|
Fluorinase
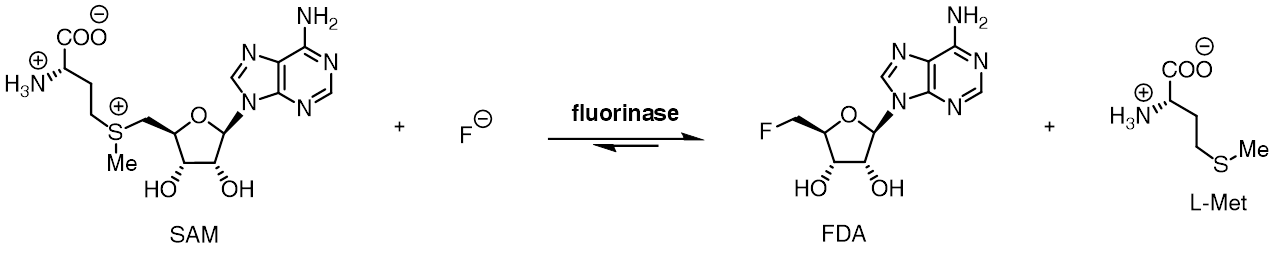
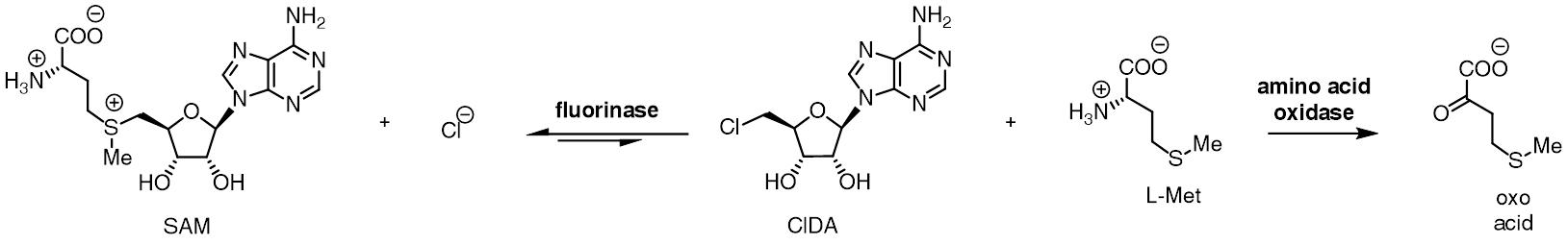
The fluorinase enzyme (, also known as adenosyl-fluoride synthase) catalyzes the reaction between fluoride ion and the co-factor '' S'' -adenosyl-L-methionine to generate L-methionine and 5'-fluoro-5'-deoxyadenosine, the first committed product of the fluorometabolite biosynthesis pathway. The fluorinase was originally isolated from the soil bacterium '' Streptomyces cattleya'', but homologues have since been identified in a number of other bacterial species, including ''Streptomyces'' sp. MA37, '' Nocardia brasiliensis'' and ''Actinoplanes'' sp. N902-109. This is the only known enzyme capable of catalysing the formation of a carbon-fluorine bond, the strongest single bond in organic chemistry. A homologous chlorinase enzyme, which catalyses the same reaction with chloride rather than fluoride ion, has been isolated from ''Salinospora tropica'', from the biosynthetic pathway of salinosporamide A. Reactivity The fluorinase catalyses an SN2-type nucleophilic substitution at t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorinase Reaction
The fluorinase enzyme (, also known as adenosyl-fluoride synthase) catalyzes the reaction between fluoride ion and the co-factor '' S'' -adenosyl-L-methionine to generate L-methionine and 5'-fluoro-5'-deoxyadenosine, the first committed product of the fluorometabolite biosynthesis pathway. The fluorinase was originally isolated from the soil bacterium ''Streptomyces cattleya'', but homologues have since been identified in a number of other bacterial species, including ''Streptomyces'' sp. MA37, '' Nocardia brasiliensis'' and ''Actinoplanes'' sp. N902-109. This is the only known enzyme capable of catalysing the formation of a carbon-fluorine bond, the strongest single bond in organic chemistry. A homologous chlorinase enzyme, which catalyses the same reaction with chloride rather than fluoride ion, has been isolated from ''Salinospora tropica'', from the biosynthetic pathway of salinosporamide A. Reactivity The fluorinase catalyses an SN2-type nucleophilic substitution at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organofluorine
Organofluorine chemistry describes the chemistry of the organofluorines, organic compounds that contain the carbon–fluorine bond. Organofluorine compounds find diverse applications ranging from oil and water repellents to pharmaceuticals, refrigerants, and reagents in catalysis. In addition to these applications, some organofluorine compounds are pollutants because of their contributions to ozone depletion, global warming, bioaccumulation, and toxicity. The area of organofluorine chemistry often requires special techniques associated with the handling of fluorinating agents. The carbon–fluorine bond Fluorine has several distinctive differences from all other substituents encountered in organic molecules. As a result, the physical and chemical properties of organofluorines can be distinctive in comparison to other organohalogens. # The carbon–fluorine bond is one of the strongest in organic chemistry (an average bond energy around 480 kJ/molKirsch, Peer ''Modern fluoroorga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5'-Deoxy-5'-fluoroadenosine
5′-Deoxy-5′-fluoroadenosine is the first step in the biosynthesis of organic fluorides. It is synthesized by the fluorinase catalyzed addition of a fluoride ion to ''S''-adenosyl-L-methionine, releasing L-methionine as a by product. Purine nucleoside phosphorylase Purine nucleoside phosphorylase, PNP, PNPase or inosine phosphorylase () is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''NP'' gene. It catalyzes the chemical reaction :purine nucleoside + phosphate \rightleftharpoons purine + alpha-D-ribose 1- ... mediates a phosphorolytic cleavage of the adenine base to generate 5-fluoro-5-deoxy-D-ribose-1-phosphate. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Deoxy-5'-fluoroadenosine, 5- Organofluorides Nucleosides Fluorine-containing natural products ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptomyces Cattleya
{{Streptomyces-stub ...
''Streptomyces cattleya'' is a Gram-positive bacterium which makes cephamycin, penicillin and thienamycin. The bacterium expresses a fluorinase enzyme, and the organism has been used to understand the biosynthesis of fluoroacetate and the antibacterial 4-fluoro-L-threonine. The γ-Glu-βes pathway to biosynthesis of non-traditional amino acids β-ethynylserine (βes) and L-propargylglycine (Pra) was first characterized in this species. The genome, which was sequenced in 2011, contains one chromosome with 6,283,062 base pairs and one megaplasmid with 1,809,491 bp, with an overall guanine-cytosine content of 73%. References cattleya ''Cattleya'' () is a genus of orchids from Costa Rica south to Argentina. The genus is abbreviated C in trade journals. Description Epiphytic or terrestrial orchids with cylindrical rhizome from which the fleshy noodle-like roots grow. Pseu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalysis
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quickly, very small amounts of catalyst often suffice; mixing, surface area, and temperature are important factors in reaction rate. Catalysts generally react with one or more reactants to form intermediates that subsequently give the final reaction product, in the process of regenerating the catalyst. Catalysis may be classified as either homogeneous, whose components are dispersed in the same phase (usually gaseous or liquid) as the reactant, or heterogeneous, whose components are not in the same phase. Enzymes and other biocatalysts are often considered as a third category. Catalysis is ubiquitous in chemical industry of all kinds. Estimates are that 90% of all commercially produced chemical products involve catalysts at some s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
L-amino-acid Oxidase
In enzymology, an L-amino acid oxidase (LAAO) () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :an L-amino acid + H2O + O2 \rightleftharpoons a 2-oxo acid + NH3 + H2O2 The enzyme was first described in 1944 by A. Zeller and A. Maritz. Not only are LAAOs quite variable in terms of molecular mass, they also vary widely regarding stability. In a similar vein, this enzyme performs in a myriad of biological activities including apoptosis-induction, edema-induction, hemorrhaging, and inhibition or induction of platelet aggregation. As suggested by the name of the family, LAAOs are flavoenzymes which function to catalyze the stereospecific oxidative deamination of an L-amino acid. The three substrates of the enzymatic reaction are an L-amino acid, water, and oxygen, whereas the three products are the corresponding α-keto acid (2-oxo acid), ammonia, and hydrogen peroxide. One example of the enzyme in action occurs with the conversion L-alanine into pyruvic acid (2-oxopropanoic aci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon–fluorine Bond
The carbon–fluorine bond is a polar covalent bond between carbon and fluorine that is a component of all organofluorine compounds. It is one of the strongest single bonds in chemistry (after the B–F single bond, Si–F single bond, and H–F single bond), and relatively short, due to its partial ionic character. The bond also strengthens and shortens as more fluorines are added to the same carbon on a chemical compound. As such, fluoroalkanes like tetrafluoromethane (carbon tetrafluoride) are some of the most unreactive organic compounds. Electronegativity and bond strength The high electronegativity of fluorine (4.0 for fluorine vs. 2.5 for carbon) gives the carbon–fluorine bond a significant polarity or dipole moment. The electron density is concentrated around the fluorine, leaving the carbon relatively electron poor. This introduces ionic character to the bond through partial charges (Cδ+—Fδ−). The partial charges on the fluorine and carbon are attractiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Data Bank
The Protein Data Bank (PDB) is a database for the three-dimensional structural data of large biological molecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids. The data, typically obtained by X-ray crystallography, NMR spectroscopy, or, increasingly, cryo-electron microscopy, and submitted by biologists and biochemists from around the world, are freely accessible on the Internet via the websites of its member organisations (PDBe, PDBj, RCSB, and BMRB). The PDB is overseen by an organization called the Worldwide Protein Data Bank, wwPDB. The PDB is a key in areas of structural biology, such as structural genomics. Most major scientific journals and some funding agencies now require scientists to submit their structure data to the PDB. Many other databases use protein structures deposited in the PDB. For example, SCOP and CATH classify protein structures, while PDBsum provides a graphic overview of PDB entries using information from other sources, such as Gene ontology. History Two force ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tertiary Structure
Protein tertiary structure is the three dimensional shape of a protein. The tertiary structure will have a single polypeptide chain "backbone" with one or more protein secondary structures, the protein domains. Amino acid side chains may interact and bond in a number of ways. The interactions and bonds of side chains within a particular protein determine its tertiary structure. The protein tertiary structure is defined by its atomic coordinates. These coordinates may refer either to a protein domain or to the entire tertiary structure.Branden C. and Tooze J. "Introduction to Protein Structure" Garland Publishing, New York. 1990 and 1991. A number of tertiary structures may fold into a quaternary structure.Kyte, J. "Structure in Protein Chemistry." Garland Publishing, New York. 1995. History The science of the tertiary structure of proteins has progressed from one of hypothesis to one of detailed definition. Although Emil Fischer had suggested proteins were made of polypept ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positron Emission Tomography
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radioactive substances known as radiotracers to visualize and measure changes in Metabolism, metabolic processes, and in other physiological activities including blood flow, regional chemical composition, and absorption. Different tracers are used for various imaging purposes, depending on the target process within the body. For example, 18F-FDG, -FDG is commonly used to detect cancer, Sodium fluoride#Medical imaging, NaF is widely used for detecting bone formation, and Isotopes of oxygen#Oxygen-15, oxygen-15 is sometimes used to measure blood flow. PET is a common medical imaging, imaging technique, a Scintigraphy#Process, medical scintillography technique used in nuclear medicine. A radiopharmaceutical, radiopharmaceutical — a radioisotope attached to a drug — is injected into the body as a radioactive tracer, tracer. When the radiopharmaceutical undergoes beta plus decay, a positron is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radioactive Tracer
A radioactive tracer, radiotracer, or radioactive label is a chemical compound in which one or more atoms have been replaced by a radionuclide so by virtue of its radioactive decay it can be used to explore the mechanism of chemical reactions by tracing the path that the radioisotope follows from reactants to products. Radiolabeling or radiotracing is thus the radioactive form of isotopic labeling. In biological contexts, use of radioisotope tracers are sometimes called radioisotope feeding experiments. Radioisotopes of hydrogen, carbon, phosphorus, sulfur, and iodine have been used extensively to trace the path of biochemical reactions. A radioactive tracer can also be used to track the distribution of a substance within a natural system such as a cell or tissue, or as a flow tracer to track fluid flow. Radioactive tracers are also used to determine the location of fractures created by hydraulic fracturing in natural gas production.Reis, John C. (1976). ''Environmental Cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transhalogenation
Transhalogenation is a substitution reaction in which the Halogen, halide of a halide compound is exchanged for another halide. Finkelstein reaction A common method is halide metathesis. An example is the conversion of Alkyl Chloride, alkyl chloride into alkyl fluoride: :C3H5-Cl + NaF → R-F + NaCl This kind of reaction is called Finkelstein reaction. However, it is also possible, for example, to produce phosphorus fluoride compounds by transhalogenating chlorine, bromine or iodine bound to phosphorus with a metal fluoride. Details and biological use As a halogen source for transhalogenation, metal halides (such as sodium fluoride or lithium fluoride) are often used, but also the use of Onium compound, onium halides is possible. Transhalogenation has been described as a gentle method for the synthesis of fluoroorganylboranes. It is also possible to produce aryliodides from the corresponding aryl chlorides or aryl bromides. One investigation showed a possibility to perform tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |