|
Fibrocartilaginous
Fibrocartilage consists of a mixture of white fibrous tissue and cartilaginous tissue in various proportions. It owes its inflexibility and toughness to the former of these constituents, and its Elasticity (physics), elasticity to the latter. It is the only type of cartilage that contains type I collagen in addition to the normal Type II collagen, type II. Structure The extracellular matrix of fibrocartilage is mainly made from type I collagen secreted by Chondrocyte, chondroblasts. Locations of fibrocartilage in the human body * Symphysis, secondary cartilaginous joints: ** pubic symphysis ** annulus fibrosis of Intervertebral disc, intervertebral discs ** manubriosternal joint * glenoid labrum of shoulder joint * acetabular labrum of hip joint * medial and lateral Meniscus (anatomy), menisci of the knee joint * location where Tendon, tendons and Ligament, ligaments attach to bone * Ulnar Triangular Fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) Function Repair If hyaline cartilage is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
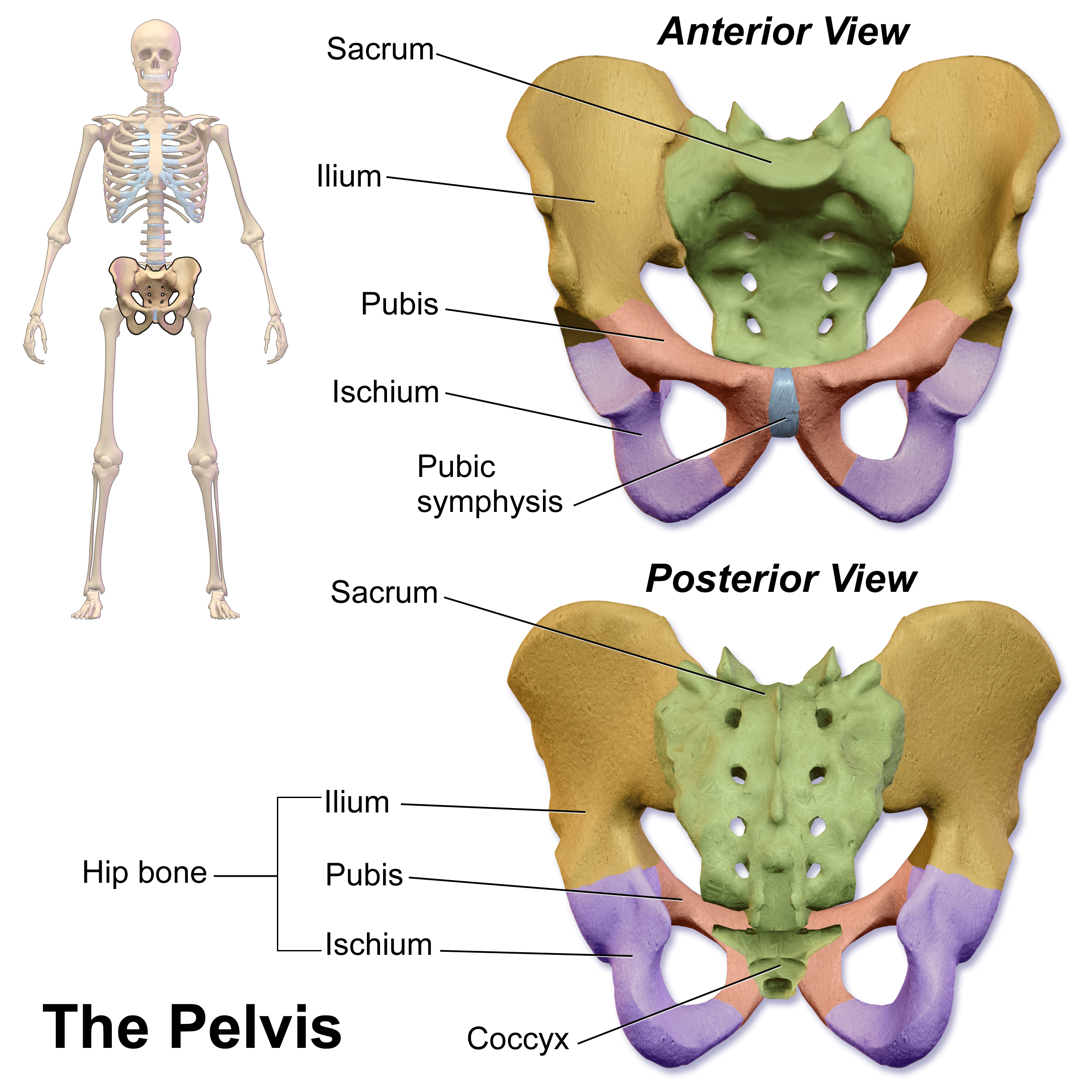
Pubic Symphysis
The pubic symphysis is a secondary cartilaginous joint between the left and right superior rami of the pubis of the hip bones. It is in front of and below the urinary bladder. In males, the suspensory ligament of the penis attaches to the pubic symphysis. In females, the pubic symphysis is close to the clitoris. In most adults it can be moved roughly 2 mm and with 1 degree rotation. This increases for women at the time of childbirth. The name comes from the Greek word ''symphysis'', meaning 'growing together'. Structure The pubic symphysis is a nonsynovial amphiarthrodial joint. The width of the pubic symphysis at the front is 3–5 mm greater than its width at the back. This joint is connected by fibrocartilage and may contain a fluid-filled cavity; the center is avascular, possibly due to the nature of the compressive forces passing through this joint, which may lead to harmful vascular disease. The ends of both pubic bones are covered by a thin layer of hyaline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meniscus (anatomy)
A meniscus is a crescent-shaped fibrocartilaginous anatomical structure that, in contrast to an articular disc, only partly divides a joint cavity.Platzer (2004), p 208 In humans they are present in the knee, wrist, acromioclavicular, sternoclavicular, and temporomandibular joints; in other animals they may be present in other joints. Generally, the term "meniscus" is used to refer to the cartilage of the knee, either to the lateral or medial meniscus. Both are cartilaginous tissues that provide structural integrity to the knee when it undergoes tension and torsion. The menisci are also known as "semi-lunar" cartilages, referring to their half-moon, crescent shape. The term "meniscus" is from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning "crescent". Structure The menisci of the knee are two pads of fibrocartilaginous tissue which serve to disperse friction in the knee joint between the lower leg (tibia) and the thigh (femur). They are concave on the top and flat on the bottom, articula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intervertebral Fibrocartilage
An intervertebral disc (or intervertebral fibrocartilage) lies between adjacent vertebrae in the vertebral column. Each disc forms a fibrocartilaginous joint (a symphysis), to allow slight movement of the vertebrae, to act as a ligament to hold the vertebrae together, and to function as a shock absorber for the spine. Structure Intervertebral discs consist of an outer fibrous ring, the anulus fibrosus disci intervertebralis, which surrounds an inner gel-like center, the nucleus pulposus. The ''anulus fibrosus'' consists of several layers (laminae) of fibrocartilage made up of both type I and type II collagen. Type I is concentrated toward the edge of the ring, where it provides greater strength. The stiff laminae can withstand compressive forces. The fibrous intervertebral disc contains the ''nucleus pulposus'' and this helps to distribute pressure evenly across the disc. This prevents the development of stress concentrations which could cause damage to the underlying vertebrae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symphysis
A symphysis (, pl. symphyses) is a fibrocartilaginous fusion between two bones. It is a type of cartilaginous joint, specifically a secondary cartilaginous joint. # A symphysis is an amphiarthrosis, a slightly movable joint. # A growing together of parts or structures. Unlike synchondroses, symphyses are permanent. Examples The more prominent symphyses are: * the pubic symphysis * sacrococcygeal symphysis * intervertebral disc between two vertebrae * in the sternum, between the manubrium and body Body may refer to: In science * Physical body, an object in physics that represents a large amount, has mass or takes up space * Body (biology), the physical material of an organism * Body plan, the physical features shared by a group of anima ... * mandibular symphysis, in the jaw Symphysis disorders Pubic symphysis diastasis Pubic symphysis diastasis, is an extremely rare complication that occurs in women who are giving birth. Separation of the two pubic bones during deli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glenoid Labrum
The glenoid labrum (glenoid ligament) is a fibrocartilaginous structure (not a fibrocartilage as previously thought) rim attached around the margin of the glenoid cavity in the shoulder blade. The shoulder joint is considered a ball and socket joint. However, in bony terms the 'socket' (the glenoid fossa of the scapula) is quite shallow and small, covering at most only a third of the 'ball' (the head of the humerus). The socket is deepened by the glenoid labrum, stabilizing the shoulder joint. The labrum is triangular in section; the base is fixed to the circumference of the cavity, while the free edge is thin and sharp. It is continuous above with the tendon of the long head of the biceps brachii, which gives off two fascicles to blend with the fibrous tissue of the labrum. Structure Clinical significance Injury Tearing of the labrum can occur from either acute trauma or repetitive shoulder motion such as in the sports of swimming, baseball and football. Acute trauma m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intervertebral Disc
An intervertebral disc (or intervertebral fibrocartilage) lies between adjacent vertebrae in the vertebral column. Each disc forms a fibrocartilaginous joint (a symphysis), to allow slight movement of the vertebrae, to act as a ligament to hold the vertebrae together, and to function as a shock absorber for the spine. Structure Intervertebral discs consist of an outer fibrous ring, the anulus fibrosus disci intervertebralis, which surrounds an inner gel-like center, the nucleus pulposus. The ''anulus fibrosus'' consists of several layers (laminae) of fibrocartilage made up of both type I and type II collagen. Type I is concentrated toward the edge of the ring, where it provides greater strength. The stiff laminae can withstand compressive forces. The fibrous intervertebral disc contains the ''nucleus pulposus'' and this helps to distribute pressure evenly across the disc. This prevents the development of stress concentrations which could cause damage to the underlying vertebrae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extracellular Matrix
In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM), also called intercellular matrix, is a three-dimensional network consisting of extracellular macromolecules and minerals, such as collagen, enzymes, glycoproteins and hydroxyapatite that provide structural and biochemical support to surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM. The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the Interstitial fluid, interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chondrocyte
Chondrocytes (, from Greek χόνδρος, ''chondros'' = cartilage + κύτος, ''kytos'' = cell) are the only cells found in healthy cartilage. They produce and maintain the cartilaginous matrix, which consists mainly of collagen and proteoglycans. Although the word ''chondroblast'' is commonly used to describe an immature chondrocyte, the term is imprecise, since the progenitor of chondrocytes (which are mesenchymal stem cells) can differentiate into various cell types, including osteoblasts. Development From least- to terminally-differentiated, the chondrocytic lineage is: # Colony-forming unit-fibroblast # Mesenchymal stem cell / marrow stromal cell # Chondrocyte # Hypertrophic chondrocyte Mesenchymal (mesoderm origin) stem cells are undifferentiated, meaning they can differentiate into a variety of generative cells commonly known as osteochondrogenic (or osteogenic, chondrogenic, osteoprogenitor, etc.) cells. When referring to bone, or in this case cartilage, the origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type II Collagen
Type II collagen is the basis for hyaline cartilage, including the articular cartilages at joint surfaces. It is formed by homotrimers of collagen, type II, alpha 1 chains. It makes up 50% of all protein in cartilage and 85–90% of collagen of articular cartilage. Type II collagen is organised into fibrils. This fibrillar network of collagen allows the cartilage to entrap the proteoglycan aggregate, as well as providing tensile strength to the tissue. Oral administration of native type II collagen induces oral tolerance to pathological immune responses and may be useful in arthritis. See also * Type I collagen * Collagen, type III, alpha 1 Type III Collagen is a homotrimer, or a protein composed of three identical peptide chains (monomers), each called an alpha 1 chain of type III collagen. Formally, the monomers are called collagen type III, alpha-1 chain and in humans are encoded ... References External links * Collagens {{gene-12-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type I Collagen
Type I collagen is the most abundant collagen of the human body. It forms large, eosinophilic fibers known as collagen fibers. It is present in scar tissue, the end product when tissue heals by repair, as well as tendons, ligaments, the endomysium of myofibrils, the organic part of bone, the dermis, the dentin, and organ capsules. Formation The gene produces the pro-alpha1(I) chain. This chain combines with another pro-alpha1(I) chain and also with a pro-alpha2(I) chain (produced by the gene) to make a molecule of type I pro-collagen. These triple-stranded, rope-like pro-collagen molecules must be processed by enzymes outside the cell. Once these molecules are processed, they arrange themselves into long, thin fibrils that cross-link to one another in the spaces around cells. The cross-links result in the formation of very strong mature type I collagen fiber. Clinical significance See Collagen, type I, alpha 1#Clinical significance Markers used to measure bone loss are not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronal Section
The coronal plane (also known as the frontal plane) is an anatomical plane that divides the body into Anatomical terms of location#Dorsal and ventral, dorsal and ventral sections. It is perpendicular to the sagittal plane, sagittal and transverse plane, transverse planes. Details The coronal plane is an example of a Anatomical terms of location#General usage, longitudinal plane. For a human, the mid-coronal plane would transect a standing body into two halves (front and back, or anterior and posterior) in an imaginary line that cuts through both shoulders. The description of the coronal plane applies to most animals as well as humans even though humans walk upright and the various planes are usually shown in the vertical orientation. The sternal plane (''planum sternale'') is a coronal plane which transects the front of the Human sternum, sternum. Etymology The term is derived from Latin ''corona'' ('garland, crown'), from Ancient Greek κορώνη (''korōnē'', 'garland, wrea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartilage
Cartilage is a resilient and smooth type of connective tissue. In tetrapods, it covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints as articular cartilage, and is a structural component of many body parts including the rib cage, the neck and the bronchial tubes, and the intervertebral discs. In other taxa, such as chondrichthyans, but also in cyclostomes, it may constitute a much greater proportion of the skeleton. It is not as hard and rigid as bone, but it is much stiffer and much less flexible than muscle. The matrix of cartilage is made up of glycosaminoglycans, proteoglycans, collagen fibers and, sometimes, elastin. Because of its rigidity, cartilage often serves the purpose of holding tubes open in the body. Examples include the rings of the trachea, such as the cricoid cartilage and carina. Cartilage is composed of specialized cells called chondrocytes that produce a large amount of collagenous extracellular matrix, abundant ground substance that is rich in pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |