|
Fdformat
Fdformat is the name of two unrelated programs: * A command-line tool for Linux that " low-level formats" a floppy disk. * A DOS tool written in Pascal by Christoph H. Hochstätter that allows users to format floppy disks to a higher than usual density, enabling the user to store up to 300 kilobytes more data on a normal high density 3.5" floppy disk. It also increases the speed of diskette I/O on these specially formatted disks using a technique called "Sector Sliding". In this technique, the physical sectors on the disk are ordered in such a way that when the drive advances to the next track, the next logical sector waiting to be read is immediately available to the read head. See also * 2M, a similar program that offers even higher capacity * DMF, a high-density diskette format used by Microsoft * VGA-Copy VGA-Copy is an MS-DOS program to copy floppy disks. It is able to read defective floppy disks. Development VGA-Copy was created by the German software develope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distribution Media Format
Distribution Media Format (DMF) is a format for floppy disks that Microsoft used to distribute software. It allowed the disk to contain 1680 KB of data on a 3-inch disk, instead of the standard 1440 KB. As a side effect, utilities had to specially support the format in order to read and write the disks, which made copying of products distributed on this medium more difficult. An Apple Macintosh computer running Disk Copy 6.3.3 on the Mac OS 7.6 or later operating system can copy and make DMF disks. The first Microsoft software product that uses DMF for distribution were the "c" revisions of Office 4.x. It also was the first software product to use CAB files, then called "Diamond". Comparison of DMF and standard 1440 KB 3-inch diskettes: DMF in the form of a 1680 KB Virtual Floppy Disk (VFD) image and IBM Extended Density Format (XDF) images are supported by Windows Virtual PC. See also * 2M, a program that allows the formatting of high-capacity fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2M (DOS)
2M is a DOS program by the Spanish programmer Ciriaco García de Celis. It enables higher than normal capacity formatting of floppy disks. It saw active development from 1993 to 1995. The last version, v3.0, was released on 6 March 1995. It was written in C and assembler and compiled using Borland C++ 3.1. The program consisted of two major components: 2M and 2MGUI (from "2M Guinness"). Of these, 2M was the main program enabling the formatting, reading and writing of high density 3.5" disks formatted to a capacity of either 1804 KiB or 1886 KB, and 2MGUI was a proof-of-concept program that demonstrated the ability to format any normal high density 3.5" disk to a capacity of over two million bytes (1972 KiB) on any disk drive. Both programs implemented disk I/O speedups in the form of "Sector Sliding" and "DiskBoost", which work on the principle of ordering the physical sectors on the disk to facilitate pauseless reading over track changes. 2MGUI utilized bit banging and tricked t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM Extended Density Format
The IBM eXtended Density Format (XDF) is a way of superformatting standard high-density 3½-inch and 5¼-inch floppy disks to larger-than-standard capacities. It is supported natively by IBM's PC DOS versions 7 and 2000 and by OS/2 Warp 3 onward, using the XDF and XDFCOPY commands (directly in OS/2). When formatted as XDF disks, 3½-inch floppies can hold 1860 kB, and 5¼-inch floppies can hold 1540 kB, using different number of sectors as well as different sector size per track (not all sectors in the same track are of the same size). However, the first cylinder uses standard formatting, providing a small FAT12 section that can be accessed without XDF support and on which can be put a ReadMe file or the XDF drivers. Floppy distributions of OS/2 3.0, PC DOS 7 and onward used XDF formatting for most of the media set. Floppy disks formatted using XDF can only be read in floppy disk drives that are attached directly to the system by way of a FDC. Thus, USB attache ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linux
Linux ( or ) is a family of open-source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged as a Linux distribution, which includes the kernel and supporting system software and libraries, many of which are provided by the GNU Project. Many Linux distributions use the word "Linux" in their name, but the Free Software Foundation uses the name "GNU/Linux" to emphasize the importance of GNU software, causing some controversy. Popular Linux distributions include Debian, Fedora Linux, and Ubuntu, the latter of which itself consists of many different distributions and modifications, including Lubuntu and Xubuntu. Commercial distributions include Red Hat Enterprise Linux and SUSE Linux Enterprise. Desktop Linux distributions include a windowing system such as X11 or Wayland, and a desktop environment such as GNOME or KDE Plasma. Distributions inten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disk Formatting
Disk formatting is the process of preparing a data storage device such as a hard disk drive, solid-state drive, floppy disk, memory card or USB flash drive for initial use. In some cases, the formatting operation may also create one or more new file systems. The first part of the formatting process that performs basic medium preparation is often referred to as "low-level formatting". Partitioning is the common term for the second part of the process, dividing the device into several sub-devices and, in some cases, writing information to the device allowing an operating system to be booted from it. The third part of the process, usually termed "high-level formatting" most often refers to the process of generating a new file system. In some operating systems all or parts of these three processes can be combined or repeated at different levels and the term "format" is understood to mean an operation in which a new disk medium is fully prepared to store files. Some formatting ut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pascal (programming Language)
Pascal is an imperative and procedural programming language, designed by Niklaus Wirth as a small, efficient language intended to encourage good programming practices using structured programming and data structuring. It is named in honour of the French mathematician, philosopher and physicist Blaise Pascal. Pascal was developed on the pattern of the ALGOL 60 language. Wirth was involved in the process to improve the language as part of the ALGOL X efforts and proposed a version named ALGOL W. This was not accepted, and the ALGOL X process bogged down. In 1968, Wirth decided to abandon the ALGOL X process and further improve ALGOL W, releasing this as Pascal in 1970. On top of ALGOL's scalars and arrays, Pascal enables defining complex datatypes and building dynamic and recursive data structures such as lists, trees and graphs. Pascal has strong typing on all objects, which means that one type of data cannot be converted to or interpreted as another without explicit conv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
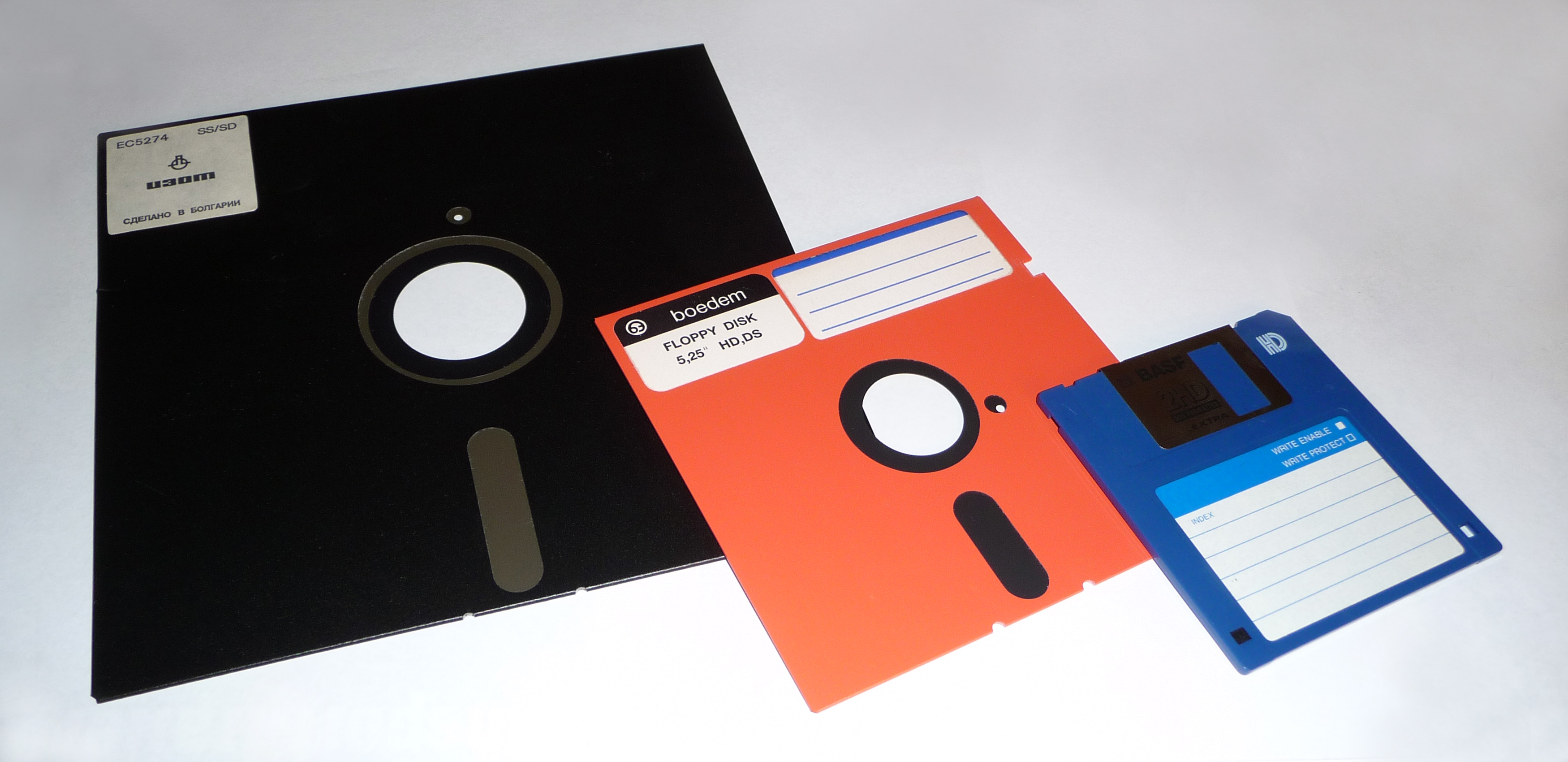
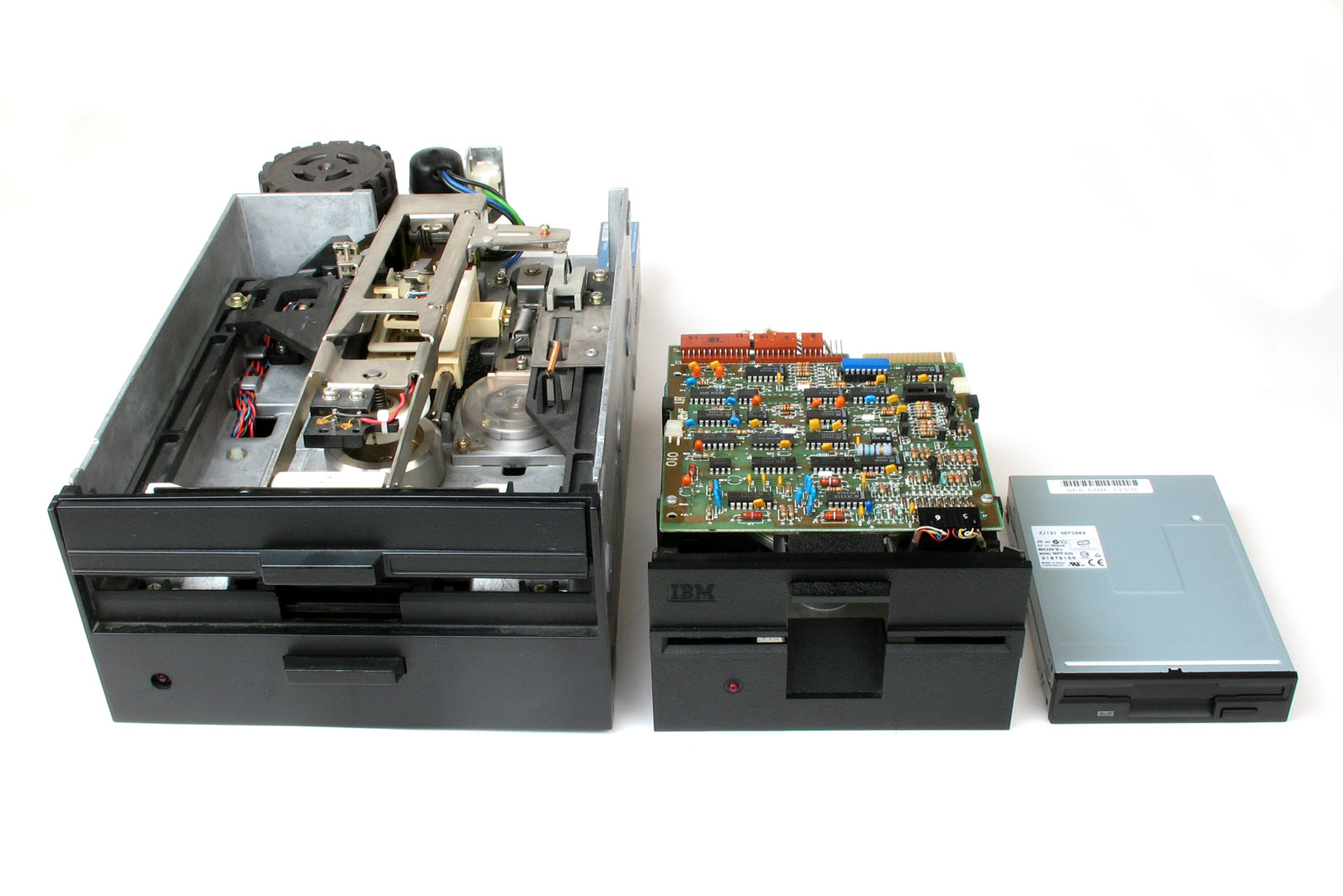
Floppy Disk
A floppy disk or floppy diskette (casually referred to as a floppy, or a diskette) is an obsolescent type of disk storage composed of a thin and flexible disk of a magnetic storage medium in a square or nearly square plastic enclosure lined with a fabric that removes dust particles from the spinning disk. Floppy disks store digital data which can be read and written when the disk is inserted into a floppy disk drive (FDD) connected to or inside a computer or other device. The first floppy disks, invented and made by IBM, had a disk diameter of . Subsequently, the 5¼-inch and then the 3½-inch became a ubiquitous form of data storage and transfer into the first years of the 21st century. 3½-inch floppy disks can still be used with an external USB floppy disk drive. USB drives for 5¼-inch, 8-inch, and other-size floppy disks are rare to non-existent. Some individuals and organizations continue to use older equipment to read or transfer data from floppy disks. Floppy disk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kilobyte
The kilobyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. The International System of Units (SI) defines the prefix '' kilo'' as 1000 (103); per this definition, one kilobyte is 1000 bytes.International Standard IEC 80000-13 Quantities and Units – Part 13: Information science and technology, International Electrotechnical Commission (2008). The internationally recommended unit symbol for the kilobyte is kB. In some areas of information technology, particularly in reference to solid-state memory capacity, ''kilobyte'' instead typically refers to 1024 (210) bytes. This arises from the prevalence of sizes that are powers of two in modern digital memory architectures, coupled with the accident that 210 differs from 103 by less than 2.5%. A kibibyte is defined by Clause 4 of IEC 80000-13 as 1024 bytes. Definitions and usage Base 10 (1000 bytes) In the International System of Units (SI) the prefix '' kilo'' means 1000 (103); therefore, one kilobyte is 1000 bytes. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VGA-Copy
VGA-Copy is an MS-DOS program to copy floppy disks. It is able to read defective floppy disks. Development VGA-Copy was created by the German software developer Thomas Mönkemeier. The main code was developed in Turbo Pascal; some low-level hardware parts were written in Turbo Assembler. VGA-Copy was originally released as shareware: A free test version was spread through bulletin board systems and shareware CDs; a license key file to turn the test version into a full version could be ordered for a payment. The shareware version had two limitations: it had a ten-second waiting time on startup and it was not able to write to individual boot sectors. Later the limitations changed to requiring to enter a 5-digit number on startup. The first public version of VGA-Copy was 2.0. Some earlier full versions were published by cdv Software Entertainment. Later versions were published under the names VGA-Copy Pro and VGA-Copy/386. VGA-Copy Pro 5.3 was the last version to work on an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floppy Disk Computer Storage
A floppy disk or floppy diskette (casually referred to as a floppy, or a diskette) is an obsolescent type of disk storage composed of a thin and flexible disk of a magnetic storage medium in a square or nearly square plastic enclosure lined with a fabric that removes dust particles from the spinning disk. Floppy disks store digital data which can be read and written when the disk is inserted into a floppy disk drive (FDD) connected to or inside a computer or other device. The first floppy disks, invented and made by IBM, had a disk diameter of . Subsequently, the 5¼-inch and then the 3½-inch became a ubiquitous form of data storage and transfer into the first years of the 21st century. 3½-inch floppy disks can still be used with an external USB floppy disk drive. USB drives for 5¼-inch, 8-inch, and other-size floppy disks are rare to non-existent. Some individuals and organizations continue to use older equipment to read or transfer data from floppy disks. Floppy disk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)