|
Filamin
Filamins are a class of proteins that hold two actin filaments at large angles. Filamin protein in mammals is made up of an actin-binding domain at its N-terminus that is followed by 24 immunoglobulin-like repeat modules of roughly 95 amino acids. There are two hinge regions; between repeats 15-16 and 23-24. Filamin gets cleaved at these hinge regions to generate smaller fragments of the protein. Filamin has two actin-binding sites with a V-linkage between them, so that it cross-links actin filaments into a network with the filaments orientated almost at right angles to one another. Filamin proteins include: * FLNA * FLNB * FLNC Over-expression of FLNA stops the regeneration of bladder carcinoma (BC) cells, by inhibiting the cell cycle and inducing apoptosis of BC cells. FLNA has also been shown to reduce the mobility Mobility may refer to: Social sciences and humanities * Economic mobility, ability of individuals or families to improve their economic status * Geographic mobi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FLNC (gene)
Filamin-C (FLN-C) also known as actin-binding-like protein (ABPL) or filamin-2 (FLN2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''FLNC'' gene. Filamin-C is mainly expressed in cardiac and skeletal muscles, and functions at Z-discs and in subsarcolemmal regions. Structure Filamin-C is a 290.8 kDa protein composed of 2725 amino acids. Filamin-C, like the ubiquitously-expressed isoform Filamin-A, have an N-terminal filamentous actin-binding domain, followed by a lengthy C-terminal self-association domain containing a series of immunoglobulin-like domains, and a membrane glycoprotein-binding domain. Filamin-C interacts with γ-sarcoglycan and δ-sarcoglycan at the sarcolemma; myotilin and FATZ/calsarcin/myozenin at Z-lines, as well as LL5β. Filamin-C has also been shown to interact with INPPL1, KCND2, and MAP2K4. Function The family of Filamin proteins crosslink actin filaments into orthogonal networks in cortical cytoplasm and participate in the anchoring of membrane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FLNA
Filamin A, alpha (FLNA) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''FLNA'' gene. Function Actin-binding protein, or filamin, is a 280-kD protein that crosslinks actin filaments into orthogonal networks in cortical cytoplasm and participates in the anchoring of membrane proteins for the actin cytoskeleton. Remodeling of the cytoskeleton is central to the modulation of cell shape and migration. Filamin A, encoded by the FLNA gene, is a widely expressed filamin that regulates the reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton by interacting with integrins, transmembrane receptor complexes, and secondary messengers. At least 31 disease-causing mutations in this gene have been discovered. Structure The protein structure includes an actin binding N terminal domain, 24 internal repeats and 2 hinge regions. Interactions Filamin has been shown to interact with: * BRCA2, * CD29 * CASR, * FBLIM1, * FILIP1, * FLNB, * NPHP1, * RALA, * SH2B3, * TRIO, and * VHL. RNA editi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FLNB
Filamin B, beta (FLNB), also known as Filamin B, beta (truncated actin binding protein 278 homolog), is a cytoplasmic protein which in humans is encoded by the ''FLNB'' gene. FLNB regulates intracellular communication and signalling by cross-linking the protein actin to allow direct communication between the cell membrane and cytoskeletal network, to control and guide proper skeletal development. Mutations in the FLNB gene are involved in several lethal bone dysplasias, including boomerang dysplasia and atelosteogenesis type I. Interactions FLNB has been shown to interact with GP1BA, Filamin, FBLIM1, PSEN1, CD29 and PSEN2. See also * Larsen syndrome Larsen syndrome (LS) is a congenital disorder discovered in 1950 by Larsen and associates when they observed dislocation of the large joints and face anomalies in six of their patients.Mitra, N., Kannan, N., Kumar, V.S., Kavita, G. "Larsen Syndrome ... References External links GeneReview/NIH/UW entry on FLNB-Related Disorders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actin Filament
Microfilaments, also called actin filaments, are protein filaments in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells that form part of the cytoskeleton. They are primarily composed of polymers of actin, but are modified by and interact with numerous other proteins in the cell. Microfilaments are usually about 7 nm in diameter and made up of two strands of actin. Microfilament functions include cytokinesis, amoeboid movement, cell motility, changes in cell shape, endocytosis and exocytosis, cell contractility, and mechanical stability. Microfilaments are flexible and relatively strong, resisting buckling by multi-piconewton compressive forces and filament fracture by nanonewton tensile forces. In inducing cell motility, one end of the actin filament elongates while the other end contracts, presumably by myosin II molecular motors. Additionally, they function as part of actomyosin-driven contractile molecular motors, wherein the thin filaments serve as tensile platforms for myosin's ATP-depend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-terminus
The N-terminus (also known as the amino-terminus, NH2-terminus, N-terminal end or amine-terminus) is the start of a protein or polypeptide, referring to the free amine group (-NH2) located at the end of a polypeptide. Within a peptide, the amine group is bonded to the carboxylic group of another amino acid, making it a chain. That leaves a free carboxylic group at one end of the peptide, called the C-terminus, and a free amine group on the other end called the N-terminus. By convention, peptide sequences are written N-terminus to C-terminus, left to right (in LTR writing systems). This correlates the translation direction to the text direction, because when a protein is translated from messenger RNA, it is created from the N-terminus to the C-terminus, as amino acids are added to the carboxyl end of the protein. Chemistry Each amino acid has an amine group and a carboxylic group. Amino acids link to one another by peptide bonds which form through a dehydration reaction that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acids
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha amino acids appear in the genetic code. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups, as Alpha and beta carbon, alpha- , beta- , gamma- or delta- amino acids; other categories relate to Chemical polarity, polarity, ionization, and side chain group type (aliphatic, Open-chain compound, acyclic, aromatic, containing hydroxyl or sulfur, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino acid '' residues'' form the second-largest component (water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis. It is thought that they played a key role in enabling lif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
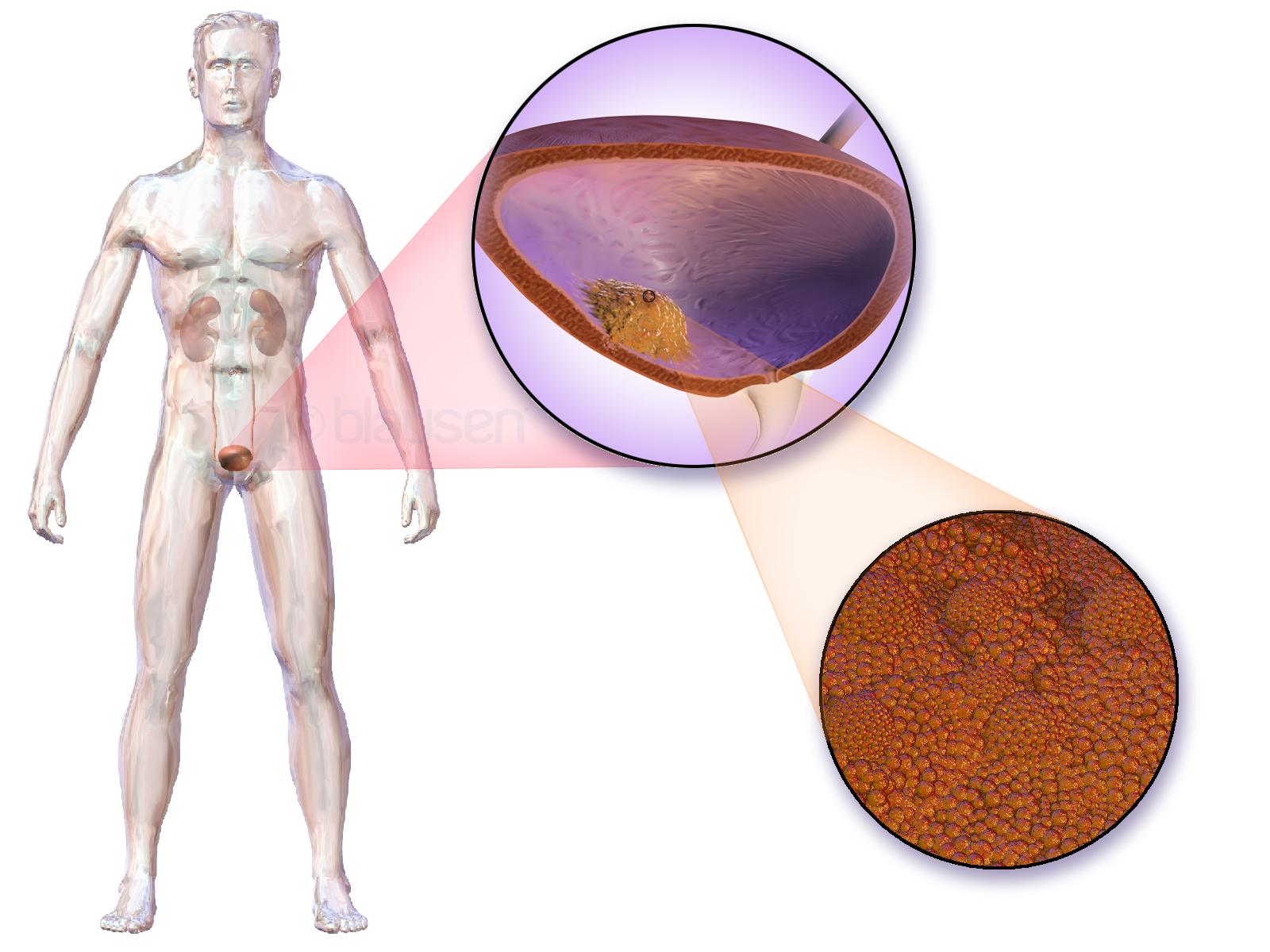
Bladder Carcinoma
Bladder cancer is any of several types of cancer arising from the tissues of the urinary bladder. Symptoms include blood in the urine, pain with urination, and low back pain. It is caused when epithelial cells that line the bladder become malignant. Risk factors for bladder cancer include smoking, family history, prior radiation therapy, frequent bladder infections, and exposure to certain chemicals. The most common type is transitional cell carcinoma. Other types include squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. Diagnosis is typically by cystoscopy with tissue biopsies. Staging of the cancer is determined by transurethral resection and medical imaging. Treatment depends on the stage of the cancer. It may include some combination of surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or immunotherapy. Surgical options may include transurethral resection, partial or complete removal of the bladder, or urinary diversion. The typical five-year survival rates in the United States is 7 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a cell that cause it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the duplication of its DNA (DNA replication) and some of its organelles, and subsequently the partitioning of its cytoplasm, chromosomes and other components into two daughter cells in a process called cell division. In cells with nuclei ( eukaryotes, i.e., animal, plant, fungal, and protist cells), the cell cycle is divided into two main stages: interphase and the mitotic (M) phase (including mitosis and cytokinesis). During interphase, the cell grows, accumulating nutrients needed for mitosis, and replicates its DNA and some of its organelles. During the mitotic phase, the replicated chromosomes, organelles, and cytoplasm separate into two new daughter cells. To ensure the proper replication of cellular components and division, there are control mechanisms known as cell cycle checkpoints after each of the key steps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (morphology) and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, DNA fragmentation, and mRNA decay. The average adult human loses between 50 and 70 billion cells each day due to apoptosis. For an average human child between eight and fourteen years old, approximately twenty to thirty billion cells die per day. In contrast to necrosis, which is a form of traumatic cell death that results from acute cellular injury, apoptosis is a highly regulated and controlled process that confers advantages during an organism's life cycle. For example, the separation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo occurs because cells between the digits undergo apoptosis. Unlike necrosis, apoptosis produces cell fragments called apoptotic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motility
Motility is the ability of an organism to move independently, using metabolic energy. Definitions Motility, the ability of an organism to move independently, using metabolic energy, can be contrasted with sessility, the state of organisms that do not possess a means of self-locomotion and are normally immobile. Motility differs from mobility, the ability of an object to be moved. The term vagility encompasses both motility and mobility; sessile organisms including plants and fungi often have vagile parts such as fruits, seeds, or spores which may be dispersed by other agents such as wind, water, or other organisms. Motility is genetically determined, but may be affected by environmental factors such as toxins. The nervous system and musculoskeletal system provide the majority of mammalian motility. In addition to animal locomotion, most animals are motile, though some are vagile, described as having passive locomotion. Many bacteria and other microorganisms, and multicellu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Proteins
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, and language. Humans are highly social and tend to live in complex social structures composed of many cooperating and competing groups, from families and kinship networks to political states. Social interactions between humans have established a wide variety of values, social norms, and rituals, which bolster human society. Its intelligence and its desire to understand and influence the environment and to explain and manipulate phenomena have motivated humanity's development of science, philosophy, mythology, religion, and other fields of study. Although some scientists equate the term ''humans'' with all members of the genus ''Homo'', in common usage, it generally refers to ''Homo sapiens'', the only extant member. Anatomically modern huma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |