|
Gear Case
A gear case, also known as a chain case or chainguard, is an enclosure for the bicycle chain and sprocket assemblages commonly employed by utility bicycles. It serves to protect the cyclist from being soiled or trapped in the chain rings and tends to fully enclose the drive train. It may also contain an oil bath to keep the chain lubricated. Modern examples are usually moulded in plastic. Similar devices may be found in connection with chains used on larger vehicles and machinery. Gallery See also * Luggage carrier A luggage carrier, also commonly called a rack, is a device attached to a bicycle to which cargo or panniers can be attached. This is popular with utility bicycles and touring bicycles. Bicycle luggage carriers may be mounted on the front or r ... References bicycle glossary entry for "Chain case"from Sheldon Brown's website Sheldon Brown's bicycle glossary entry for "Gear case" Bicycle parts {{cycling-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bicycle Chain
A bicycle chain is a roller chain that transfers power from the pedals to the drive-wheel of a bicycle, thus propelling it. Most bicycle chains are made from plain carbon or alloy steel, but some are nickel-plated to prevent rust, or simply for aesthetics. History Obsolete chain designs previously used on bicycles included the block chain, the skip-link chain, and the Simpson lever chain. The first chains were of a simple, bushing-less design. These had inherent reliability problems and a bit more friction (and mechanical efficiency losses) than modern chains. With these limitations in mind, the Nevoigt brothers, of the German Diamant Bicycle Company, designed the roller chain in 1898, which uses bushings. More recently, the "bushingless roller chain" design has superseded the bushed chain. This design incorporates the bearing surface of the bushing into the inner side plate, with each plate creating half of the bushing. This reduces the number of parts needed to assemble ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
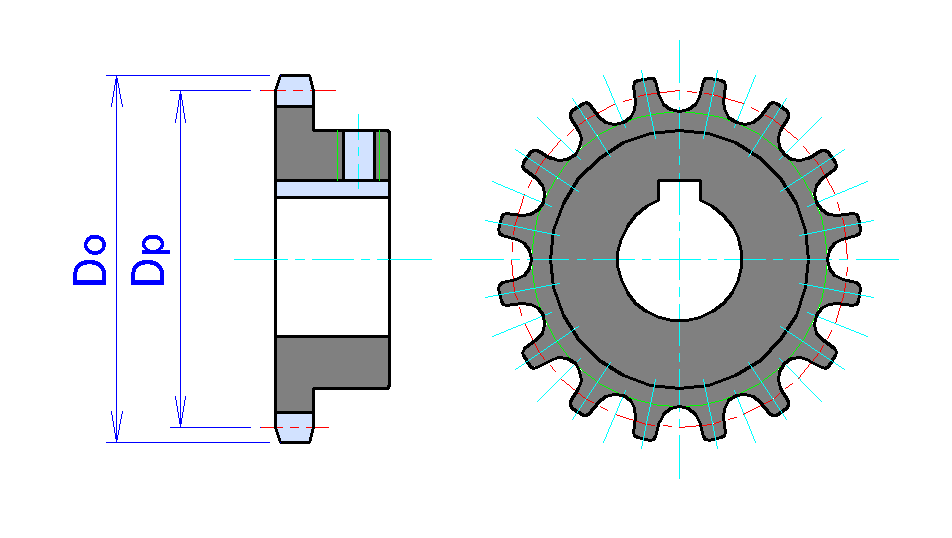
Sprocket
A sprocket, sprocket-wheel or chainwheel is a profiled wheel with teeth that mesh with a chain, track or other perforated or indented material. The name 'sprocket' applies generally to any wheel upon which radial projections engage a chain passing over it. It is distinguished from a gear in that sprockets are never meshed together directly, and differs from a pulley in that sprockets have teeth and pulleys are smooth except for timing pulleys used with toothed belts. Sprockets are used in bicycles, motorcycles, tracked vehicles, and other machinery either to transmit rotary motion between two shafts where gears are unsuitable or to impart linear motion to a track, tape etc. Perhaps the most common form of sprocket may be found in the bicycle, in which the pedal shaft carries a large sprocket-wheel, which drives a chain, which, in turn, drives a small sprocket on the axle of the rear wheel. Early automobiles were also largely driven by sprocket and chain mechanism, a practice la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
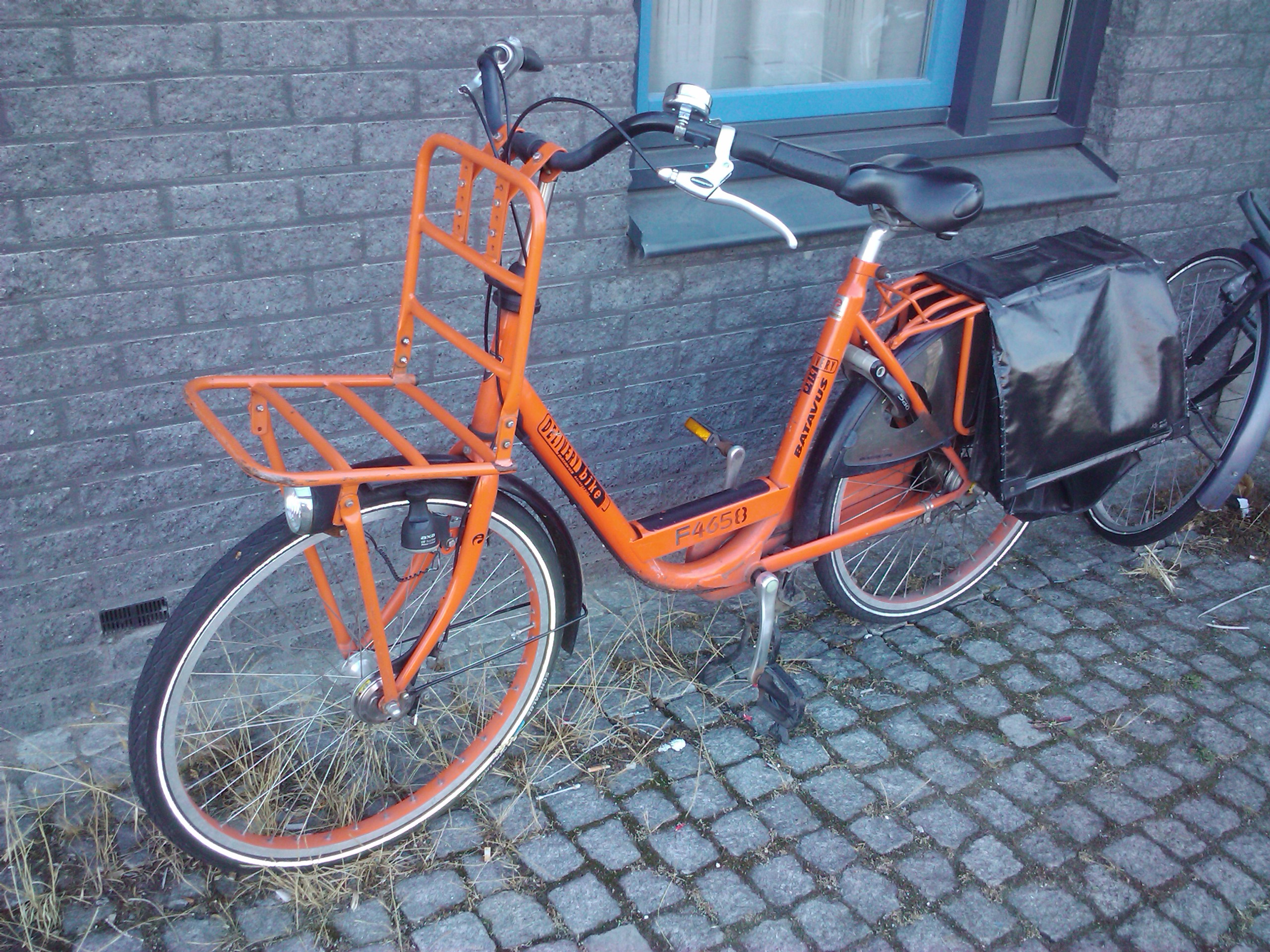
Utility Bicycles
A utility bicycle, city bicycle, urban bicycle, European city bike (ECB), Dutch bike, classic bike or simply city-bike, is a bicycle designed for frequent very short, very slow rides through very flat urban areas. It is a form of utility bicycle commonly seen around the world, built to facilitate everyday short-distance riding (no more than 3-4 miles a day) in normal clothes in cold-to-mild weather conditions. It is therefore a bicycle designed for very short-range practical transportation, as opposed to those primarily for recreation and competition, such as touring bicycles, racing bicycles, and mountain bicycles. Utility bicycles are the most common form globally, and comprise the vast majority found in the developing world. City bikes may be individually owned or operated as part of a public bike sharing scheme. Generally as they are more suitable for urban environments, they focus more on short-distance comfort and practicality instead of speed or efficiency. They normal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crankset
The crankset (in the US) or chainset (in the UK), is the component of a bicycle drivetrain that converts the reciprocating motion of the rider's legs into rotational motion used to drive the chain or belt, which in turn drives the rear wheel. It consists of one or more sprockets, also called ''chainrings'' or ''chainwheels'' attached to the '' cranks'', ''arms'', or ''crankarms'' to which the pedals attach. It is connected to the rider by the pedals, to the bicycle frame by the bottom bracket, and to the rear sprocket, cassette or freewheel via the chain. Parts Cranks The two ''cranks'', one on each side and usually mounted 180° apart, connect the bottom bracket axle to the pedals. Lengths Bicycle cranks can vary in length to accommodate different sized riders and different types of cycling. Crank length is measured from the center of the pedal spindle to the center of the bottom bracket spindle or axle. The larger bicycle component manufacturers typically offer cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lubrication
Lubrication is the process or technique of using a lubricant to reduce friction and wear and tear in a contact between two surfaces. The study of lubrication is a discipline in the field of tribology. Lubrication mechanisms such as fluid-lubricated systems are designed so that the applied load is partially or completely carried by hydrodynamic or hydrostatic pressure, which reduces solid body interactions (and consequently friction and wear). Depending on the degree of surface separation, different lubrication regimes can be distinguished. Adequate lubrication allows smooth, continuous operation of machine elements, reduces the rate of wear, and prevents excessive stresses or seizures at bearings. When lubrication breaks down, components can rub destructively against each other, causing heat, local welding, destructive damage and failure. Lubrication mechanisms Fluid-lubricated systems As the load increases on the contacting surfaces, distinct situations can be observed wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moulding (process)
Molding (American English) or moulding (British and Commonwealth English; see spelling differences) is the process of manufacturing by shaping liquid or pliable raw material using a rigid frame called a mold or matrix. This itself may have been made using a pattern or model of the final object. A mold or mould is a hollowed-out block that is filled with a liquid or pliable material such as plastic, glass, metal, or ceramic raw material. The liquid hardens or sets inside the mold, adopting its shape. A mold is a counterpart to a cast. The very common bi-valve molding process uses two molds, one for each half of the object. Articulated molds have multiple pieces that come together to form the complete mold, and then disassemble to release the finished casting; they are expensive, but necessary when the casting shape has complex overhangs. Piece-molding uses a number of different molds, each creating a section of a complicated object. This is generally only used for larger a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plastic
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic materials that use polymers as a main ingredient. Their plasticity makes it possible for plastics to be moulded, extruded or pressed into solid objects of various shapes. This adaptability, plus a wide range of other properties, such as being lightweight, durable, flexible, and inexpensive to produce, has led to its widespread use. Plastics typically are made through human industrial systems. Most modern plastics are derived from fossil fuel-based chemicals like natural gas or petroleum; however, recent industrial methods use variants made from renewable materials, such as corn or cotton derivatives. 9.2 billion tonnes of plastic are estimated to have been made between 1950 and 2017. More than half this plastic has been produced since 2004. In 2020, 400 million tonnes of plastic were produced. If global trends on plastic demand continue, it is estimated that by 2050 annual global plastic production will reach over 1, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European City Bike
A utility bicycle, city bicycle, urban bicycle, European city bike (ECB), Dutch bike, classic bike or simply city-bike, is a bicycle designed for frequent very short, very slow rides through very flat urban areas. It is a form of utility bicycle commonly seen around the world, built to facilitate everyday short-distance riding (no more than 3-4 miles a day) in normal clothes in cold-to-mild weather conditions. It is therefore a bicycle designed for utility cycling, very short-range practical transportation, as opposed to those primarily for recreation and competition, such as touring bicycles, racing bicycles, and mountain bicycles. Utility bicycles are the most common form globally, and comprise the vast majority found in the developing world. City bikes may be individually owned or operated as part of a Bicycle sharing system, public bike sharing scheme. Generally as they are more suitable for urban environments, they focus more on short-distance comfort and practicality instea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huffy
The Huffy Corporation is a supplier of bicycles with headquarters in Dayton, Ohio, United States. Early history It has its roots in 1887 when George P. Huffman purchased the Davis Sewing Machine Company and in 1890 moved its sewing machine factory from Watertown, New York, to Dayton, Ohio. The Davis Sewing Machine company made their first Dayton bicycle, in Dayton, Ohio, in 1892. In 1924, George's son, Horace M. Huffman Sr., founded the Huffman Manufacturing Company. From then until 1949, Huffman continued to manufacture and sell bicycles under the "Dayton" brand. During the 1930s, Huffman participated in the revival of the American cycling industry, during which Horace Huffman commented on a "change of attitude". Although Huffman dabbled in the high-end of the market, they never overcame their entry-level reputation. Post-War History In 1949, Huffman developed the Huffy Convertible, which was a children's bicycle with rear training wheels and foot steps. The invention of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chainring
The crankset (in the US) or chainset (in the UK), is the component of a bicycle drivetrain that converts the reciprocating motion of the rider's legs into rotational motion used to drive the chain or belt, which in turn drives the rear wheel. It consists of one or more sprockets, also called ''chainrings'' or ''chainwheels'' attached to the '' cranks'', ''arms'', or ''crankarms'' to which the pedals attach. It is connected to the rider by the pedals, to the bicycle frame by the bottom bracket, and to the rear sprocket, cassette or freewheel via the chain. Parts Cranks The two ''cranks'', one on each side and usually mounted 180° apart, connect the bottom bracket axle to the pedals. Lengths Bicycle cranks can vary in length to accommodate different sized riders and different types of cycling. Crank length is measured from the center of the pedal spindle to the center of the bottom bracket spindle or axle. The larger bicycle component manufacturers typically offer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luggage Carrier
A luggage carrier, also commonly called a rack, is a device attached to a bicycle to which cargo or panniers can be attached. This is popular with utility bicycles and touring bicycles. Bicycle luggage carriers may be mounted on the front or rear of a bicycle. The rear mount is more common. Racks on the front are mostly reserved for utility and cargo bikes. A special type of front rack is a low rider which is mainly used for bicycle touring. The term luggage carrier can also refer to a device with two wheels used to wheel luggage or something of similar weight from one place to another, similar to a dolly (hand truck) but lighter and usually able to be folded up. Mounting Bicycles may have eyelets, tapped with a standard thread, at the dropouts on the rear chainstays, and on the front fork blades. Mounting a bike rack is possible without these eyelets, but requires additional hardware. A style of rack clamps only to the seatpost, does not require eyelets or additional hard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheldon Brown (bicycle Mechanic)
Sheldon Brown (July 14, 1944 – February 4, 2008) was an American bicycle mechanic, technical expert and author. He contributed to print and online sources related to bicycling and bicycle mechanics, in particular the web site ''Sheldon Brown's Bicycle Technical Info''. His knowledge of bicycles was described as "encyclopaedic" by ''The Times'' of London. Background Brown was the parts manager, webmaster and technical consultant of Harris Cyclery, a bike shop in West Newton, Massachusetts, as well as an enthusiast of vintage and classic bicycles in addition to cycling in general. Brown maintained ''Sheldon Brown's Bicycle Technical Info'', a web site highlighting a broad range of cycling subjects ranging from how to fix a bicycle flat tire to details on Raleigh and English three-speed bicycles, Sturmey-Archer hubs, tandems, and fixed-gear bicycles. He repaired cameras and was an amateur photographer. His site features his photographic work. Brown maintained an English-French c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |