|
Folliculin
The tumor suppressor gene ''FLCN'' encodes the protein folliculin, also known as Birt–Hogg–Dubé syndrome protein, which functions as an inhibitor of Lactate dehydrogenase A, Lactate Dehydrogenase-A and a regulator of the Warburg effect (oncology), Warburg effect. Folliculin (FLCN) is also associated with Birt–Hogg–Dubé syndrome, which is an autosomal dominant inherited cancer syndrome in which affected individuals are at risk for the development of benign cutaneous tumors (folliculomas), pulmonary cysts (often associated with pneumothorax), and kidney tumors. Gene Structure The ''FLCN'' gene consists of 14 exons. Location Cytogenetic location: The ''FLCN'' gene is located on the short (p) arm of chromosome 17 at position 11.2. (17p11.2). Molecular location on chromosome 17: base pairs 17,056,252 to 17,081,230 (NCI Build 36.1) Clinical significance Germline mutations in the ''FLCN'' gene cause Birt–Hogg–Dubé syndrome (BHD), an autosomal dominant disease that pred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birt–Hogg–Dubé Syndrome
Birt–Hogg–Dubé syndrome (BHD), also Hornstein–Birt–Hogg–Dubé syndrome, Hornstein–Knickenberg syndrome, and fibrofolliculomas with trichodiscomas and acrochordons is a human autosomal dominant genetic disorder that can cause susceptibility to kidney cancer, renal and pulmonary cysts, and noncancerous tumors of the hair follicles, called fibrofolliculomas. The symptoms seen in each family are unique, and can include any combination of the three symptoms. Fibrofolliculomas are the most common manifestation, found on the face and upper trunk in over 80% of people with BHD over the age of 40. Pulmonary cysts are equally common (84%), but only 24% of people with BHD eventually experience a collapsed lung (spontaneous pneumothorax). Kidney tumors, both cancerous and benign, occur in 14–34% of people with BHD; the associated kidney cancers are often rare hybrid tumors. Any of these conditions that occurs in a family can indicate a diagnosis of Birt–Hogg–Dubé syndr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tumor Suppressor Gene
A tumor suppressor gene (TSG), or anti-oncogene, is a gene that regulates a cell during cell division and replication. If the cell grows uncontrollably, it will result in cancer. When a tumor suppressor gene is mutated, it results in a loss or reduction in its function. In combination with other genetic mutations, this could allow the cell to grow abnormally. The loss of function for these genes may be even more significant in the development of human cancers, compared to the activation of oncogenes. TSGs can be grouped into the following categories: caretaker genes, gatekeeper genes, and more recently landscaper genes. Caretaker genes ensure stability of the genome via DNA repair and subsequently when mutated allow mutations to accumulate. Meanwhile, gatekeeper genes directly regulate cell growth by either inhibiting cell cycle progression or inducing apoptosis. Lastly landscaper genes regulate growth by contributing to the surrounding environment, when mutated can cause an envir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoplasm
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists in growing abnormally, even if the original trigger is removed. This abnormal growth usually forms a mass, when it may be called a tumor. ICD-10 classifies neoplasms into four main groups: benign neoplasms, in situ neoplasms, malignant neoplasms, and neoplasms of uncertain or unknown behavior. Malignant neoplasms are also simply known as cancers and are the focus of oncology. Prior to the abnormal growth of tissue, as neoplasia, cells often undergo an abnormal pattern of growth, such as metaplasia or dysplasia. However, metaplasia or dysplasia does not always progress to neoplasia and can occur in other conditions as well. The word is from Ancient Greek 'new' and 'formation, creation'. Types A neoplasm can be benign, potentially ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
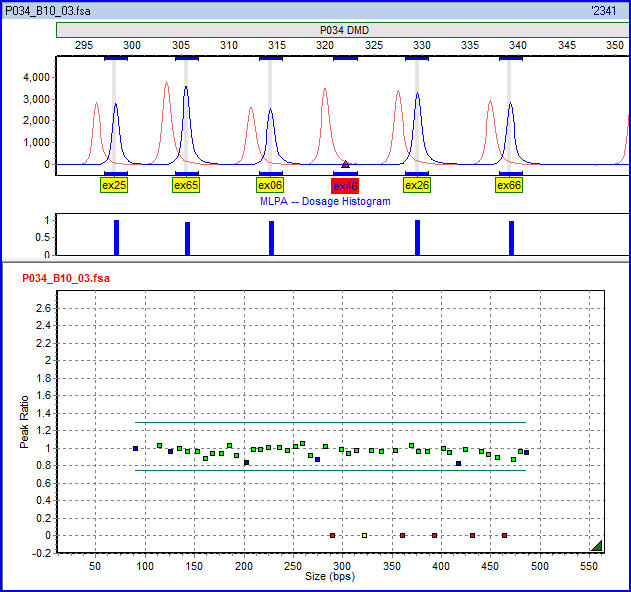
Multiplex Ligation-dependent Probe Amplification
Multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA) is a variation of the multiplex polymerase chain reaction that permits amplification of multiple targets with only a single primer pair. It detects copy number changes at the molecular level, and software programs are used for analysis. Identification of deletions or duplications can indicate pathogenic mutations, thus MLPA is an important diagnostic tool used in clinical pathology laboratories worldwide. History Multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification was invented by Jan Schouten, a Dutch scientist. The method was first described in 2002 in the scientific journal ''Nucleic Acid Research''. The first applications included the detection of exon deletions in the human genes BRCA1, MSH2 and MLH1, which are linked to hereditary breast and colon cancer. Now MLPA is used to detect hundreds of hereditary disorders, as well as for tumour profiling. Description MLPA quantifies the presence of particular sequences in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Sequencing
DNA sequencing is the process of determining the nucleic acid sequence – the order of nucleotides in DNA. It includes any method or technology that is used to determine the order of the four bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. The advent of rapid DNA sequencing methods has greatly accelerated biological and medical research and discovery. Knowledge of DNA sequences has become indispensable for basic biological research, DNA Genographic Projects and in numerous applied fields such as medical diagnosis, biotechnology, forensic biology, virology and biological systematics. Comparing healthy and mutated DNA sequences can diagnose different diseases including various cancers, characterize antibody repertoire, and can be used to guide patient treatment. Having a quick way to sequence DNA allows for faster and more individualized medical care to be administered, and for more organisms to be identified and cataloged. The rapid speed of sequencing attained with modern D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha amino acids appear in the genetic code. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups, as Alpha and beta carbon, alpha- , beta- , gamma- or delta- amino acids; other categories relate to Chemical polarity, polarity, ionization, and side chain group type (aliphatic, Open-chain compound, acyclic, aromatic, containing hydroxyl or sulfur, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino acid '' residues'' form the second-largest component (water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis. It is thought that they played a key role in enabling life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleotide
Nucleotides are organic molecules consisting of a nucleoside and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecules within all life-forms on Earth. Nucleotides are obtained in the diet and are also synthesized from common nutrients by the liver. Nucleotides are composed of three subunit molecules: a nucleobase, a five-carbon sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), and a phosphate group consisting of one to three phosphates. The four nucleobases in DNA are guanine, adenine, cytosine and thymine; in RNA, uracil is used in place of thymine. Nucleotides also play a central role in metabolism at a fundamental, cellular level. They provide chemical energy—in the form of the nucleoside triphosphates, adenosine triphosphate (ATP), guanosine triphosphate (GTP), cytidine triphosphate (CTP) and uridine triphosphate (UTP)—throughout the cell for the many cellular func ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
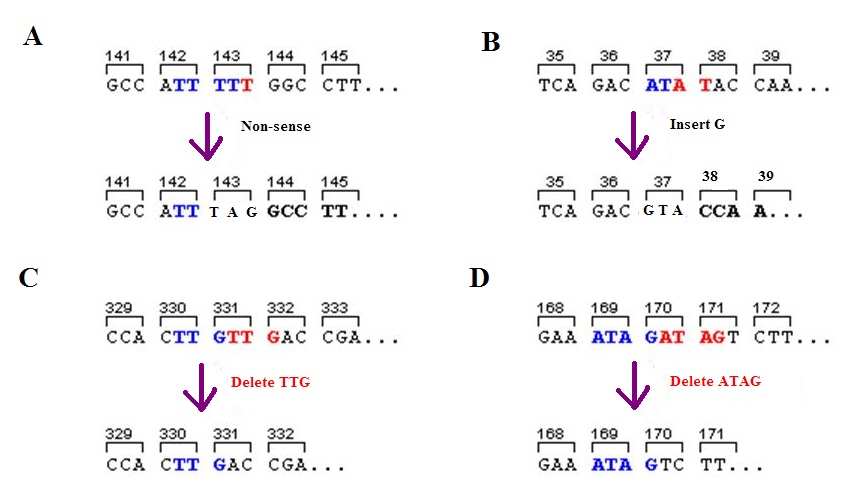
Missense Mutations
In genetics, a missense mutation is a point mutation in which a single nucleotide change results in a codon that codes for a different amino acid. It is a type of nonsynonymous substitution. Substitution of protein from DNA mutations Missense mutation refers to a change in one amino acid in a protein, arising from a point mutation in a single nucleotide. Missense mutation is a type of nonsynonymous substitution in a DNA sequence. Two other types of nonsynonymous substitution are the nonsense mutations, in which a codon is changed to a premature stop codon that results in truncation of the resulting protein, and the nonstop mutations, in which a stop codon erasement results in a longer, nonfunctional protein. Missense mutations can render the resulting protein nonfunctional, and such mutations are responsible for human diseases such as Epidermolysis bullosa, sickle-cell disease, SOD1 mediated ALS, and a substantial number of cancers. In the most common variant of sickle-cell dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Splice Site Mutation
A splice site mutation is a genetic mutation that inserts, deletes or changes a number of nucleotides in the specific site at which splicing takes place during the processing of precursor messenger RNA into mature messenger RNA. Splice site consensus sequences that drive exon recognition are located at the very termini of introns. The deletion of the splicing site results in one or more introns remaining in mature mRNA and may lead to the production of abnormal proteins. When a splice site mutation occurs, the mRNA transcript possesses information from these introns that normally should not be included. Introns are supposed to be removed, while the exons are expressed. The mutation must occur at the specific site at which intron splicing occurs: within non-coding sites in a gene, directly next to the location of the exon. The mutation can be an insertion, deletion, frameshift, etc. The splicing process itself is controlled by the given sequences, known as splice-donor and splic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonsense Mutations
In genetics, a nonsense mutation is a point mutation in a sequence of DNA that results in a premature stop codon, or a ''nonsense codon'' in the transcribed mRNA, and in leading to a truncated, incomplete, and usually nonfunctional protein product. The functional effect of a nonsense mutation depends on the location of the stop codon within the coding DNA. For example, the effect of a nonsense mutation depends on the proximity of the nonsense mutation to the original stop codon, and the degree to which functional subdomains of the protein are affected. As nonsense mutations leads to premature termination of polypeptide chains; they are also called chain termination mutations. Missense mutations differ from nonsense mutations since they are point mutations that exhibit a single nucleotide change to cause substitution of a different amino acid. A nonsense mutation also differs from a nonstop mutation, which is a point mutation that removes a stop codon. About 10% of patients facin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frameshift Mutations
A frameshift mutation (also called a framing error or a reading frame shift) is a genetic mutation caused by indels ( insertions or deletions) of a number of nucleotides in a DNA sequence that is not divisible by three. Due to the triplet nature of gene expression by codons, the insertion or deletion can change the reading frame (the grouping of the codons), resulting in a completely different translation from the original. The earlier in the sequence the deletion or insertion occurs, the more altered the protein. A frameshift mutation is not the same as a single-nucleotide polymorphism in which a nucleotide is replaced, rather than inserted or deleted. A frameshift mutation will in general cause the reading of the codons after the mutation to code for different amino acids. The frameshift mutation will also alter the first stop codon ("UAA", "UGA" or "UAG") encountered in the sequence. The polypeptide being created could be abnormally short or abnormally long, and will most likel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loss-of-function Mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitosis, or meiosis or other types of damage to DNA (such as pyrimidine dimers caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation), which then may undergo error-prone repair (especially microhomology-mediated end joining), cause an error during other forms of repair, or cause an error during replication (translesion synthesis). Mutations may also result from insertion or deletion of segments of DNA due to mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce detectable changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity. Mutation is the ultimate source of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |