|
Flag Of Thailand
, RTGS: ''thong trai rong''), 'Tricolour flag' , Morenicks = , Use = 111110 , Symbol = , Proportion = 2:3 , Adoption = 28 September 1917 (standardized on 30 September 2017) , Design = Five horizontal stripes of red, white, blue, white and red, the middle stripe twice as wide as the others , Designer = King Vajiravudh (Rama VI) , Image2 = Naval Ensign of Thailand.svg , Nickname2 = th, ธงราชนาวี ( RTGS: ''thong ratcha nawi''), 'Royal Navy flag' , Morenicks2 = , Use2 = 000001 , Symbol2 = , Proportion2= 2:3 , Adoption2 = 28 September 1917 (''de jure'') , Design2 = A red disc containing a white elephant (Airavata) in regalia centered on the national flag , Designer2 = The flag of Thailand ( th, ธงไตรรงค์; , meaning 'tricolour flag') shows five horizontal stripes in the colours red, white, blue, white and red, with the central blue stripe being twice as wide as each of the other four. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Thai General System Of Transcription
The Royal Thai General System of Transcription (RTGS) is the official system for rendering Thai words in the Latin alphabet. It was published by the Royal Institute of Thailand. It is used in road signs and government publications and is the closest method to a standard of transcription for Thai, but its use, even by the government, is inconsistent. The system is almost identical to the one that is defined by ISO 11940-2. Features Prominent features of the system are: *It uses only unmodified letters from the Latin alphabet without diacritics. *It spells all vowels and diphthongs with vowel letters: , , , , . **Single letters , , , , are monophthongs (simple vowels), with the same value as in the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA). ** Digraphs with trailing are monophthongs; , , sound like respectively and are perhaps chosen for their similarity to IPA ligatures . **Digraphs and trigraphs with trailing , , are diphthongs and are indicated by IPA respectively. * It uses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
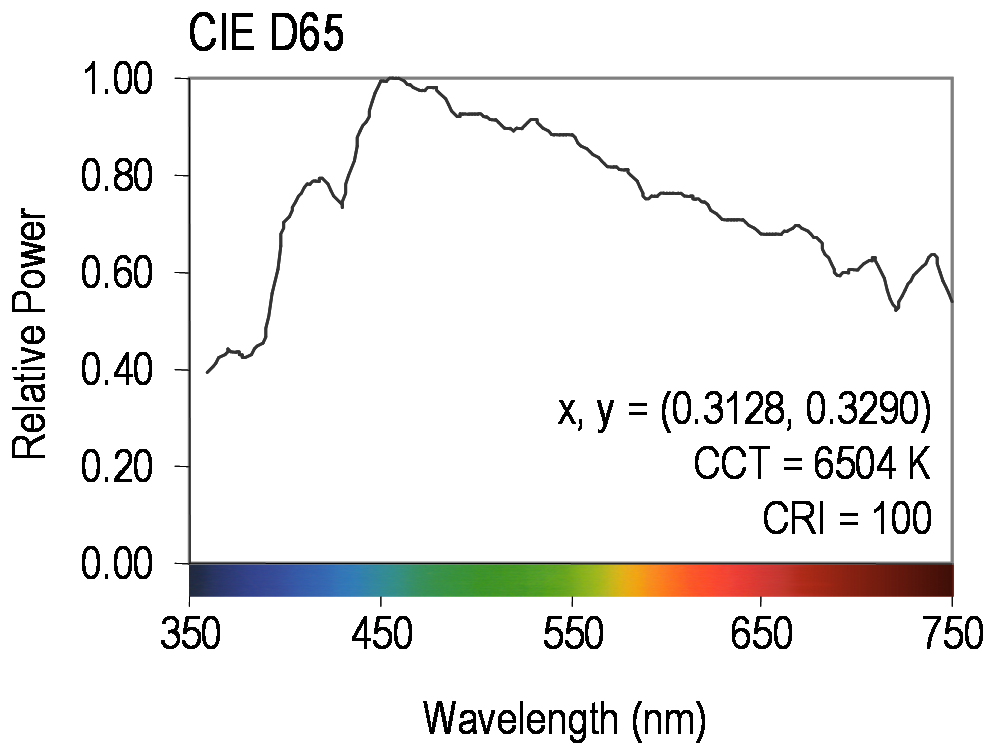
Illuminant D65
CIE standard illuminant D65 (sometimes written D65) is a commonly used standard illuminant defined by the International Commission on Illumination (CIE). It is part of the D series of illuminants that try to portray standard illumination conditions at open-air in different parts of the world. D65 corresponds roughly to the average midday light in Western Europe / Northern Europe (comprising both direct sunlight and the light diffused by a clear sky), hence it is also called a daylight illuminant. As any standard illuminant is represented as a table of averaged spectrophotometric data, any light source which statistically has the same relative spectral power distribution (SPD) can be considered a D65 light source. There are no actual D65 light sources, only simulators. The quality of a simulator can be assessed with the CIE metamerism index. The CIE positions D65 as the standard daylight illuminant: History The CIE introduced three standard illuminants in 1931: * A: Inca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Thonburi
The Thonburi Kingdom ( th, ธนบุรี) was a major Siamese kingdom which existed in Southeast Asia from 1767 to 1782, centered around the city of Thonburi, in Siam or present-day Thailand. The kingdom was founded by Taksin the Great, who reunited Siam following the collapse of the Ayutthaya Kingdom, which saw the country separate into five warring regional states. The Thonburi Kingdom oversaw the rapid reunification and reestablishment of Siam as a preeminient military power within mainland Southeast Asia, overseeing the country's expansion to its greatest territorial extent up to that point in its history, incorporating Lan Na, the Laotian kingdoms (Luang Prabang, Vientiane, Champasak), and Cambodia under the Siamese sphere of influence. The Thonburi Kingdom saw the consolidation and continued growth of Chinese trade from Qing China, a continuation from the late Ayutthaya period (1688-1767), and the increased influence of the Chinese community in Siam, with Taksin a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |