|
Fluctuation Electrodynamics , price fluctuation
{{disambiguation ...
Fluctuation may refer to: Physics and mathematics * Statistical fluctuations, in statistics, statistical mechanics, and thermodynamics ** Thermal fluctuations, statistical fluctuations in a thermodynamic variable * Quantum fluctuation, arising from the uncertainty principle ** Primordial fluctuations, density variations in the early universe ** Universal conductance fluctuations, a quantum physics phenomenon encountered in electrical transport experiments in mesoscopic species Finance and economics * Economic conjuncture, a critical combination of events in economics * Volatility (finance) In finance, volatility (usually denoted by ''σ'') is the degree of variation of a trading price series over time, usually measured by the standard deviation of logarithmic returns. Historic volatility measures a time series of past market price ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistical Fluctuations
Statistical fluctuations are fluctuations in quantities derived from many identical random processes. They are fundamental and unavoidable. It can be proved that the relative fluctuations reduce as the square root of the number of identical processes. Statistical fluctuations are responsible for many results of statistical mechanics and thermodynamics, including phenomena such as shot noise in electronics. Description When a number of random processes occur, it can be shown that the outcomes fluctuate (vary in time) and that the fluctuations are inversely proportional to the square root of the number of processes. Examples As an example that will be familiar to all, if a fair coin is tossed many times and the number of heads and tails counted, the ratio of heads to tails will be very close to 1 (about as many heads as tails); but after only a few throws, outcomes with a significant excess of heads over tails or vice versa are common; if an experiment with a few throws is repe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Fluctuations
In statistical mechanics, thermal fluctuations are random deviations of a system from its average state, that occur in a system at equilibrium.In statistical mechanics they are often simply referred to as fluctuations. All thermal fluctuations become larger and more frequent as the temperature increases, and likewise they decrease as temperature approaches absolute zero. Thermal fluctuations are a basic manifestation of the temperature of systems: A system at nonzero temperature does not stay in its equilibrium microscopic state, but instead randomly samples all possible states, with probabilities given by the Boltzmann distribution. Thermal fluctuations generally affect all the degrees of freedom of a system: There can be random vibrations (phonons), random rotations ( rotons), random electronic excitations, and so forth. Thermodynamic variables, such as pressure, temperature, or entropy, likewise undergo thermal fluctuations. For example, for a system that has an equilibriu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Fluctuation
In quantum physics, a quantum fluctuation (also known as a vacuum state fluctuation or vacuum fluctuation) is the temporary random change in the amount of energy in a point in space, as prescribed by Werner Heisenberg's uncertainty principle. They are minute random fluctuations in the values of the fields which represent elementary particles, such as electric and magnetic fields which represent the electromagnetic force carried by photons, W and Z fields which carry the weak force, and gluon fields which carry the strong force. Vacuum fluctuations appear as virtual particles, which are always created in particle-antiparticle pairs. Since they are created spontaneously without a source of energy, vacuum fluctuations and virtual particles are said to violate the conservation of energy. This is theoretically allowable because the particles annihilate each other within a time limit determined by the uncertainty principle so they are not directly observable. The uncertainty prin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primordial Fluctuations
Primordial fluctuations are density variations in the early universe which are considered the seeds of all structure in the universe. Currently, the most widely accepted explanation for their origin is in the context of cosmic inflation. According to the inflationary paradigm, the exponential growth of the scale factor during inflation caused quantum fluctuations of the inflation field to be stretched to macroscopic scales, and, upon leaving the horizon, to "freeze in". At the later stages of radiation- and matter-domination, these fluctuations re-entered the horizon, and thus set the initial conditions for structure formation. The statistical properties of the primordial fluctuations can be inferred from observations of anisotropies in the cosmic microwave background and from measurements of the distribution of matter, e.g., galaxy redshift surveys. Since the fluctuations are believed to arise from inflation, such measurements can also set constraints on parameters within inflation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Universal Conductance Fluctuations
Universal conductance fluctuations (UCF) in mesoscopic physics is a phenomenon encountered in electrical transport experiments in mesoscopic species. The measured electrical conductance will vary from sample to sample, mainly due to inhomogeneous scattering sites. Fluctuations originate from coherence effects for electronic wavefunctions and thus the phase-coherence length \textstyle l_\phi needs be larger than the momentum relaxation length \textstyle l_m. UCF is more profound when electrical transport is in weak localization regime. \textstyle l_\phi [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
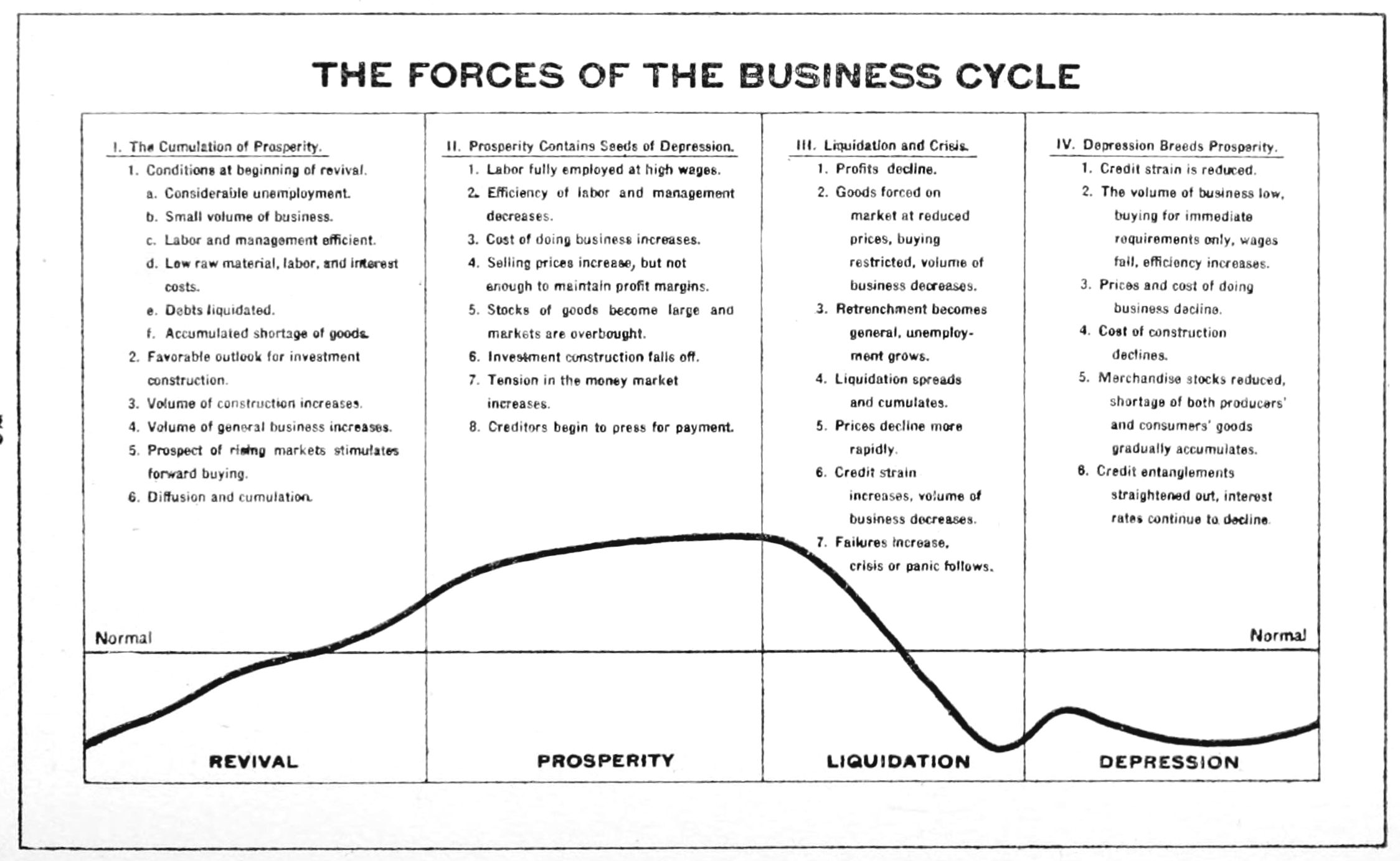
Economic Conjuncture
Business cycles are intervals of expansion followed by recession in economic activity. These changes have implications for the welfare of the broad population as well as for private institutions. Typically business cycles are measured by examining trends in a broad economic indicator such as Real Gross Domestic Production. Business cycle fluctuations are usually characterized by general upswings and downturns in a span of macroeconomic variables. The individual episodes of expansion/recession occur with changing duration and intensity over time. Typically their periodicity has a wide range from around 2 to 10 years (the technical phrase "stochastic cycle" is often used in statistics to describe this kind of process.) As in arvey, Trimbur, and van Dijk, 2007, ''Journal of Econometrics'' such flexible knowledge about the frequency of business cycles can actually be included in their mathematical study, using a Bayesian statistical paradigm. There are numerous sources of business ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |