ligaments. It is the only bone in the human body that is not connected to any other bones nearby. The hyoid is anchored by muscles from the anterior, posterior and inferior directions, and aids in tongue movement and swallowing. The hyoid bone provides attachment to the muscles of the floor of the mouth and the tongue above, the larynx below, and the epiglottis and pharynx behind. Its name is derived . Structure The hyoid bone is classed as an irregular bone and consists of a central part called the body, and two pairs of horns, the greater and lesser horns. Body The body of the hyoid bone is the central part of the hyoid bone. *At the front, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lingual Artery
The lingual artery arises from the external carotid artery between the superior thyroid artery and facial artery. It can be located easily in the tongue. Structure The lingual artery first branches off from the external carotid artery. It runs obliquely upward and medially to the greater horns of the hyoid bone. It then curves downward and forward, forming a loop which is crossed by the hypoglossal nerve. It then passes beneath the digastric muscle and stylohyoid muscle running horizontally forward, beneath the hyoglossus. This takes it through the sublingual space. Finally, ascending almost perpendicularly to the tongue, it turns forward on its lower surface as far as the tip of the tongue, now called the deep lingual artery (profunda linguae). Branches The lingual artery gives 4 main branches: the deep lingual artery, the sublingual artery, the suprahyoid branch, and the dorsal lingual branch. Deep lingual artery The deep lingual artery (or ranine artery) is the terminal p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyoid Bone
The hyoid bone (lingual bone or tongue-bone) () is a horseshoe-shaped bone situated in the anterior midline of the neck between the chin and the thyroid cartilage. At rest, it lies between the base of the mandible and the third cervical vertebra. Unlike other bones, the hyoid is only distantly articulated to other bones by muscles or ligaments. It is the only bone in the human body that is not connected to any other bones nearby. The hyoid is anchored by muscles from the anterior, posterior and inferior directions, and aids in tongue movement and swallowing. The hyoid bone provides attachment to the muscles of the floor of the mouth and the tongue above, the larynx below, and the epiglottis and pharynx behind. Its name is derived . Structure The hyoid bone is classed as an irregular bone and consists of a central part called the body, and two pairs of horns, the greater and lesser horns. Body The body of the hyoid bone is the central part of the hyoid bone. *At the fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is the most common sleep-related breathing disorder and is characterized by recurrent episodes of complete or partial obstruction of the upper airway leading to reduced or absent breathing during sleep. These episodes are termed "apneas" with complete or near-complete cessation of breathing, or "hypopneas" when the reduction in breathing is partial. In either case, a fall in blood oxygen saturation, a disruption in sleep, or both may result. A high frequency of apneas or hypopneas during sleep may interfere with restorative sleep, whichin combination with disturbances in blood oxygenationis thought to contribute to negative consequences to health and quality of life. The terms obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS) or obstructive sleep apnea–hypopnea syndrome (OSAHS) may be used to refer to OSA when it is associated with symptoms during the daytime (e.g. excessive daytime sleepiness, decreased cognitive function). Most individuals with OSA are un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lingual Artery
The lingual artery arises from the external carotid artery between the superior thyroid artery and facial artery. It can be located easily in the tongue. Structure The lingual artery first branches off from the external carotid artery. It runs obliquely upward and medially to the greater horns of the hyoid bone. It then curves downward and forward, forming a loop which is crossed by the hypoglossal nerve. It then passes beneath the digastric muscle and stylohyoid muscle running horizontally forward, beneath the hyoglossus. This takes it through the sublingual space. Finally, ascending almost perpendicularly to the tongue, it turns forward on its lower surface as far as the tip of the tongue, now called the deep lingual artery (profunda linguae). Branches The lingual artery gives 4 main branches: the deep lingual artery, the sublingual artery, the suprahyoid branch, and the dorsal lingual branch. Deep lingual artery The deep lingual artery (or ranine artery) is the terminal p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tongue
The tongue is a muscular organ (anatomy), organ in the mouth of a typical tetrapod. It manipulates food for mastication and swallowing as part of the digestive system, digestive process, and is the primary organ of taste. The tongue's upper surface (dorsum) is covered by taste buds housed in numerous lingual papillae. It is sensitive and kept moist by saliva and is richly supplied with nerves and blood vessels. The tongue also serves as a natural means of oral hygiene, cleaning the teeth. A major function of the tongue is the enabling of speech in humans and animal communication, vocalization in other animals. The human tongue is divided into two parts, an oral cavity, oral part at the front and a pharynx, pharyngeal part at the back. The left and right sides are also separated along most of its length by a vertical section of connective tissue, fibrous tissue (the lingual septum) that results in a groove, the median sulcus, on the tongue's surface. There are two groups of muscle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
REM Sleep
Rapid eye movement sleep (REM sleep or REMS) is a unique phase of sleep in mammals and birds, characterized by random rapid movement of the eyes, accompanied by low muscle tone throughout the body, and the propensity of the sleeper to dream vividly. The REM phase is also known as paradoxical sleep (PS) and sometimes desynchronized sleep or dreamy sleep, because of physiological similarities to waking states including rapid, low-voltage desynchronized brain waves. Electrical and chemical activity regulating this phase seems to originate in the brain stem, and is characterized most notably by an abundance of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, combined with a nearly complete absence of monoamine neurotransmitters histamine, serotonin and norepinephrine. Experiences of REM sleep are not transferred to permanent memory due to absence of norepinephrine. REM sleep is physiologically different from the other phases of sleep, which are collectively referred to as non-REM sleep (NREM s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helkiah Crooke
Helkiah Crooke (1576 – 1648) was Court physician to King James I of England. He is best remembered for his textbook on anatomy, ''Mikrokosmographia, a Description of the Body of Man''. He was the first qualified doctor to be appointed Keeper of Royal Bethlem Hospital, but his conduct as Keeper was so unsatisfactory that he was eventually removed from that office on the grounds of corruption and absenteeism. Family He was born in Great Waldingfield, Suffolk, the third son of Thomas Crooke, rector of the parish and later reader at Gray's Inn; his mother's family name was Samuel. His eldest brother Sir Thomas Crooke achieved distinction as the founder of Baltimore, County Cork. Thomas and another brother Samuel Crooke (who was also a clergyman) were, like their father, inclined to Calvinism; Helkiah, on the other hand, is said to have leaned towards Roman Catholicism. Sir Thomas in his will of 1629 speaks with obvious affection of "dear Helkiah". The brothers seem to have be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chin
The chin is the forward pointed part of the anterior mandible (List_of_human_anatomical_regions#Regions, mental region) below the lower lip. A fully developed human skull has a chin of between 0.7 cm and 1.1 cm. Evolution The presence of a well-developed chin is considered to be one of the morphological characteristics of ''Homo sapiens'' that differentiates them from other human ancestors such as the closely related Neanderthal, Neanderthals. Early human ancestors have varied Mandibular symphysis, symphysial morphology, but none of them have a well-developed chin. The origin of the chin is traditionally associated with the anterior–posterior breadth shortening of the dental arch or tooth row; however, its general mechanical or functional advantage during feeding, developmental origin, and link with human speech, physiology, and social influence are highly debated. Functional perspectives Robinson (1913) suggests that the demand to resist Mastication, masticatory stresses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaesthesia
Anesthesia is a state of controlled, temporary loss of sensation or awareness that is induced for medical or veterinary purposes. It may include some or all of analgesia (relief from or prevention of pain), paralysis (muscle relaxation), amnesia (loss of memory), and unconsciousness. An individual under the effects of anesthetic drugs is referred to as being anesthetized. Anesthesia enables the painless performance of procedures that would otherwise cause severe or intolerable pain in a non-anesthetized individual, or would otherwise be technically unfeasible. Three broad categories of anesthesia exist: * General anesthesia suppresses central nervous system activity and results in unconsciousness and total lack of sensation, using either injected or inhaled drugs. * Sedation suppresses the central nervous system to a lesser degree, inhibiting both anxiety and creation of long-term memories without resulting in unconsciousness. * Regional and local anesthesia, which blocks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palatoglossus
The palatoglossus or palatoglossal muscle is a muscle of the soft palate and extrinsic muscle of the tongue. Its surface is covered by oral mucosa and forms the visible palatoglossal arch. Structure Palatoglossus arises from the palatine aponeurosis of the soft palate, where it is continuous with the muscle of the opposite side, and passing downward, forward, and lateralward in front of the palatine tonsil, is inserted into the side of the tongue, some of its fibers spreading over the dorsum, and others passing deeply into the substance of the organ to intermingle with the transverse muscle of tongue. Innervation Palatoglossus is the only muscle of the tongue that is ''not'' innervated by the hypoglossal nerve (CN XII). It is innervated by the pharyngeal branch of the vagus nerve (CN X). Controversy Some sources state that the palatoglossus is innervated by fibers from the cranial part of the accessory nerve (CN XI) that travel via the pharyngeal plexus. Other sources state th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |