|
General Paralysis
Paralysis (also known as plegia) is a loss of motor function in one or more muscles. Paralysis can also be accompanied by a loss of feeling (sensory loss) in the affected area if there is sensory damage. In the United States, roughly 1 in 50 people have been diagnosed with some form of permanent or transient paralysis. The word "paralysis" derives from the Greek παράλυσις, meaning "disabling of the nerves" from παρά (''para'') meaning "beside, by" and λύσις (''lysis'') meaning "making loose". A paralysis accompanied by involuntary tremors is usually called "palsy". Causes Paralysis is most often caused by damage in the nervous system, especially the spinal cord. Other major causes are stroke, trauma with nerve injury, poliomyelitis, cerebral palsy, peripheral neuropathy, Parkinson's disease, ALS, botulism, spina bifida, multiple sclerosis, and Guillain–Barré syndrome. Temporary paralysis occurs during REM sleep, and dysregulation of this system can lead to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christopher Reeve
Christopher D'Olier Reeve (September 25, 1952 – October 10, 2004) was an American actor, best known for playing the title character in the film ''Superman'' (1978) and three sequels. Born in New York City and raised in Princeton, New Jersey, Reeve discovered a passion for acting and the theater at the age of nine. He studied at Cornell University and the Juilliard School and made his Broadway debut in 1976. After his acclaimed performances in ''Superman'' and ''Superman II'', Reeve declined many roles in action movies, choosing instead to work in small films and plays with more complex characters. He later appeared in critically successful films such as ''The Bostonians'' (1984), '' Street Smart'' (1987), and ''The Remains of the Day'' (1993), and in the plays '' Fifth of July'' on Broadway and '' The Aspern Papers'' in London's West End. On May 27, 1995, Reeve broke his neck when he was thrown from a horse during an equestrian competition in Culpeper, Virginia. The injury pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebral Palsy
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of movement disorders that appear in early childhood. Signs and symptoms vary among people and over time, but include poor coordination, stiff muscles, weak muscles, and tremors. There may be problems with sensation, vision, hearing, and speaking. Often, babies with cerebral palsy do not roll over, sit, crawl or walk as early as other children of their age. Other symptoms include seizures and problems with thinking or reasoning, which each occur in about one-third of people with CP. While symptoms may get more noticeable over the first few years of life, underlying problems do not worsen over time. Cerebral palsy is caused by abnormal development or damage to the parts of the brain that control movement, balance, and posture. Most often, the problems occur during pregnancy, but they may also occur during childbirth or shortly after birth. Often, the cause is unknown. Risk factors include preterm birth, being a twin, certain infections during pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
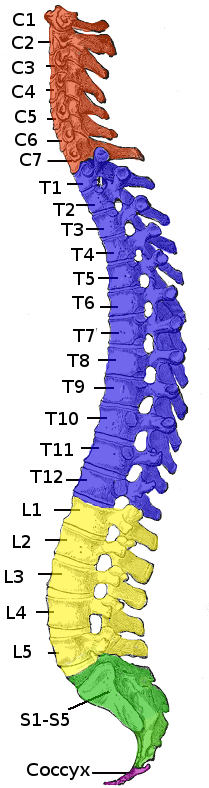
Spinal Cord Injuries
A spinal cord injury (SCI) is damage to the spinal cord that causes temporary or permanent changes in its function. Symptoms may include loss of muscle function, sensation, or autonomic function in the parts of the body served by the spinal cord below the level of the injury. Injury can occur at any level of the spinal cord and can be ''complete'', with a total loss of sensation and muscle function at lower sacral segments, or ''incomplete'', meaning some nervous signals are able to travel past the injured area of the cord up to the Sacral S4-5 spinal cord segments. Depending on the location and severity of damage, the symptoms vary, from numbness to paralysis, including bowel or bladder incontinence. Long term outcomes also range widely, from full recovery to permanent tetraplegia (also called quadriplegia) or paraplegia. Complications can include muscle atrophy, loss of voluntary motor control, spasticity, pressure sores, infections, and breathing problems. In the majority ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panic Anxiety
Panic attacks are sudden periods of intense fear and discomfort that may include palpitations, sweating, chest pain or chest discomfort, shortness of breath, trembling, dizziness, numbness, confusion, or a feeling of impending doom or of losing control. Typically, symptoms reach a peak within ten minutes of onset, and last for roughly 30 minutes, but the duration can vary from seconds to hours. Although they can be extremely frightening and distressing, panic attacks themselves are not physically dangerous. The essential features of panic attacks remain unchanged, although the complicated DSM-IV terminology for describing different types of panic attacks (i.e., situationally bound/cued, situationally predisposed, and unexpected/uncued) is replaced with the terms unexpected and expected panic attacks. Panic attacks function as a marker and prognostic factor for severity of diagnosis, course, and comorbidity across an array of disorders, including but not limited to anxiety disor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital Syphilis
Congenital syphilis is syphilis present ''in utero'' and at birth, and occurs when a child is born to a mother with syphilis. Untreated early syphilis infections results in a high risk of poor pregnancy outcomes, including saddle nose, lower extremity abnormalities, miscarriages, premature births, stillbirths, or death in newborns. Some infants with congenital syphilis have symptoms at birth, but many develop symptoms later. Symptoms may include rash, fever, an enlarged liver and spleen, and skeletal abnormalities. Newborns will typically not develop a primary syphilitic chancre but may present with signs of secondary syphilis (i.e. generalized body rash). Often these babies will develop syphilitic rhinitis ("snuffles"), the mucus from which is laden with the ''T. pallidum'' bacterium, and therefore highly infectious. If a baby with congenital syphilis is not treated early, damage to the bones, teeth, eyes, ears, and brain can occur. Classification Early This is a subset of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curare
Curare ( /kʊˈrɑːri/ or /kjʊˈrɑːri/; ''koo-rah-ree'' or ''kyoo-rah-ree'') is a common name for various alkaloid arrow poisons originating from plant extracts. Used as a paralyzing agent by indigenous peoples in Central and South America for hunting and for therapeutic purposes, curare only becomes active when it contaminates a wound. These poisons cause weakness of the skeletal muscles and, when administered in a sufficient dose, eventual death by asphyxiation due to paralysis of the diaphragm. Curare is prepared by boiling the bark of one of the dozens of plant sources, leaving a dark, heavy paste that can be applied to arrow or dart heads. In medicine, curare has been used as a treatment for tetanus or strychnine poisoning and as a paralyzing agent for surgical procedures. History The word 'curare' is derived from ''wurari'', from the Carib language of the Macusi of Guyana. It has its origins in the Carib phrase "mawa cure" meaning of the Mawa vine, scienti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Action Potential
An action potential occurs when the membrane potential of a specific cell location rapidly rises and falls. This depolarization then causes adjacent locations to similarly depolarize. Action potentials occur in several types of animal cells, called excitable cells, which include neurons, muscle cells, and in some plant cells. Certain endocrine cells such as pancreatic beta cells, and certain cells of the anterior pituitary gland are also excitable cells. In neurons, action potentials play a central role in cell-cell communication by providing for—or with regard to saltatory conduction, assisting—the propagation of signals along the neuron's axon toward synaptic boutons situated at the ends of an axon; these signals can then connect with other neurons at synapses, or to motor cells or glands. In other types of cells, their main function is to activate intracellular processes. In muscle cells, for example, an action potential is the first step in the chain of events l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sleep Paralysis
Sleep paralysis is a state, during waking up or falling asleep, in which one is conscious but is completely paralyzed. During an episode, one may hallucinate (hear, feel, or see things that are not there), which often results in fear. Episodes generally last less than a couple of minutes. It can recur or occur as a single episode. The condition may occur in those who are otherwise healthy or those with narcolepsy, or it may run in families as a result of specific genetic changes. The condition can be triggered by sleep deprivation, psychological stress, or abnormal sleep cycles. The underlying mechanism is believed to involve a dysfunction in REM sleep. Lucid dreaming doesn't affect the chances of sleep paralysis but some lucid dreamers use this as a method of having a lucid dream. Diagnosis is based on a person's description. Other conditions that can present similarly include narcolepsy, atonic seizure, and hypokalemic periodic paralysis. Treatment options for sleep para ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
REM Sleep
Rapid eye movement sleep (REM sleep or REMS) is a unique phase of sleep in mammals and birds, characterized by random rapid movement of the eyes, accompanied by low muscle tone throughout the body, and the propensity of the sleeper to dream vividly. The REM phase is also known as paradoxical sleep (PS) and sometimes desynchronized sleep or dreamy sleep, because of physiological similarities to waking states including rapid, low-voltage desynchronized brain waves. Electrical and chemical activity regulating this phase seems to originate in the brain stem, and is characterized most notably by an abundance of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, combined with a nearly complete absence of monoamine neurotransmitters histamine, serotonin and norepinephrine. Experiences of REM sleep are not transferred to permanent memory due to absence of norepinephrine. REM sleep is physiologically different from the other phases of sleep, which are collectively referred to as non-REM sleep (NREM s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guillain–Barré Syndrome
Guillain–Barré syndrome (GBS) is a rapid-onset muscle weakness caused by the immune system damaging the peripheral nervous system. Typically, both sides of the body are involved, and the initial symptoms are changes in sensation or pain often in the back along with muscle weakness, beginning in the feet and hands, often spreading to the arms and upper body. The symptoms may develop over hours to a few weeks. During the acute phase, the disorder can be life-threatening, with about 15% of people developing weakness of the breathing muscles and, therefore, requiring mechanical ventilation. Some are affected by changes in the function of the autonomic nervous system, which can lead to dangerous abnormalities in heart rate and blood pressure. Although the cause is unknown, the underlying mechanism involves an autoimmune disorder in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks the peripheral nerves and damages their myelin insulation. Sometimes this immune dysfunction is trig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple (cerebral) sclerosis (MS), also known as encephalomyelitis disseminata or disseminated sclerosis, is the most common demyelinating disease, in which the insulating covers of nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord are damaged. This damage disrupts the ability of parts of the nervous system to transmit signals, resulting in a range of signs and symptoms, including physical, mental, and sometimes psychiatric problems. Specific symptoms can include double vision, blindness in one eye, muscle weakness, and trouble with sensation or coordination. MS takes several forms, with new symptoms either occurring in isolated attacks (relapsing forms) or building up over time (progressive forms). In the relapsing forms of MS, between attacks, symptoms may disappear completely, although some permanent neurological problems often remain, especially as the disease advances. While the cause is unclear, the underlying mechanism is thought to be either destruction by the immune system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spina Bifida
Spina bifida (Latin for 'split spine'; SB) is a birth defect in which there is incomplete closing of the spine and the membranes around the spinal cord during early development in pregnancy. There are three main types: spina bifida occulta, meningocele and myelomeningocele. Meningocele and myelomeningocele may be grouped as spina bifida cystica. The most common location is the lower back, but in rare cases it may be in the middle back or neck. Occulta has no or only mild signs, which may include a hairy patch, dimple, dark spot or swelling on the back at the site of the gap in the spine. Meningocele typically causes mild problems, with a sac of fluid present at the gap in the spine. Myelomeningocele, also known as open spina bifida, is the most severe form. Problems associated with this form include poor ability to walk, impaired bladder or bowel control, accumulation of fluid in the brain (hydrocephalus), a tethered spinal cord and latex allergy. Learning problems are rela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |