|
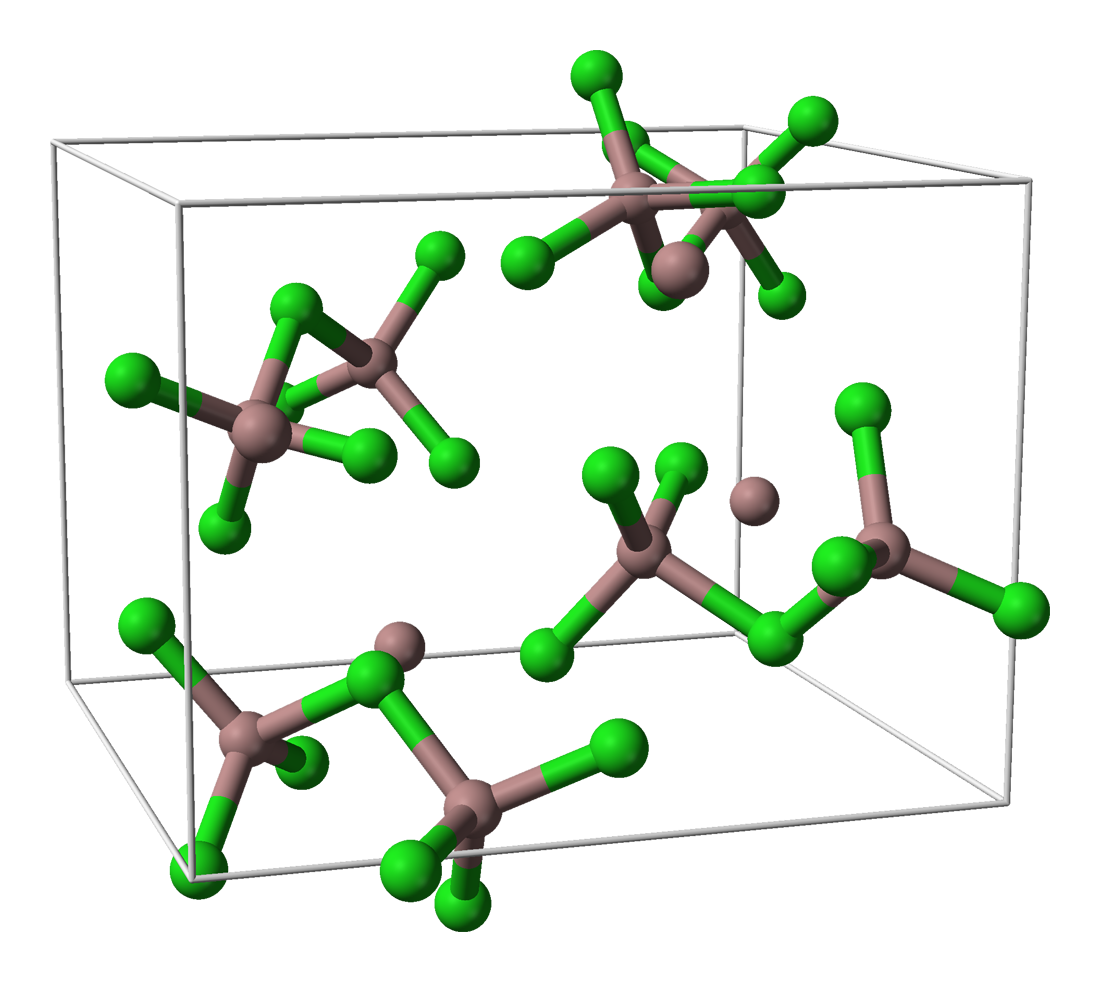
Gallium Triiodide
Gallium(III) iodide is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula, formula Gallium, GaIodine, I3. A yellow hygroscopic solid, it is the most common iodide of gallium. In the chemical vapor transport method of growing crystals of gallium arsenide uses iodine as the transport agent. In the solid state, it exists as the dimer Ga2I6. "Gallium(I) iodide" Gallium triiodide can be reduced with gallium metal to give a green-colored solid called Solid "GaI" Precursor, "gallium(I) iodide." The nature of this species is unclear, but it is useful for the preparation of compounds of gallium(I) and gallium(II) and is reported as useful in organic syntheses.GaI: A new reagent for chemo- and diastereoselective C–C bond forming reactions, Green SP, Jones C., Stasch A., Rose R.P, New J. Chem., 2007, 31, 127 - 134, See also *Gallium halides *Solid "GaI" Precursor, "GaI" References Iodides Gallium compounds Metal halides {{inorganic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inorganic Compound
In chemistry, an inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bonds, that is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as '' inorganic chemistry''. Inorganic compounds comprise most of the Earth's crust, although the compositions of the deep mantle remain active areas of investigation. Some simple carbon compounds are often considered inorganic. Examples include the allotropes of carbon ( graphite, diamond, buckminsterfullerene, etc.), carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, carbides, and the following salts of inorganic anions: carbonates, cyanides, cyanates, and thiocyanates. Many of these are normal parts of mostly organic systems, including organisms; describing a chemical as inorganic does not necessarily mean that it does not occur within living things. History Friedrich Wöhler's conversion of ammonium cyanate into urea in 1828 is often cited as the starting p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Formula
In chemistry, a chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as parentheses, dashes, brackets, commas and ''plus'' (+) and ''minus'' (−) signs. These are limited to a single typographic line of symbols, which may include subscripts and superscripts. A chemical formula is not a chemical name, and it contains no words. Although a chemical formula may imply certain simple chemical structures, it is not the same as a full chemical structural formula. Chemical formulae can fully specify the structure of only the simplest of molecules and chemical substances, and are generally more limited in power than chemical names and structural formulae. The simplest types of chemical formulae are called '' empirical formulae'', which use letters and numbers indicating the numerical ''proportions'' of ato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallium
Gallium is a chemical element with the symbol Ga and atomic number 31. Discovered by French chemist Paul-Émile Lecoq de Boisbaudran in 1875, Gallium is in group 13 of the periodic table and is similar to the other metals of the group ( aluminium, indium, and thallium). Elemental gallium is a soft, silvery metal in standard temperature and pressure. In its liquid state, it becomes silvery white. If too much force is applied, the gallium may fracture conchoidally. Since its discovery in 1875, gallium has widely been used to make alloys with low melting points. It is also used in semiconductors, as a dopant in semiconductor substrates. The melting point of gallium is used as a temperature reference point. Gallium alloys are used in thermometers as a non-toxic and environmentally friendly alternative to mercury, and can withstand higher temperatures than mercury. An even lower melting point of , well below the freezing point of water, is claimed for the alloy galinstan ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iodine
Iodine is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol I and atomic number 53. The heaviest of the stable halogens, it exists as a semi-lustrous, non-metallic solid at standard conditions that melts to form a deep violet liquid at , and boils to a violet gas at . The element was discovered by the French chemist Bernard Courtois in 1811 and was named two years later by Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac, after the Ancient Greek 'violet-coloured'. Iodine occurs in many oxidation states, including iodide (I−), iodate (), and the various periodate anions. It is the least abundant of the stable halogens, being the sixty-first most abundant element. As the heaviest essential mineral nutrient, iodine is required for the synthesis of thyroid hormones. Iodine deficiency affects about two billion people and is the leading preventable cause of intellectual disabilities. The dominant producers of iodine today are Chile and Japan. Due to its high atomic number and ease of attachment to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Vapor Transport
In chemistry, a chemical transport reaction describes a process for purification and crystallization of non- volatile solids. The process is also responsible for certain aspects of mineral growth from the effluent of volcanoes. The technique is distinct from chemical vapor deposition, which usually entails decomposition of molecular precursors and which gives conformal coatings. The technique, which was popularized by Harald Schäfer, entails the reversible conversion of nonvolatile elements and chemical compounds into volatile derivatives. The volatile derivative migrates throughout a sealed reactor, typically a sealed and evacuated glass tube heated in a tube furnace. Because the tube is under a temperature gradient, the volatile derivative reverts to the parent solid and the transport agent is released at the end opposite to which it originated (see next section). The transport agent is thus catalytic. The technique requires that the two ends of the tube (which conta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallium Arsenide
Gallium arsenide (GaAs) is a III-V direct band gap semiconductor with a zinc blende crystal structure. Gallium arsenide is used in the manufacture of devices such as microwave frequency integrated circuits, monolithic microwave integrated circuits, infrared light-emitting diodes, laser diodes, solar cells and optical windows. GaAs is often used as a substrate material for the epitaxial growth of other III-V semiconductors, including indium gallium arsenide, aluminum gallium arsenide and others. Preparation and chemistry In the compound, gallium has a +3 oxidation state. Gallium arsenide single crystals can be prepared by three industrial processes: * The vertical gradient freeze (VGF) process. * Crystal growth using a horizontal zone furnace in the Bridgman-Stockbarger technique, in which gallium and arsenic vapors react, and free molecules deposit on a seed crystal at the cooler end of the furnace. * Liquid encapsulated Czochralski (LEC) growth is used for prod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solid "GaI" Precursor
Gallium monoiodide (GaI or Ga4I4) is a low-valent gallium species that acts as a reactive intermediate for many gallium-based products. Gallium(I) halides were first crystallographically characterized by Schnöckel and coworkers and have allowed a synthetic route to many low-valent gallium species. However, chemical syntheses that employ “GaI” rather than gallium(I) halide precursors have been increasingly investigated given the ease of synthesis of this reagent. While the synthetic method of Schnöckel and coworkers to synthesize gallium(I) halides require extraordinarily high temperatures, the straightforward preparation of “GaI” at near room temperature has allowed for the exploration of new gallium-based chemistries. Synthesis In 1990, Malcolm Green and coworkers synthesized a “GaI” species, whose method of preparation is most widely followed. They found that ultrasonication of liquid gallium metal with iodine in a toluene solvent yields a new pale green powder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallium Halides
There are three sets of gallium halides, the trihalides where gallium has oxidation state +3, the intermediate halides containing gallium in oxidation states +1, +2 and +3 and some unstable monohalides, where gallium has oxidation state +1. Trihalides All four trihalides are known. They all contain gallium in the +3 oxidation state. Their proper names are gallium(III) fluoride, gallium(III) chloride, gallium(III) bromide and gallium(III) iodide. ; GaF3 :GaF3 is a white solid which sublimes before it melts, with an estimated melting point above 1000 °C. It contains 6 co-ordinate gallium atoms with a three-dimensional network of GaF6 octahedra sharing common corners. ; GaCl3, GaBr3 and GaI3 :These all have lower melting points than GaF3, ( GaCl3 mp 78 °C, GaBr3 mp 122 °C, GaI3 mp 212 °C) reflecting the fact that their structures all contain dimers with 4 coordinate gallium atoms and 2 bridging halogen atoms. Thus, this halides have molecular formula Ga2Cl6, G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iodides
An iodide ion is the ion I−. Compounds with iodine in formal oxidation state −1 are called iodides. In everyday life, iodide is most commonly encountered as a component of iodized salt, which many governments mandate. Worldwide, iodine deficiency affects two billion people and is the leading preventable cause of intellectual disability. Structure and characteristics of inorganic iodides Iodide is one of the largest monatomic anions. It is assigned a radius of around 206 picometers. For comparison, the lighter halides are considerably smaller: bromide (196 pm), chloride (181 pm), and fluoride (133 pm). In part because of its size, iodide forms relatively weak bonds with most elements. Most iodide salts are soluble in water, but often less so than the related chlorides and bromides. Iodide, being large, is less hydrophilic compared to the smaller anions. One consequence of this is that sodium iodide is highly soluble in acetone, whereas sodium chloride is n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallium Compounds
Gallium compounds compounds containing the element gallium. These compounds are found primarily in the +3 oxidation state. The +1 oxidation state is also found in some compounds, although it is less common than it is for gallium's heavier congeners indium and thallium. For example, the very stable GaCl2 contains both gallium(I) and gallium(III) and can be formulated as GaIGaIIICl4; in contrast, the monochloride is unstable above 0 °C, disproportionating into elemental gallium and gallium(III) chloride. Compounds containing Ga–Ga bonds are true gallium(II) compounds, such as GaS (which can be formulated as Ga24+(S2−)2) and the dioxan complex Ga2Cl4(C4H8O2)2.Greenwood and Earnshaw, p. 240 Aqueous chemistry Strong acids dissolve gallium, forming gallium(III) salts such as (gallium nitrate). Aqueous solutions of gallium(III) salts contain the hydrated gallium ion, . Gallium(III) hydroxide, , may be precipitated from gallium(III) solutions by adding ammonia. Dehydrati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |