|
Fibulin-2
Fibulin (FY-beau-lin) (now known as Fibulin-1 FBLN1) is the prototypic member of a multigene family, currently with seven members. Fibulin-1 is a calcium-binding glycoprotein. In vertebrates, fibulin-1 is found in blood and extracellular matrices. In the extracellular matrix, fibulin-1 associates with basement membranes and elastic fibers. The association with these matrix structures is mediated by its ability to interact with numerous extracellular matrix constituents including fibronectin, proteoglycans, laminins and tropoelastin. In blood, fibulin-1 binds to fibrinogen and incorporates into clots. Fibulins are secreted glycoproteins that become incorporated into a fibrillar extracellular matrix when expressed by cultured cells or added exogenously to cell monolayers. The five known members of the family share an elongated structure and many calcium-binding sites, owing to the presence of tandem arrays of epidermal growth factor-like domains. They have overlapping binding sites ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FBLN2
Fibulin-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''FBLN2'' gene. This gene encodes an extracellular matrix protein, which belongs to the fibulin family. This protein binds various extracellular ligands and calcium. It may play a role during organ development, in particular, during the differentiation of heart, skeletal and neuronal structures. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified. "FBLN2 fibulin 2 Homo sapiens (human) Its role as a biomarker for meningiomas (a common tumour affecting the central nervous system) was recently described where a blood test can predict whether patients have a grade II meningiomas (poor outcome) and not a grade I meningioma (better outcome), without the need for a surgical biopsy. Interactions FBLN2 has been shown to interact with Laminin, alpha 1, Laminin, alpha 5 and Perlecan Perlecan (PLC) also known as basement membrane-specific heparan sulfate proteoglycan core protein (HSPG) or hepa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FBLN1
FBLN1 is the gene encoding fibulin-1, an extracellular matrix and plasma protein. Function Fibulin-1 is a secreted glycoprotein that is found in association with extracellular matrix structures including fibronectin-containing fibers, elastin-containing fibers and basement membranes. Fibulin-1 binds to a number of extracellular matrix constituents including fibronectin, entactin, nidogen-1, and the proteoglycan, versican. Fibulin-1 is also a blood protein capable of binding to fibrinogen. Structure Fibulin-1 has modular domain structure and includes a series of nine epidermal growth factor-like modules followed by a fibulin-type module, a module found in all members of the fibulin gene family. The human fibulin-1 gene, FBLN1, encodes four alternative splicing, splice variants designated fibulin-1A, B, C and D, which differ in their C-terminus, carboxy terminal regions. In mouse, chicken and the nematode, ''Caenorhabditis elegans, C. elegans'', only two fibulin-1 variants are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropoelastin
Elastin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ELN'' gene. Elastin is a key component of the extracellular matrix in gnathostomes (jawed vertebrates). It is highly elastic and present in connective tissue allowing many tissues in the body to resume their shape after stretching or contracting. Elastin helps skin to return to its original position when it is poked or pinched. Elastin is also an important load-bearing tissue in the bodies of vertebrates and used in places where mechanical energy is required to be stored. Function The ''ELN'' gene encodes a protein that is one of the two components of elastic fibers. The encoded protein is rich in hydrophobic amino acids such as glycine and proline, which form mobile hydrophobic regions bounded by crosslinks between lysine residues. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. Elastin's soluble precursor is tropoelastin. The characterization of disorder is consistent with an en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMCN1
Hemicentin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''HMCN1'' gene In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b .... This gene encodes a large extracellular member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. A similar protein in C. elegans forms long, fine tracks at specific extracellular sites that are involved in many processes such as stabilization of the germline syncytium, anchorage of mechanosensory neurons to the epidermis, and organization of hemidesmosomes in the epidermis. Mutations in this gene may be associated with age-related macular degeneration. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-1-stub Extracellular matrix proteins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FBLN5
Fibulin-5 (also known as DANCE (developmental arteries and neural crest epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like)) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''FBLN5'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a secreted, extracellular matrix protein containing an Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) motif and calcium-binding EGF-like domains. It promotes adhesion of endothelial cells through interaction of integrins and the RGD motif. It is prominently expressed in developing arteries but less so in adult vessels. However, its expression is reinduced in balloon-injured vessels and atherosclerotic lesions, notably in intimal vascular smooth muscle cells and endothelial cells. Therefore, the protein encoded by this gene may play a role in vascular development and remodeling. Interactions FBLN5 has been shown to interact with LOXL1 and apolipoprotein(a). Clinical relevance FBLN5 mutations have been described in patients with age-related macular degeneration Macular degeneration, also k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FBLN4
EGF-containing fibulin-like extracellular matrix protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''EFEMP2'' gene. A large number of extracellular matrix proteins have been found to contain variations of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) domain and have been implicated in functions as diverse as blood coagulation, activation of complement and determination of cell fate during development. EFEMP2 (also known as fibulin-4) contains four EGF2 domains and six calcium-binding EGF2 domains. This gene is widely expressed in a range of adult and fetal tissues. Interactions EFEMP2 has been shown to interact with P53 p53, also known as Tumor protein P53, cellular tumor antigen p53 (UniProt name), or transformation-related protein 53 (TRP53) is a regulatory protein that is often mutated in human cancers. The p53 proteins (originally thought to be, and often s .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * External links GeneReview/NCBI/NIH/UW entry on EFEMP2-Relat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FBLN3
EGF-containing fibulin-like extracellular matrix protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''EFEMP1'' gene. Gene This gene encodes a member of the fibulin family of extracellular matrix glycoproteins. Like all members of this family, the encoded protein contains tandemly repeated epidermal growth factor-like repeats followed by a C-terminus fibulin-type domain. This gene is upregulated in malignant gliomas and may play a role in the aggressive nature of these tumors. Mutations in this gene are associated with Doyne honeycomb retinal dystrophy and with predisposition to hernias. Alternatively spliced transcript variants that encode the same protein have been described. rovided by RefSeq, Nov 2009 This gene spans approximately 18 kb of genomic DNA and consists of 12 exons. Alternative splice patterns in the 5' UTR result in three transcript variants encoding the same extracellular matrix protein. Clinical significance Mutations in this gene are associated with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaphylatoxin
Anaphylatoxins, or complement peptides, are fragments ( C3a, C4a and C5a) that are produced as part of the activation of the complement system. Complement components C3, C4 and C5 are large glycoproteins that have important functions in the immune response and host defense. They have a wide variety of biological activities and are proteolytically activated by cleavage at a specific site, forming a- and b-fragments. A-fragments form distinct structural domains of approximately 76 amino acids, coded for by a single exon within the complement protein gene. The C3a, C4a and C5a components are referred to as anaphylatoxins: they cause smooth muscle contraction, vasodilation, histamine release from mast cells, and enhanced vascular permeability. They also mediate chemotaxis, inflammation, and generation of cytotoxic oxygen radicals. The proteins are highly hydrophilic, with a mainly alpha-helical structure held together by 3 disulfide bridges. Function Anaphylatoxins are able to tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibrinogen
Fibrinogen (factor I) is a glycoprotein complex, produced in the liver, that circulates in the blood of all vertebrates. During tissue and vascular injury, it is converted enzymatically by thrombin to fibrin and then to a fibrin-based blood clot. Fibrin clots function primarily to occlude blood vessels to stop bleeding. Fibrin also binds and reduces the activity of thrombin. This activity, sometimes referred to as antithrombin I, limits clotting. Fibrin also mediates blood platelet and endothelial cell spreading, tissue fibroblast proliferation, capillary tube formation, and angiogenesis and thereby promotes revascularization and wound healing. Reduced and/or dysfunctional fibrinogens occur in various congenital and acquired human fibrinogen-related disorders. These disorders represent a group of rare conditions in which individuals may present with severe episodes of pathological bleeding and thrombosis; these conditions are treated by supplementing blood fibrinogen levels an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
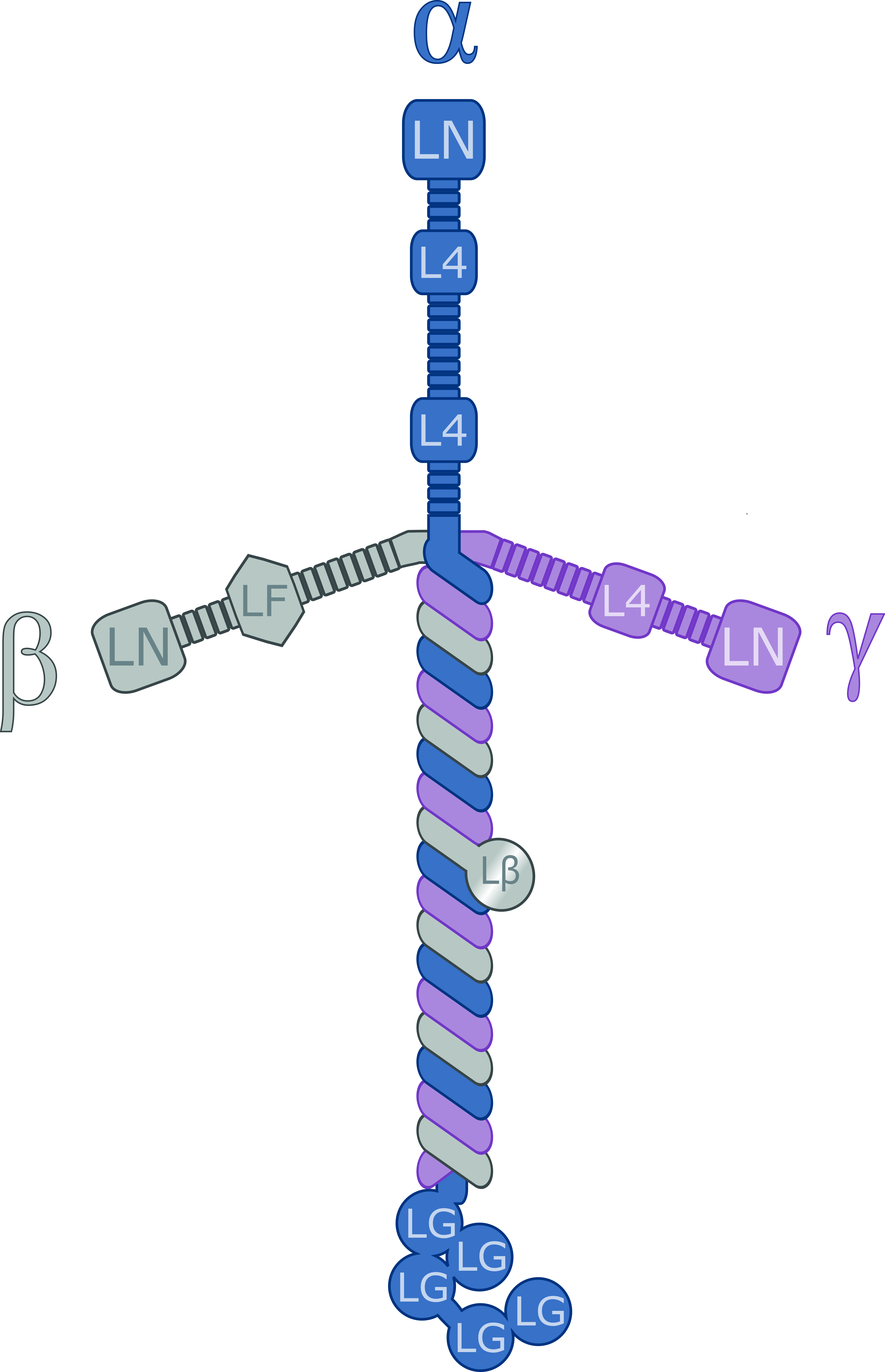
Laminin
Laminins are a family of glycoproteins of the extracellular matrix of all animals. They are major components of the basal lamina (one of the layers of the basement membrane), the protein network foundation for most cells and organs. The laminins are an important and biologically active part of the basal lamina, influencing cell differentiation, migration, and adhesion. Laminins are heterotrimeric proteins with a high molecular mass (~400 to ~900 kDa). They contain three different chains (α, β and γ) encoded by five, four, and three paralogous genes in humans, respectively. The laminin molecules are named according to their chain composition. Thus, laminin-511 contains α5, β1, and γ1 chains. Fourteen other chain combinations have been identified ''in vivo''. The trimeric proteins intersect to form a cross-like structure that can bind to other cell membrane and extracellular matrix molecules. The three shorter arms are particularly good at binding to other laminin molecules, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium-binding Glycoprotein
Calcium-binding proteins are proteins that participate in calcium signaling, calcium cell signalling pathways by binding to Ca2+, the calcium ion that plays an important role in many cellular processes. Calcium-binding proteins have specific domains that bind to calcium and are known to be heterogeneous. One of the functions of calcium binding proteins is to regulate the amount of free (unbound) Ca2+ in the cytosol of the cell. The cellular regulation of calcium is known as Calcium metabolism, calcium homeostasis. Types Many different calcium-binding proteins exist, with different cellular and tissue distribution and involvement in specific functions. Calcium binding proteins also serve an important physiological role for cells. The most ubiquitous Ca2+-sensing protein, found in all eukaryotic organisms including yeasts, is calmodulin. Intracellular storage and release of Ca2+ from the sarcoplasmic reticulum is associated with the high-capacity, low-affinity calcium-binding protein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |