|
Fractionalization
In quantum mechanics, fractionalization is the phenomenon whereby the quasiparticles of a system cannot be constructed as combinations of its elementary constituents. One of the earliest and most prominent examples is the fractional quantum Hall effect, where the constituent particles are electrons but the quasiparticles carry fractions of the electron charge. Fractionalization can be understood as deconfinement of quasiparticles that together are viewed as comprising the elementary constituents. In the case of spin–charge separation, for example, the electron can be viewed as a bound state of a 'spinon' and a ' chargon', which under certain conditions can become free to move separately. History Quantized Hall conductance was discovered in 1980, related to the electron charge. Laughlin proposed a fluid of fractional charges in 1983, to explain the Fractional quantum Hall effect seen in 1982, for which he shared the 1998 Physics Nobel Prize. In 1997, experiments directly observ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spin–charge Separation
In condensed matter physics, spin–charge separation is an unusual behavior of electrons in some materials in which they 'split' into three independent particles, the spinon, the orbiton and the holon (or chargon). The electron can always be theoretically considered as a bound state of the three, with the spinon carrying the spin of the electron, the orbiton carrying the orbital degree of freedom and the chargon carrying the charge, but in certain conditions they can behave as independent quasiparticles. The theory of spin–charge separation originates with the work of Sin-Itiro Tomonaga who developed an approximate method for treating one-dimensional interacting quantum systems in 1950. This was then developed by Joaquin Mazdak Luttinger in 1963 with an exactly solvable model which demonstrated spin–charge separation. In 1981 F. Duncan M. Haldane generalized Luttinger's model to the Tomonaga–Luttinger liquid concept whereby the physics of Luttinger's model was shown the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
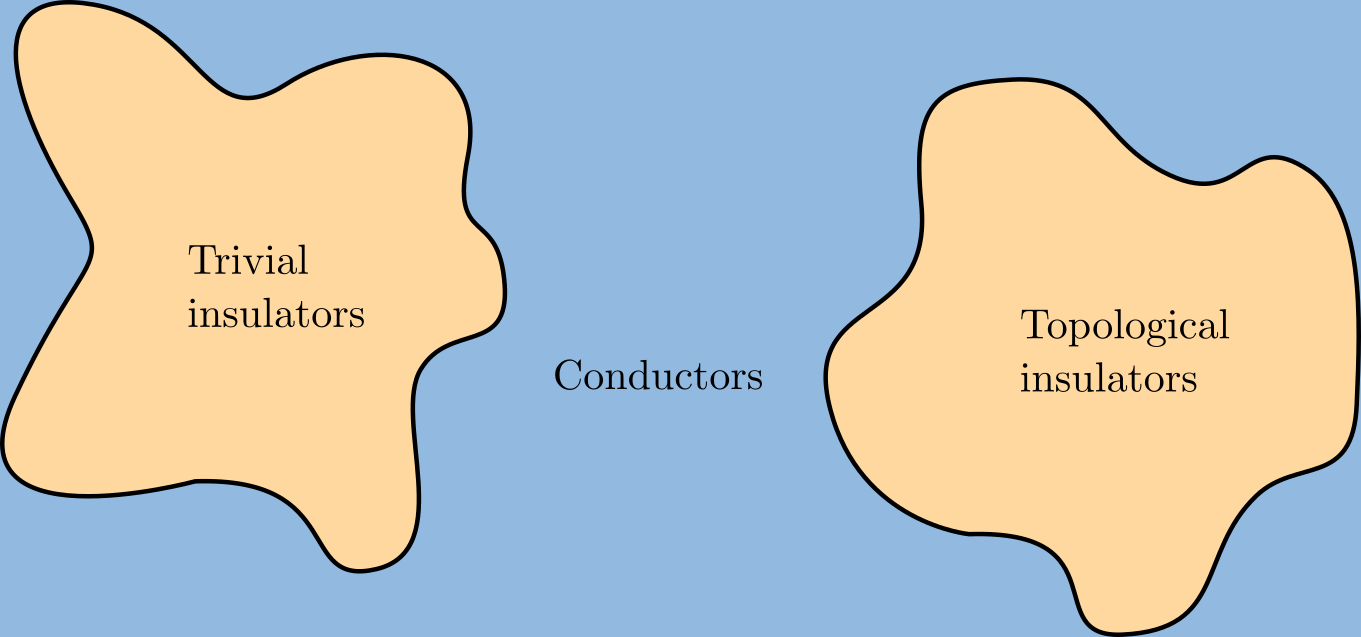
Topological Insulator
A topological insulator is a material whose interior behaves as an electrical insulator while its surface behaves as an electrical conductor, meaning that electrons can only move along the surface of the material. A topological insulator is an insulator for the same reason a "trivial" (ordinary) insulator is: there exists an energy gap between the valence and conduction bands of the material. But in a topological insulator, these bands are, in an informal sense, "twisted", relative to a trivial insulator. The topological insulator cannot be continuously transformed into a trivial one without untwisting the bands, which closes the band gap and creates a conducting state. Thus, due to the continuity of the underlying field, the border of a topological insulator with a trivial insulator (including vacuum, which is topologically trivial) is forced to support a conducting state. Since this results from a global property of the topological insulator's band structure, local (symmetry- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fractional Quantum Hall Effect
The fractional quantum Hall effect (FQHE) is a physical phenomenon in which the Hall conductance of 2-dimensional (2D) electrons shows precisely quantized plateaus at fractional values of e^2/h. It is a property of a collective state in which electrons bind magnetic flux lines to make new quasiparticles, and excitations have a fractional elementary charge and possibly also fractional statistics. The 1998 Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to Robert Laughlin, Horst Störmer, and Daniel Tsui "for their discovery of a new form of quantum fluid with fractionally charged excitations" Laughlin's explanation only applies to fillings \nu = 1/m where m is an odd integer. The microscopic origin of the FQHE is a major research topic in condensed matter physics. Introduction The fractional quantum Hall effect (FQHE) is a collective behavior in a 2D system of electrons. In particular magnetic fields, the electron gas condenses into a remarkable liquid state, which is very delicate, requ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fractional Quantum Hall Effect
The fractional quantum Hall effect (FQHE) is a physical phenomenon in which the Hall conductance of 2-dimensional (2D) electrons shows precisely quantized plateaus at fractional values of e^2/h. It is a property of a collective state in which electrons bind magnetic flux lines to make new quasiparticles, and excitations have a fractional elementary charge and possibly also fractional statistics. The 1998 Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to Robert Laughlin, Horst Störmer, and Daniel Tsui "for their discovery of a new form of quantum fluid with fractionally charged excitations" Laughlin's explanation only applies to fillings \nu = 1/m where m is an odd integer. The microscopic origin of the FQHE is a major research topic in condensed matter physics. Introduction The fractional quantum Hall effect (FQHE) is a collective behavior in a 2D system of electrons. In particular magnetic fields, the electron gas condenses into a remarkable liquid state, which is very delicate, requ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Mechanics
Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles. It is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, quantum field theory, quantum technology, and quantum information science. Classical physics, the collection of theories that existed before the advent of quantum mechanics, describes many aspects of nature at an ordinary (macroscopic) scale, but is not sufficient for describing them at small (atomic and subatomic) scales. Most theories in classical physics can be derived from quantum mechanics as an approximation valid at large (macroscopic) scale. Quantum mechanics differs from classical physics in that energy, momentum, angular momentum, and other quantities of a bound system are restricted to discrete values ( quantization); objects have characteristics of both particles and waves (wave–particle duality); and there are limits to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
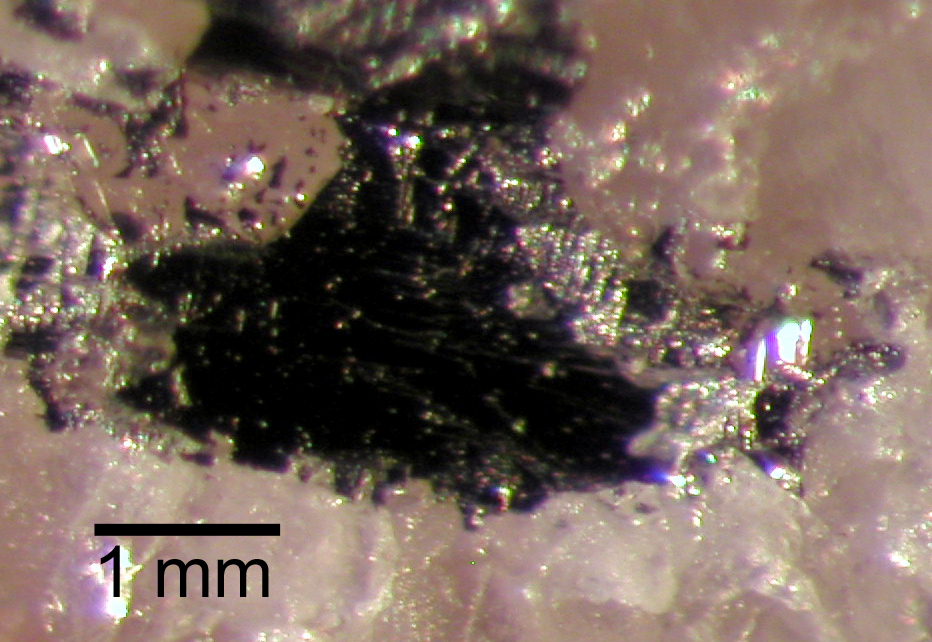
Herbertsmithite
Herbertsmithite is a mineral with chemical structure Zn Cu3( OH)6 Cl2. It is named after the mineralogist Herbert Smith (1872–1953) and was first found in 1972 in Chile. It is polymorphous with kapellasite and closely related to paratacamite. Herbertsmithite is generally found in and around Anarak, Iran, hence its other name, anarakite. Herbertsmithite is associated with copper mineralizations in syenitic porphyries and granites in Chile and in Triassic dolomite formations in Iran. It has also been reported from the Osborn District in the Big Horn Mountains of Maricopa County, Arizona and the Lavrion District Mines of Attica, Greece. Herbertsmithite has a vitreous luster and is fairly transparent with a light-green to blue green color. Herbertsmithite has a Mohs hardness of between 3 and 3.5 and is known to have a brittle tenacity. The crystal's density has been calculated at 3.76 g/cm3. Herbertsmithite, in a pure synthetic form, was discovered in 2012 to be able to exhi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bismuth
Bismuth is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Bi and atomic number 83. It is a post-transition metal and one of the pnictogens, with chemical properties resembling its lighter group 15 siblings arsenic and antimony. Elemental bismuth occurs naturally, and its sulfide and oxide forms are important commercial ores. The free element is 86% as dense as lead. It is a brittle metal with a silvery-white color when freshly produced. Passivation (chemistry), Surface oxidation generally gives samples of the metal a somewhat rosy cast. Further oxidation under heat can give bismuth a vividly Iridescence, iridescent appearance due to thin-film interference. Bismuth is both the most Diamagnetism, diamagnetic element and one of the least Thermal conductivity, thermally conductive metals known. Bismuth was long considered the element with the highest atomic mass whose nuclei do not spontaneously decay. However, in 2003 it was discovered to be extremely weakly radioactive. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antimony
Antimony is a chemical element with the symbol Sb (from la, stibium) and atomic number 51. A lustrous gray metalloid, it is found in nature mainly as the sulfide mineral stibnite (Sb2S3). Antimony compounds have been known since ancient times and were powdered for use as medicine and cosmetics, often known by the Arabic name kohl. The earliest known description of the metal in the West was written in 1540 by Vannoccio Biringuccio. China is the largest producer of antimony and its compounds, with most production coming from the Xikuangshan Mine in Hunan. The industrial methods for refining antimony from stibnite are roasting followed by reduction with carbon, or direct reduction of stibnite with iron. The largest applications for metallic antimony are in alloys with lead and tin, which have improved properties for solders, bullets, and plain bearings. It improves the rigidity of lead-alloy plates in lead–acid batteries. Antimony trioxide is a prominent additive for halo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tellurium
Tellurium is a chemical element with the symbol Te and atomic number 52. It is a brittle, mildly toxic, rare, silver-white metalloid. Tellurium is chemically related to selenium and sulfur, all three of which are chalcogens. It is occasionally found in native form as elemental crystals. Tellurium is far more common in the Universe as a whole than on Earth. Its extreme rarity in the Earth's crust, comparable to that of platinum, is due partly to its formation of a volatile hydride that caused tellurium to be lost to space as a gas during the hot nebular formation of Earth.Anderson, Don L.; "Chemical Composition of the Mantle" in ''Theory of the Earth'', pp. 147-175 Tellurium-bearing compounds were first discovered in 1782 in a gold mine in Kleinschlatten, Transylvania (now Zlatna, Romania) by Austrian mineralogist Franz-Joseph Müller von Reichenstein, although it was Martin Heinrich Klaproth who named the new element in 1798 after the Latin 'earth'. Gold telluride minerals ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Numbers
In quantum physics and chemistry, quantum numbers describe values of conserved quantities in the dynamics of a quantum system. Quantum numbers correspond to eigenvalues of operators that commute with the Hamiltonian—quantities that can be known with precision at the same time as the system's energyspecifically, observables \widehat that commute with the Hamiltonian are simultaneously diagonalizable with it and so the eigenvalues a and the energy (eigenvalues of the Hamiltonian) are not limited by an uncertainty relation arising from non-commutativity.—and their corresponding eigenspaces. Together, a specification of all of the quantum numbers of a quantum system fully characterize a basis state of the system, and can in principle be measured together. An important aspect of quantum mechanics is the quantization of many observable quantities of interest.Many observables have discrete spectra (sets of eigenvalues) in quantum mechanics, so the quantities can only be measure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cooper Pair
In condensed matter physics, a Cooper pair or BCS pair (Bardeen–Cooper–Schrieffer pair) is a pair of electrons (or other fermions) bound together at low temperatures in a certain manner first described in 1956 by American physicist Leon Cooper. Cooper pair Cooper showed that an arbitrarily small attraction between electrons in a metal can cause a paired state of electrons to have a lower energy than the Fermi energy, which implies that the pair is bound. In conventional superconductors, this attraction is due to the electron–phonon interaction. The Cooper pair state is responsible for superconductivity, as described in the BCS theory developed by John Bardeen, Leon Cooper, and John Schrieffer for which they shared the 1972 Nobel Prize. Although Cooper pairing is a quantum effect, the reason for the pairing can be seen from a simplified classical explanation. An electron in a metal normally behaves as a free particle. The electron is repelled from other electrons due to thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnon
A magnon is a quasiparticle, a collective excitation of the electrons' spin structure in a crystal lattice. In the equivalent wave picture of quantum mechanics, a magnon can be viewed as a quantized spin wave. Magnons carry a fixed amount of energy and lattice momentum, and are spin-1, indicating they obey boson behavior. Brief history The concept of a magnon was introduced in 1930 by Felix Bloch in order to explain the reduction of the spontaneous magnetization in a ferromagnet. At absolute zero temperature (0 K), a Heisenberg ferromagnet reaches the state of lowest energy (so-called ground state), in which all of the atomic spins (and hence magnetic moments) point in the same direction. As the temperature increases, more and more spins deviate randomly from the alignment, increasing the internal energy and reducing the net magnetization. If one views the perfectly magnetized state at zero temperature as the vacuum state of the ferromagnet, the low-temperature state with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |