|
Fluorene
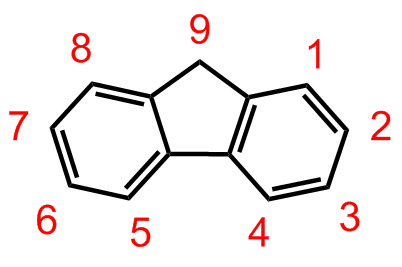
Fluorene , or 9''H''-fluorene is an organic compound with the formula (C6H4)2CH2. It forms white crystals that exhibit a characteristic, aromatic odor similar to that of naphthalene. It has a violet fluorescence, hence its name. For commercial purposes it is obtained from coal tar. It is insoluble in water and soluble in many organic solvents. Although sometimes classified as a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, the five-membered ring has no aromatic properties. Fluorene is mildly acidic. Synthesis, structure, and reactivity Although fluorene is obtained from coal tar, it can also be prepared by dehydrogenation of diphenylmethane. Alternatively, it can be prepared by the reduction of fluorenone with zinc or hypophosphorous acid–iodine. The fluorene molecule is nearly planar,D. M. Burns, John Iball (1954), ''Molecular Structure of Fluorene'' Nature volume 173, p. 635. although each of the two benzene rings is coplanar with the central carbon 9. Fluorene can be found after the i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyfluorene
Polyfluorene is a polymer with formula , consisting of fluorene units linked in a linear chain — specifically, at carbon atoms 2 and 7 in the standard fluorene numbering. It can also be described as a chain of benzene rings linked in ''para'' positions (a polyparaphenylene) with an extra methylene bridge connecting every pair of rings. The two benzene rings in each unit make polyfluorene an aromatic hydrocarbon, specifically conjugated polymer, and give it notable optical and electrical properties, such as efficient photoluminescence. When spoken about as a class, polyfluorenes are derivatives of this polymer, obtained by replacing some of the hydrogen atoms by other chemical groups, and/or by substituting other monomers for some fluorene units. These polymers are being investigated for possible use in light-emitting diodes, field-effect transistors, plastic solar cells, and other organic electronic applications. They stand out among other luminescent conjugated polymers b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon
A polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) is a class of organic compounds that is composed of multiple aromatic rings. The simplest representative is naphthalene, having two aromatic rings and the three-ring compounds anthracene and phenanthrene. PAHs are uncharged, non-polar and planar. Many are colorless. Many of them are found in coal and in oil deposits, and are also produced by the combustion of organic matter—for example, in engines and incinerators or when biomass burns in forest fires. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons are discussed as possible starting materials for abiotic syntheses of materials required by the earliest forms of life. Nomenclature and structure The terms polyaromatic hydrocarbon or polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbon are also used for this concept. By definition, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons have multiple rings, precluding benzene from being considered a PAH. Some sources, such as the US EPA and CDC, consider naphthalene to be the simplest PAH. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peptide Synthesis
In organic chemistry, peptide synthesis is the production of peptides, compounds where multiple amino acids are linked via amide bonds, also known as peptide bonds. Peptides are chemically synthesized by the condensation reaction of the carboxyl group of one amino acid to the amino group of another. Protecting group strategies are usually necessary to prevent undesirable side reactions with the various amino acid side chains. Chemical peptide synthesis most commonly starts at the carboxyl end of the peptide (C-terminus), and proceeds toward the amino-terminus (N-terminus). Protein biosynthesis (long peptides) in living organisms occurs in the opposite direction. The chemical synthesis of peptides can be carried out using classical solution-phase techniques, although these have been replaced in most research and development settings by solid-phase methods (see below). Solution-phase synthesis retains its usefulness in large-scale production of peptides for industrial purposes how ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorenone
Fluorenone is an aromatic organic compound with the chemical formula C13H8O. It is bright fluorescent yellow in color and is a solid at room temperature. It can be synthesised from fluorene with the addition of glacial acetic acid and sodium hypochlorite solution, undergoing an oxidation reaction. Several substituted fluorenones are biologically active as antibiotic, anticancer, antiviral, or neuromodulatory compounds. Some substituted azafluorenones are biologically active, such as the naturally occurring antimicrobial compound onychine (1-methyl-4-azafluorenone). The compound 1,8-diazafluoren-9-one is used for fingerprint detection. Medicine uses Fluorenone has uses in medicinal chemistry, for example in the synthesis of Paranyline, IPS-339 0979-28-4 Fanthridone, & SKF 550 8776-87-3among others. A pair of patents was disclosed for an analog of amitriptyline that relies on fluorenone starting material 684-13-3Dr Kurt Stach, et al. DE1150976 (1963 to Roche Diagnostics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coal Tar
Coal tar is a thick dark liquid which is a by-product of the production of coke and coal gas from coal. It is a type of creosote. It has both medical and industrial uses. Medicinally it is a topical medication applied to skin to treat psoriasis and seborrheic dermatitis (dandruff). It may be used in combination with ultraviolet light therapy. Industrially it is a railroad tie preservative and used in the surfacing of roads. Coal tar was listed as a known human carcinogen in the first Report on Carcinogens from the U.S. Federal Government. Coal tar was discovered circa 1665 and used for medical purposes as early as the 1800s. Circa 1850, the discovery that it could be used as the main ingredient in synthetic dyes engendered an entire industry. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Coal tar is available as a generic medication and over the counter. Side effects include skin irritation, sun sensitivity, allergic reactions, and skin discoloration. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphenylmethane
Diphenylmethane is an organic compound with the formula (C6H5)2CH2 (often abbreviated ). The compound consists of methane wherein two hydrogen atoms are replaced by two phenyl groups. It is a white solid. Diphenylmethane is a common skeleton in organic chemistry. The diphenylmethyl group is also known as ''benzhydryl''. Synthesis It is prepared by the Friedel–Crafts alkylation of benzyl chloride with benzene in the presence of a Lewis acid such as aluminium chloride: :C6H5CH2Cl + C6H6 → (C6H5)2CH2 + HCl Reactivity of the C-H bond The methylene group in diphenylmethane is mildly acidic with a p''K''a of 32.2, and so can be deprotonated with sodium amide. :(C6H5)2CH2 + NH2− → (C6H5)2CH− + NH3 The resulting carbanion can be alkylated. For example, treatment with ''n''-bromobutane produces 1,1-diphenylpentane in 92% yield. :(C6H5)2CH− + CH3CH2CH2CH2Br → (C6H5)2CHCH2CH2CH2CH3 + Br− Alkylation of various benzhydryl compounds has been demonstrated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
9-Fluorenylmethyl Chloroformate
Fluorenylmethyloxycarbonyl chloride (Fmoc-Cl) is a chloroformate ester. It is used to introduce the fluorenylmethyloxycarbonyl protecting group as the Fmoc carbamate. Preparation This compound may be prepared by reacting 9-fluorenylmethanol with phosgene Phosgene is the organic chemical compound with the formula COCl2. It is a toxic, colorless gas; in low concentrations, its musty odor resembles that of freshly cut hay or grass. Phosgene is a valued and important industrial building block, espe ...: : References {{reflist Chloroformates Reagents for organic chemistry Reagents for biochemistry Biochemistry methods ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimethyl Sulfoxide
Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) is an organosulfur compound with the formula ( CH3)2. This colorless liquid is the sulfoxide most widely used commercially. It is an important polar aprotic solvent that dissolves both polar and nonpolar compounds and is miscible in a wide range of organic solvents as well as water. It has a relatively high boiling point. DMSO has the unusual property that many individuals perceive a garlic-like taste in the mouth after DMSO makes contact with their skin. In terms of chemical structure, the molecule has idealized Cs symmetry. It has a trigonal pyramidal molecular geometry consistent with other three-coordinate S(IV) compounds, with a nonbonded electron pair on the approximately tetrahedral sulfur atom. Synthesis and production Dimethyl sulfoxide was first synthesized in 1866 by the Russian scientist Alexander Zaytsev, who reported his findings in 1867. Dimethyl sulfoxide is produced industrially from dimethyl sulfide, a by-product of the Kraf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
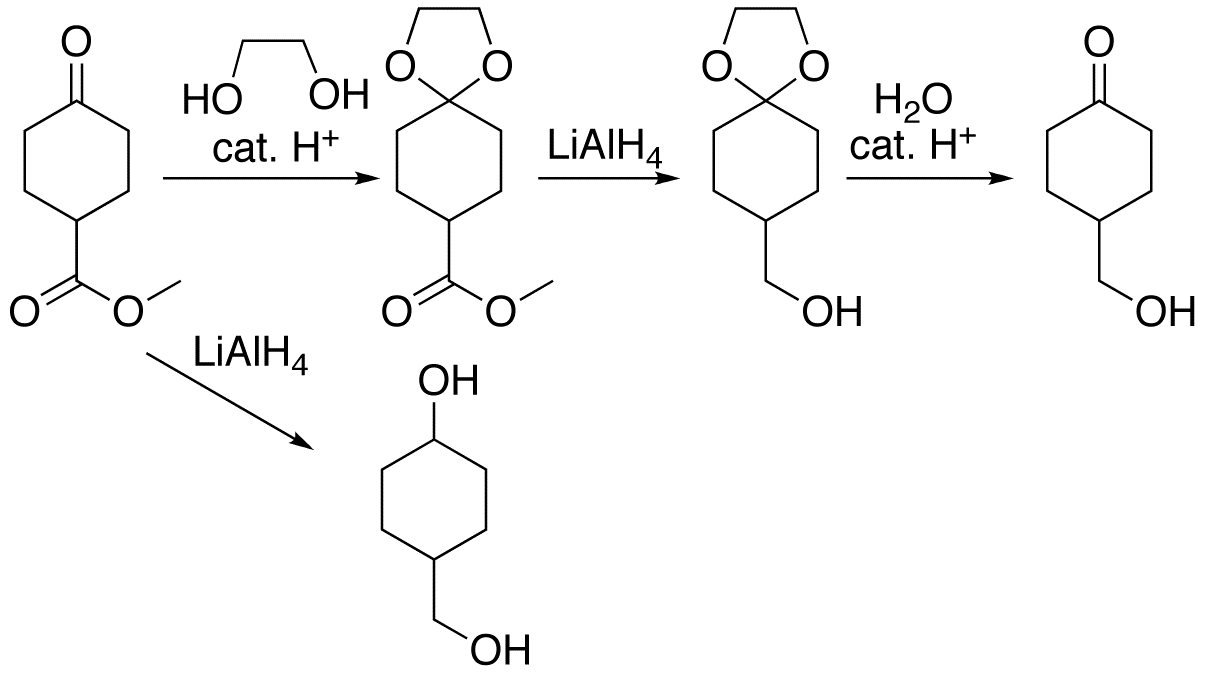
Protecting Group
A protecting group or protective group is introduced into a molecule by chemical modification of a functional group to obtain chemoselectivity in a subsequent chemical reaction. It plays an important role in multistep organic synthesis. In many preparations of delicate organic compounds, some specific parts of their molecules cannot survive the required reagents or chemical environments. Then, these parts, or groups, must be protected. For example, lithium aluminium hydride is a highly reactive but useful reagent capable of reducing esters to alcohols. It will always react with carbonyl groups, and this cannot be discouraged by any means. When a reduction of an ester is required in the presence of a carbonyl, the attack of the hydride on the carbonyl has to be prevented. For example, the carbonyl is converted into an acetal, which does not react with hydrides. The acetal is then called a protecting group for the carbonyl. After the step involving the hydride is complete, the acet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclopentadienide
In chemistry, the cyclopentadienyl anion or cyclopentadienide is an aromatic species with a formula of and abbreviated as Cp−. It is formed from the deprotonation of the molecule cyclopentadiene. Properties The cyclopentadienyl anion is a planar, cyclic, regular-pentagonal ion; it has 6 π-electrons (4''n'' + 2, where ''n'' = 1), which fulfills Hückel's rule of aromaticity. The structure shown is a composite of five resonance contributors in which each carbon atom carries part of the negative charge. Salts of the cyclopentadienyl anion can be stable, e.g., sodium cyclopentadienide. It can also coordinate as a ligand to metal atoms, forming coordination compounds known as cyclopentadienyl complexes. Biscyclopentadienyl complexes are called metallocenes. Cyclopentadienyl, , and cyclopentadiene, , can substitute one or more hydrogens, forming derivatives having covalent bonds. (See Cyclopentadiene#Derivatives) Abbreviation The abbreviation Cp for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule (functional group) that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs, often through Lewis bases. The nature of metal–ligand bonding can range from covalent to ionic. Furthermore, the metal–ligand bond order can range from one to three. Ligands are viewed as Lewis bases, although rare cases are known to involve Lewis acidic "ligands". Metals and metalloids are bound to ligands in almost all circumstances, although gaseous "naked" metal ions can be generated in a high vacuum. Ligands in a complex dictate the reactivity of the central atom, including ligand substitution rates, the reactivity of the ligands themselves, and redox. Ligand selection requires critical consideration in many practical areas, including bioinorganic and medicinal chemistry, homogeneous catalysis, and environmental chemi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



4-3D-balls.png)