|
Focal-plane Array (radio Astronomy)
Focal-plane arrays (FPAs) are widely used in radio astronomy. FPAs are arrays of receivers placed at the focus of the optical system in a radio-telescope. The optical system may be a reflector or a lens. Traditional radio-telescopes have only one receiver at the focus of the telescope, but radio-telescopes are now starting to be equipped with focal plane arrays, which are of three different types: multi-beam feed arrays, bolometer arrays, and the experimental phased-array feeds. Multi-beam feed arrays Multi-beam feed arrays consist of a small array of feed horns at the focus of a radio-telescope. Each feed horn is connected to a receiver to measure the received power and each horn and receiver pair is sensitive to radio waves from a slightly different direction in the sky. A feed array with receivers will increase the survey speed of the telescope by a factor of , making them very powerful survey instruments. Because radio wavelengths are large, the resulting feed arrays are am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Focal-plane Array
A staring array, also known as staring-plane array or focal-plane array (FPA), is an image sensor consisting of an array (typically rectangular) of light-sensing pixels at the focal plane of a lens. FPAs are used most commonly for imaging purposes (e.g. taking pictures or video imagery), but can also be used for non-imaging purposes such as spectrometry, LIDAR, and wave-front sensing. In radio astronomy, the FPA is at the focus of a radio telescope. At optical and infrared wavelengths, it can refer to a variety of imaging device types, but in common usage it refers to two-dimensional devices that are sensitive in the infrared spectrum. Devices sensitive in other spectra are usually referred to by other terms, such as CCD (charge-coupled device) and CMOS image sensor in the visible spectrum. FPAs operate by detecting photons at particular wavelengths and then generating an electrical charge, voltage, or resistance in relation to the number of photons detected at each pixel. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolometer
A bolometer is a device for measuring radiant heat by means of a material having a temperature-dependent electrical resistance. It was invented in 1878 by the American astronomer Samuel Pierpont Langley. Principle of operation A bolometer consists of an absorptive element, such as a thin layer of metal, connected to a thermal reservoir (a body of constant temperature) through a thermal link. The result is that any radiation impinging on the absorptive element raises its temperature above that of the reservoir – the greater the absorbed power, the higher the temperature. The intrinsic thermal time constant, which sets the speed of the detector, is equal to the ratio of the heat capacity of the absorptive element to the thermal conductivity, thermal conductance between the absorptive element and the reservoir. The temperature change can be measured directly with an attached resistive thermometer, or the resistance of the absorptive element itself can be used as a thermometer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staring Array
A staring array, also known as staring-plane array or focal-plane array (FPA), is an image sensor consisting of an array (typically rectangular) of light-sensing pixels at the focal plane of a lens. FPAs are used most commonly for imaging purposes (e.g. taking pictures or video imagery), but can also be used for non-imaging purposes such as spectrometry, LIDAR, and wave-front sensing. In radio astronomy, the FPA is at the focus of a radio telescope. At optical and infrared wavelengths, it can refer to a variety of imaging device types, but in common usage it refers to two-dimensional devices that are sensitive in the infrared spectrum. Devices sensitive in other spectra are usually referred to by other terms, such as CCD ( charge-coupled device) and CMOS image sensor in the visible spectrum. FPAs operate by detecting photons at particular wavelengths and then generating an electrical charge, voltage, or resistance in relation to the number of photons detected at each pixe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Square Kilometre Array Pathfinder
The Australian Square Kilometre Array Pathfinder (ASKAP) is a radio telescope array located at Murchison Radio-astronomy Observatory (MRO) in the Mid West region of Western Australia. The facility began as a technology demonstrator for the international Square Kilometre Array (SKA), an internationally-planned radio telescope which will be larger and more sensitive. The ASKAP site has been selected as one of the SKA's two central locations. It is operated by the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO) and forms part of the Australia Telescope National Facility. Construction commenced in late 2009 and first light was in October 2012. ASKAP consists of 36 identical parabolic antennas, each in diameter, working together as a single astronomical interferometer with a total collecting area of approximately . Each antenna is equipped with a phased-array feed (PAF), significantly increasing the field of view. This design provides both fast survey s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Westerbork Synthesis Radio Telescope
The Westerbork Synthesis Radio Telescope (WSRT) is an aperture synthesis interferometer built on the site of the former World War II Nazi detention and transit camp Westerbork, north of the village of Westerbork, Midden-Drenthe, in the northeastern Netherlands. Overview The WRST comprises fourteen 25-metre radio telescopes deployed in a linear array arranged on a East-West line, of which 10 are in a fixed equidistant position, 2 are nearby on a 300 m rail track, and 2 are located a kilometer eastwards on another 200 m rail track. It has a similar arrangement to other radio telescopes such as the One-Mile Telescope, Australia Telescope Compact Array and the Ryle Telescope. Its Equatorial mount is what sets it apart from most other radio telescopes, most of which have an Altazimuth mount. This makes it specifically useful for specific types of science, like polarized emission research as the detectors maintain a constant orientation on the sky during an observation. Ten of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beamformer
Beamforming or spatial filtering is a signal processing technique used in sensor arrays for directional signal transmission or reception. This is achieved by combining elements in an antenna array in such a way that signals at particular angles experience constructive interference while others experience destructive interference. Beamforming can be used at both the transmitting and receiving ends in order to achieve spatial selectivity. The improvement compared with omnidirectional reception/transmission is known as the directivity of the array. Beamforming can be used for radio or sound waves. It has found numerous applications in radar, sonar, seismology, wireless communications, radio astronomy, acoustics and biomedicine. Adaptive beamforming is used to detect and estimate the signal of interest at the output of a sensor array by means of optimal (e.g. least-squares) spatial filtering and interference rejection. Techniques To change the directionality of the array when tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
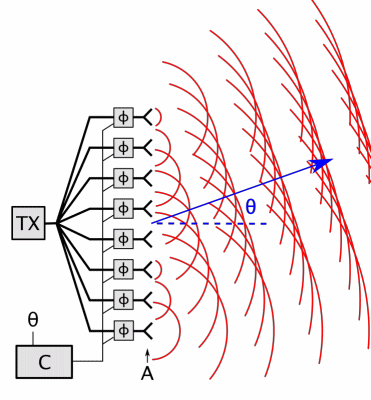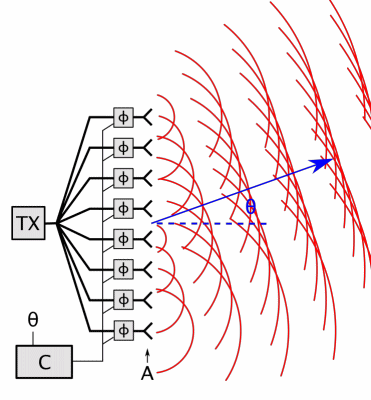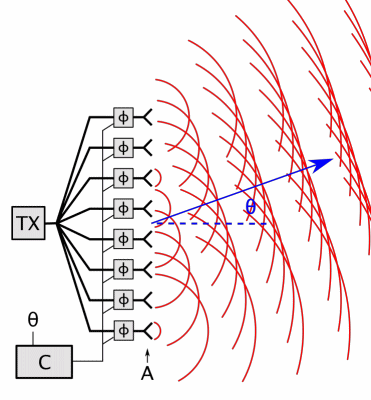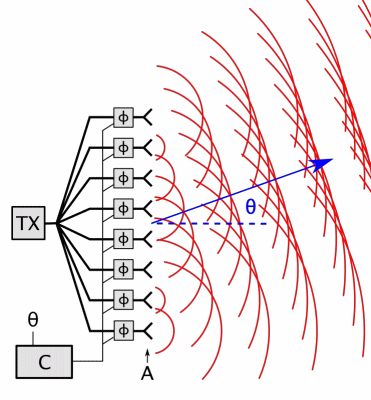
Phased Array
In antenna theory, a phased array usually means an electronically scanned array, a computer-controlled array of antennas which creates a beam of radio waves that can be electronically steered to point in different directions without moving the antennas. In a simple array antenna, the radio frequency current from the transmitter is fed to multiple individual antenna elements with the proper phase relationship so that the radio waves from the separate elements combine ( superpose) to form beams, to increase power radiated in desired directions and suppress radiation in undesired directions. In a phased array, the power from the transmitter is fed to the radiating elements through devices called '' phase shifters'', controlled by a computer system, which can alter the phase or signal delay electronically, thus steering the beam of radio waves to a different direction. Since the size of an antenna array must extend many wavelengths to achieve the high gain needed for narrow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atacama Pathfinder Experiment
The Atacama Pathfinder Experiment (APEX) is a radio telescope 5,064 meters above sea level, at the Llano de Chajnantor Observatory in the Atacama desert in northern Chile, 50 km east of San Pedro de Atacama built and operated by 3 European research institutes. The main dish has a diameter of 12 m and consists of 264 aluminium panels with an average surface accuracy of 17 micrometres ( rms). The telescope was officially inaugurated on September 25, 2005. The APEX telescope is a modified ALMA (Atacama Large Millimeter Array) prototype antenna and is at the site of the ALMA observatory. APEX is designed to work at sub-millimetre wavelengths, in the 0.2 to 1.5 mm range — between infrared light and radio waves — and to find targets that ALMA will be able to study in greater detail. Submillimetre astronomy provides a window into the cold, dusty and distant Universe, but the faint signals from space are heavily absorbed by water vapour in the Earth's atmosphere. Chajnant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Clerk Maxwell Telescope
The James Clerk Maxwell Telescope (JCMT) is a submillimetre-wavelength radio telescope at Mauna Kea Observatory in Hawaii, US. The telescope is near the summit of Mauna Kea at . Its primary mirror is 15 metres (16.4 yards) across: it is the largest single-dish telescope that operates in submillimetre wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum ( far-infrared to microwave).W.S. Holland et al., SCUBA: a common-user submillimetre camera operating on the James Clerk Maxwell Telescope, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society: Letters Volume 303 Issue 4, Pages 659–672, 2002 Scientists use it to study the Solar System, interstellar dust and gas, and distant galaxies. The JCMT started operations in 1987, and was funded until February 2015 by a partnership between the United Kingdom and Canada, and the Netherlands. It was operated by the Joint Astronomy Centre and was named in honour of mathematical physicist James Clerk Maxwell. In March 2015 the operation of the JCMT w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submillimetre Common-User Bolometer Array
Two instruments known as the Submillimetre Common-User Bolometer Array, or SCUBA, have been used for detecting submillimetre radiation on the James Clerk Maxwell Telescope in Hawaii. SCUBA-1 The older continuum single pixel UKT14 bolometer receiver was replaced in the 1990s by the Submillimeter Common-User Bolometer Array (SCUBA). The SCUBA project was green-lighted in 1987 by the JCMT board and was in development for nearly a decade before it saw first light on the telescope. While it was not the first bolometer array it was "unique in combining an unparallel sensitivity with an extensive wavelength range and field-of-view". SCUBA operated simultaneously at wavelengths of 450 and 850 micron (with 91 and 37 pixels, respectively), and was sensitive to the thermal emission from interstellar dust. SCUBA is ranked second only to the Hubble Space Telescope in terms of publication of high-impact astronomical research. SCUBA was retired from service in 2005, and it is now in the Nation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, galaxies, and comets. Relevant phenomena include supernova explosions, gamma ray bursts, quasars, blazars, pulsars, and cosmic microwave background radiation. More generally, astronomy studies everything that originates beyond Earth's atmosphere. Cosmology is a branch of astronomy that studies the universe as a whole. Astronomy is one of the oldest natural sciences. The early civilizations in recorded history made methodical observations of the night sky. These include the Babylonians, Greeks, Indians, Egyptians, Chinese, Maya, and many ancient indigenous peoples of the Americas. In the past, astronomy included disciplines as diverse as astrometry, celestial navigation, observational astronomy, and the making of calendars. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
