|
Flip Clock
A flip clock (also known as a "flap clock") is an electromechanical, digital time keeping device with the time indicated by numbers that are sequentially revealed by a split-flap display. The study, collection and repair of flip clocks is termed horopalettology (from horology - the study and measurement of time and palette - and the Italian "orologio a palette" - Italian for "flip clock"). People interested in the collection, restoration, buying and selling of flip clocks are known as horopalettologists. Method of operation An electric motor (often synchronous, if directly connected to the AC line) turns two sets of wheels continuously via a reduction gear train: the faster at a rate of 1 revolution per hour, the slower at a rate of 1 revolution per 24 hours. The wheels move continuously, not in steps. The faster wheel has connected to it a ring of 60 flat plastic leaves. On the leaves are printed numerals so that, when a person holds two adjacent leaves apart like an open book ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copal Japan 1970s Alarm Flip Number Electric Clock
Copal is tree resin, particularly the aromatic resins from the copal tree ''Protium copal'' (Burseraceae) used by the cultures of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica as ceremonially burned incense and for other purposes. More generally, copal includes resinous substances in an intermediate stage of polymerization and hardening between "gummier" resins and amber. Copal that is partly mineralized is known as copaline. It is available in different forms; the hard, amber-like yellow copal is a less expensive version, while the milky white copal is more expensive. Etymology The word "copal" is derived from the Nahuatl language word , meaning "incense". History and uses Subfossil copal is well known from New Zealand (kauri gum from ''Agathis australis'' (Araucariaceae)), Japan, the Dominican Republic, Colombia, and Madagascar. It often has inclusions and is sometimes sold as "young amber". When it is treated or enhanced in an autoclave (as is sometimes done to industrialized Baltic amb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Split-flap Display
A split-flap display, or sometimes simply a flap display, is a digital electromechanical display device that presents changeable alphanumeric text, and occasionally fixed graphics. Often used as a public transport timetable in airports or railway stations, as such they are often called Solari boards after Italian display manufacturer Solari di Udine, or in Central European countries they are called Pragotron after the Czech manufacturer. Split-flap displays were once commonly used in consumer digital clocks known as flip clocks. Description Each character position or graphic position has a collection of flaps on which the characters or graphics are painted or silkscreened. These flaps are precisely rotated to show the desired character or graphic. These displays are often found in railway stations and airports, where they serve as flight information display system and typically display departure or arrival information. Sometimes the flaps are large and display whole word ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analog Clock With Digital Display
A flip clock (also known as a "flap clock") is an electromechanical, digital time keeping device with the time indicated by numbers that are sequentially revealed by a split-flap display. The study, collection and repair of flip clocks is termed horopalettology (from horology - the study and measurement of time and palette - and the Italian "orologio a palette" - Italian for "flip clock"). People interested in the collection, restoration, buying and selling of flip clocks are known as horopalettologists. Method of operation An electric motor (often synchronous, if directly connected to the AC line) turns two sets of wheels continuously via a reduction gear train: the faster at a rate of 1 revolution per hour, the slower at a rate of 1 revolution per 24 hours. The wheels move continuously, not in steps. The faster wheel has connected to it a ring of 60 flat plastic leaves. On the leaves are printed numerals so that, when a person holds two adjacent leaves apart like an open book ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Motor
An electric motor is an Electric machine, electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a Electromagnetic coil, wire winding to generate force in the form of torque applied on the motor's shaft. An electric generator is mechanically identical to an electric motor, but operates with a reversed flow of power, converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. Electric motors can be powered by direct current (DC) sources, such as from batteries, or rectifiers, or by alternating current (AC) sources, such as a power grid, Inverter (electrical), inverters or electrical generators. Electric motors may be classified by considerations such as power source type, construction, application and type of motion output. They can be powered by AC or DC, be Brushed motor, brushed or Brushless motor, brushless, single-phase, Two-phase electric power, two-p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synchronous Motor
A synchronous electric motor is an AC electric motor in which, at steady state, the rotation of the shaft is synchronized with the frequency of the supply current; the rotation period is exactly equal to an integral number of AC cycles. Synchronous motors contain multiphase AC electromagnets on the stator of the motor that create a magnetic field which rotates in time with the oscillations of the line current. The rotor with permanent magnets or electromagnets turns in step with the stator field at the same rate and as a result, provides the second synchronized rotating magnet field of any AC motor. A synchronous motor is termed ''doubly fed'' if it is supplied with independently excited multiphase AC electromagnets on both the rotor and stator. The synchronous motor and the induction motor are the most widely used types of AC motors. The difference between the two types is that the synchronous motor rotates at a rate locked to the line frequency since it does not rely on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Split-flap Display
A split-flap display, or sometimes simply a flap display, is a digital electromechanical display device that presents changeable alphanumeric text, and occasionally fixed graphics. Often used as a public transport timetable in airports or railway stations, as such they are often called Solari boards after Italian display manufacturer Solari di Udine, or in Central European countries they are called Pragotron after the Czech manufacturer. Split-flap displays were once commonly used in consumer digital clocks known as flip clocks. Description Each character position or graphic position has a collection of flaps on which the characters or graphics are painted or silkscreened. These flaps are precisely rotated to show the desired character or graphic. These displays are often found in railway stations and airports, where they serve as flight information display system and typically display departure or arrival information. Sometimes the flaps are large and display whole word ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
12-hour Clock
The 12-hour clock is a time convention in which the 24 hours of the day are divided into two periods: a.m. (from Latin , translating to "before midday") and p.m. (from Latin , translating to "after midday"). For different opinions on representation of midday and midnight, see #Confusion at noon and midnight Each period consists of 12 hours numbered: 12 (acting as 0), 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 and 11. The daily cycle starts at 12 midnight, runs through 12 noon, and continues until just before midnight at the end of the day. There is no widely accepted convention for how midday and midnight should be represented. The 12-hour clock was developed from the second millennium BC and reached its modern form in the 16th century AD. The 12-hour time convention is common in several English-speaking nations and former British colonies, as well as a few other countries. History and use The natural day-and-night division of a calendar day forms the fundamental basis as to why e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
24-hour Clock
The modern 24-hour clock, popularly referred to in the United States as military time, is the convention of timekeeping in which the day runs from midnight to midnight and is divided into 24 hours. This is indicated by the hours (and minutes) passed since midnight, from 0(:00) to 23(:59). This system, as opposed to the 12-hour clock, is the most commonly used time notation in the world today,See the Common Locale Data Repository for detailed data about the preferred date and time notations used across the world, as well the locale settings of major computer operating systems, and the article Date and time representation by country. and is used by the international standard ISO 8601.International Standard ISO 8601: Data elements and interchange formats – Information interchange – Representation of dates and times. International Organization for Standardization, 3rd ed., 2004. A number of countries, particularly English-speaking, use the 12-hour clock, or a mixture of the 24- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daylight Saving Time
Daylight saving time (DST), also referred to as daylight savings time or simply daylight time (United States, Canada, and Australia), and summer time (United Kingdom, European Union, and others), is the practice of advancing clocks (typically by one hour) during warmer months so that darkness falls at a later clock time. The typical implementation of DST is to set clocks forward by one hour in the spring ("spring forward"), and to set clocks back by one hour in the fall ("fall back") to return to standard time. As a result, there is one 23-hour day in early spring and one 25-hour day in the middle of autumn. The idea of aligning waking hours to daylight hours to conserve candles was first proposed in 1784 by U.S. polymath Benjamin Franklin. In a satirical letter to the editor of ''The Journal of Paris'', Franklin suggested that waking up earlier in the summer would economize on candle usage; and calculated considerable savings. In 1895, New Zealand entomologist and astronome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
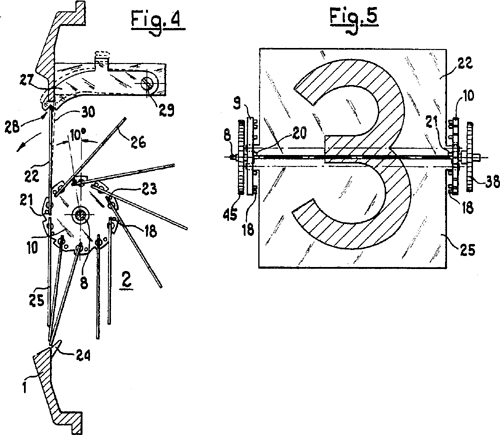
Cifra 3
The Cifra 3 is a digital flip clock manufactured by Solari di Udine, S.p.A., Italy designed by Italian architect Gino Valle (1923–2003) in 1965, with significant contribution from John Myer, a Belgian inventor. The Cifra 3 is widely considered a masterpiece of industrial design, using a split-flap display to display hours and minutes. The clock won the prestigious Compasso d'Oro prize for design and is on permanent display in the "Humble Masterpieces" exhibition at the Museum of Modern Art in New York and holds a place in the permanent collection of the Science Museum (London), Science Museum in London. Design idea Gino Valle's relationship with the Solari company began in 1954 with the design of the Cifra 5 electromechanical digit-snap clock (patented in 1957), consisting of 4 vertical pallets of 10 numbers each making up all the hours. The Cifra 5 clock was the progenitor of a full-fledged family of industrial-type clocks, awarded the Compasso d'Oro in 1956. With the help of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Sundial
A digital sundial is a clock that indicates the current time with numerals formed by the sunlight striking it. Like a classical sundial, the device contains no moving parts. It uses no electricity nor other manufactured sources of energy. The digital display changes as the sun advances in its daily course. Technique There are two basic types of digital sundials. One type uses optical waveguides, while the other is inspired by fractal geometry. Optical fiber sundial Sunlight enters into the device through a slit and moves as the sun advances. The sun's rays shine on ten linearly distributed sockets of optical waveguides that transport the light to a seven-segment display. Each socket fiber is connected to a few segments forming the digit corresponding to the position of the sun. Fractal sundial The theoretical basis for the other construction comes from fractal geometry. For the sake of simplicity, we describe a two-dimensional (planar) version. Let denote a straight line p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |