|
Falling (sensation)
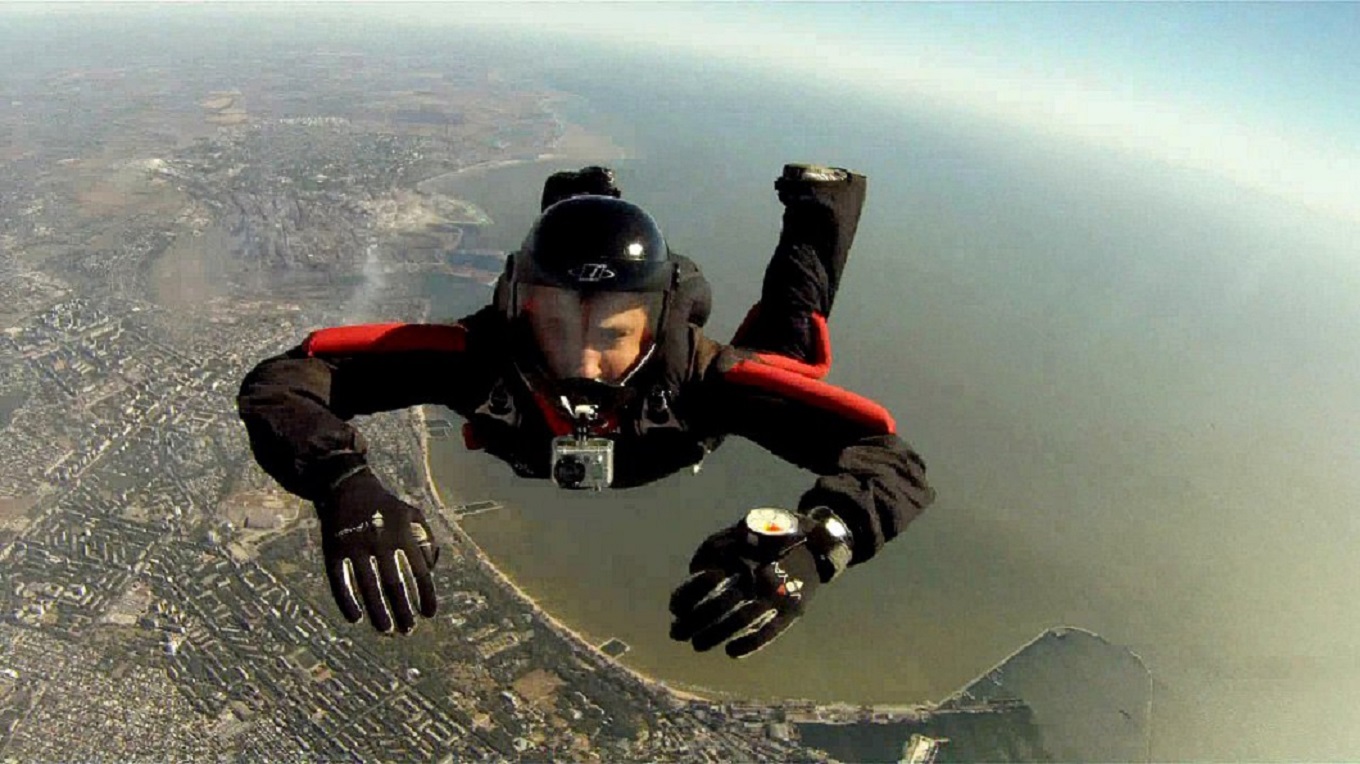
A sensation of falling occurs when the labyrinth or ''vestibular apparatus'', a system of fluid-filled passages in the inner ear, detects changes in acceleration. This sensation can occur when a person begins to fall, which in terms of mechanics amounts to a sudden acceleration increase from zero to roughly 9.81 m/s2. If the body is in free fall (for example, during skydiving) with no other momenta (rotation, etc.) there is no falling sensation. This almost never occurs in real-life falling situations because when the faller leaves their support there are usually very significant quantities of residual momenta such as rotation and these momenta continue as the person falls, causing a sensation of dysphoria. The faller doesn't fall straight down but spins, flips, etc. due to these residual momenta and also due to the asymmetric forces of air resistance on their asymmetric body. While velocity continues to increase, the downward acceleration due to gravity remains constant. Increasin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sense
A sense is a biological system used by an organism for sensation, the process of gathering information about the world through the detection of Stimulus (physiology), stimuli. (For example, in the human body, the brain which is part of the central nervous system receives signals from the senses which continuously receive information from the environment, interprets these signals, and causes the body to respond, either chemically or physically.) Although traditionally five human senses were identified as such (namely Visual perception, sight, Olfaction, smell, Somatosensory system, touch, taste, and hearing), it is now recognized that there are many more. Senses used by non-human organisms are even greater in variety and number. During sensation, sense organs collect various stimuli (such as a sound or smell) for Transduction (physiology), transduction, meaning transformation into a form that can be understood by the brain. Sensation and perception are fundamental to nearly every ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labyrinth (inner Ear)
The bony labyrinth (also osseous labyrinth or otic capsule) is the rigid, bony outer wall of the inner ear in the temporal bone. It consists of three parts: the vestibule, semicircular canals, and cochlea. These are cavities hollowed out of the substance of the bone, and lined by periosteum. They contain a clear fluid, the perilymph, in which the membranous labyrinth is situated. A fracture classification system in which temporal bone fractures detected by computed tomography are delineated based on disruption of the otic capsule has been found to be predictive for complications of temporal bone trauma such as facial nerve injury, sensorineural deafness and cerebrospinal fluid otorrhea. On radiographic images, the otic capsule is the densest portion of the temporal bone. In otospongiosis, a leading cause of adult-onset hearing loss, the otic capsule is exclusively affected. This area normally undergoes no remodeling in adult life and is extremely dense. With otospongiosis, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanics
Mechanics (from Ancient Greek: μηχανική, ''mēkhanikḗ'', "of machines") is the area of mathematics and physics concerned with the relationships between force, matter, and motion among physical objects. Forces applied to objects result in displacements, or changes of an object's position relative to its environment. Theoretical expositions of this branch of physics has its origins in Ancient Greece, for instance, in the writings of Aristotle and Archimedes (see History of classical mechanics and Timeline of classical mechanics). During the early modern period, scientists such as Galileo, Kepler, Huygens, and Newton laid the foundation for what is now known as classical mechanics. As a branch of classical physics, mechanics deals with bodies that are either at rest or are moving with velocities significantly less than the speed of light. It can also be defined as the physical science that deals with the motion of and forces on bodies not in the quantum realm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravitational Acceleration
In physics, gravitational acceleration is the acceleration of an object in free fall within a vacuum (and thus without experiencing drag). This is the steady gain in speed caused exclusively by the force of gravitational attraction. All bodies accelerate in vacuum at the same rate, regardless of the masses or compositions of the bodies; the measurement and analysis of these rates is known as gravimetry. At a fixed point on the surface, the magnitude of Earth's gravity results from combined effect of gravitation and the centrifugal force from Earth's rotation. At different points on Earth's surface, the free fall acceleration ranges from , depending on altitude, latitude, and longitude. A conventional standard value is defined exactly as . Locations of significant variation from this value are known as gravity anomalies. This does not take into account other effects, such as buoyancy or drag. Relation to the Universal Law Newton's law of universal gravitation states that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Fall
In Newtonian physics, free fall is any motion of a body where gravity is the only force acting upon it. In the context of general relativity, where gravitation is reduced to a space-time curvature, a body in free fall has no force acting on it. An object in the technical sense of the term "free fall" may not necessarily be falling down in the usual sense of the term. An object moving upwards might not normally be considered to be falling, but if it is subject to only the force of gravity, it is said to be in free fall. The Moon is thus in free fall around the Earth, though its orbital speed keeps it in very far orbit from the Earth's surface. In a roughly uniform gravitational field gravity acts on each part of a body approximately equally. When there are no other forces, such as the normal force exerted between a body (e.g. an astronaut in orbit) and its surrounding objects, it will result in the sensation of weightlessness, a condition that also occurs when the gravitati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skydiving
Parachuting, including also skydiving, is a method of transiting from a high point in the atmosphere to the surface of Earth with the aid of gravity, involving the control of speed during the descent using a parachute or parachutes. For human skydiving, it may involve a phase of more or less free-falling (the skydiving segment) which is a period when the parachute has not yet been deployed and the body gradually accelerates to terminal velocity. For cargo parachuting, the parachute descent may begin immediately, such as a parachute-airdrop in the lower atmosphere of Earth, or be significantly delayed, such as in a planetary atmosphere where an object is descending "under parachute" following atmospheric entry from space, and may begin only after the hypersonic entry phase and initial deceleration that occurs due to friction with the thin upper atmosphere. History Common uses Parachuting is performed as a recreational activity and a competitive sport, and is widel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravity
In physics, gravity () is a fundamental interaction which causes mutual attraction between all things with mass or energy. Gravity is, by far, the weakest of the four fundamental interactions, approximately 1038 times weaker than the strong interaction, 1036 times weaker than the electromagnetic force and 1029 times weaker than the weak interaction. As a result, it has no significant influence at the level of subatomic particles. However, gravity is the most significant interaction between objects at the macroscopic scale, and it determines the motion of planets, stars, galaxies, and even light. On Earth, gravity gives weight to physical objects, and the Moon's gravity is responsible for sublunar tides in the oceans (the corresponding antipodal tide is caused by the inertia of the Earth and Moon orbiting one another). Gravity also has many important biological functions, helping to guide the growth of plants through the process of gravitropism and influencing the circ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drag (physics)
In fluid dynamics, drag (sometimes called air resistance, a type of friction, or fluid resistance, another type of friction or fluid friction) is a force acting opposite to the relative motion of any object moving with respect to a surrounding fluid. This can exist between two fluid layers (or surfaces) or between a fluid and a solid surface. Unlike other resistive forces, such as dry friction, which are nearly independent of velocity, the drag force depends on velocity. Drag force is proportional to the velocity for low-speed flow and the squared velocity for high speed flow, where the distinction between low and high speed is measured by the Reynolds number. Even though the ultimate cause of drag is viscous friction, turbulent drag is independent of viscosity. Drag forces always tend to decrease fluid velocity relative to the solid object in the fluid's path. Examples Examples of drag include the component of the net aerodynamic or hydrodynamic force acting opposite to the di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balance Disorder
A balance disorder is a disturbance that causes an individual to feel unsteady, for example when standing or walking. It may be accompanied by feelings of giddiness, or wooziness, or having a sensation of movement, spinning, or floating. Balance is the result of several body systems working together: the visual system (eyes), vestibular system (ears) and proprioception (the body's sense of where it is in space). Degeneration or loss of function in any of these systems can lead to balance deficits. Signs and symptoms Cognitive dysfunction (disorientation) may occur with vestibular disorders. Cognitive deficits are not just spatial in nature, but also include non-spatial functions such as object recognition memory. Vestibular dysfunction has been shown to adversely affect processes of attention and increased demands of attention can worsen the postural sway associated with vestibular disorders. Recent MRI studies also show that humans with bilateral vestibular damage (damage to bot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypnagogia
Hypnagogia is the experience of the transitional state from wakefulness to sleep: the ''hypnagogic'' state of consciousness, during the onset of sleep. Its opposite state is described as the transitional state from sleep into wakefulness. Mental phenomena that may occur during this "threshold consciousness" phase include hypnagogic hallucinations, lucid thought, exploding head syndrome, lucid dreaming, and sleep paralysis. The latter two phenomena are themselves separate sleep conditions that are sometimes experienced during the hypnagogic state. Definitions The word ''hypnagogia'' is sometimes used in a restricted sense to refer to the onset of sleep, and contrasted with ''hypnopompia'', Frederic Myers's term for waking up. However, ''hypnagogia'' is also regularly employed in a more general sense that covers both falling asleep and waking up. Indeed, it is not always possible in practice to assign a particular episode of any given phenomenon to one or the other, given that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypnic Jerk
A hypnic jerk, hypnagogic jerk, sleep start, sleep twitch, myoclonic jerk, or night start is a brief and sudden involuntary contraction of the muscles of the body which occurs when a person is beginning to fall asleep, often causing the person to jump and awaken suddenly for a moment. Hypnic jerks are one form of involuntary muscle twitches called myoclonus. Physically, hypnic jerks resemble the "jump" experienced by a person when startled, sometimes accompanied by a falling sensation. Hypnic jerks are associated with a rapid heartbeat, quickened breathing, sweat, and sometimes "a peculiar sensory feeling of 'shock' or 'falling into the void'". It can also be accompanied by a vivid dream experience or hallucination. A higher occurrence is reported in people with irregular sleep schedules. Men have also been known to experience this at a higher rate than women. Moreover, when they are particularly frequent and severe, hypnic jerks have been reported as a cause of sleep-onset in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vestibular System
The vestibular system, in vertebrates, is a sensory system that creates the sense of balance and spatial orientation for the purpose of coordinating movement with balance. Together with the cochlea, a part of the auditory system, it constitutes the labyrinth of the inner ear in most mammals. As movements consist of rotations and translations, the vestibular system comprises two components: the semicircular canals, which indicate rotational movements; and the otoliths, which indicate linear accelerations. The vestibular system sends signals primarily to the neural structures that control eye movement; these provide the anatomical basis of the vestibulo-ocular reflex, which is required for clear vision. Signals are also sent to the muscles that keep an animal upright and in general control posture; these provide the anatomical means required to enable an animal to maintain its desired position in space. The brain uses information from the vestibular system in the head and fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |