|
Fairy Bluebird
The three fairy-bluebirds are small passerine bird species found in forests and plantations in tropical southern Asia and the Philippines. They are the sole members of the genus ''Irena'' and family (biology), family Irenidae, and are related to the ioras and leafbirds. These are bulbul-like birds of open forest or thorn scrub, but whereas that group tends to be drab in colouration, fairy-bluebirds are sexually dimorphic, with the males being dark blue in plumage, and the females duller green. These species eat fruit, especially figs, and possibly some insects. They lay two to three eggs in a tree nest. The call of the Asian fairy-bluebird is a liquid two note ''Glue-It''. As the names would suggest, the Asian fairy-bluebird (''I. puella'') occurs across southern Asia, the Philippine fairy-bluebird (''I. cyanogastra'') in that archipelago, and the Palawan fairy-bluebird (''I. tweeddalii'') on the island of Palawan (island), Palawan. Taxonomy The first scientists to examine fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asian Fairy-bluebird
The Asian fairy-bluebird (''Irena puella'') is a medium-sized, arboreal passerine bird. This fairy-bluebird is found in forests across tropical southern Asia, Indochina and the Greater Sundas. Two or three eggs are laid in a small cup nest in a tree. It was described by British ornithologist John Latham in 1790. The only other member of the genus and family is the Philippine fairy-bluebird, ''I. cyanogastra'', which replaces the Asian fairy-bluebird in most of the Philippines. Both species are considered as sacred to the Tagalog people as they are perceived as tigmamanukan omens. The adult Asian fairy bluebird is about . The male has glossy, iridescent blue upperparts, and black underparts and flight feathers. The female and first year male are entirely dull blue-green. The Asian fairy bluebird eats fruits, nectar and some insects. Its call is a liquid two note ''glue-it''. Description The Asian fairy bluebird measures in length. The iris is crimson and eyelids pinkish; the bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philippine Fairy-bluebird
The Philippine fairy-bluebird (''Irena cyanogastra'') is a species of bird in the family Irenidae. It is endemic to the Philippines being found in the islands of Luzon, Mindanao, Samar and Bohol. Its natural habitats are tropical moist lowland forest and tropical moist montane forest. They are seen in mixed flocks along with Philippine bulbuls, Blue-headed fantails and other forest birds. It is threatened by habitat loss and hunting for both food and pet trade. Mythology This species is considered as sacred to the Tagalog people as this is perceived as tigmamanukan omen, and therefore, the sacred omen and messenger of Bathala, the supreme god in indigenous Tagalog religious practices. In old Tagalog mythology in southern Luzon (Philippines), the Philippine fairy-bluebirds were known as the tigmamanukan omen birds. All of which were the omen birds of Bathala, the supreme god of the Tagalog people prior to the arrival of the Spanish. According to legend, Bathala ordered a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations average to between 73–55 ka.", "Modern human beings—''Homo sapiens''—originated in Africa. Then, int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beak
The beak, bill, or rostrum is an external anatomical structure found mostly in birds, but also in turtles, non-avian dinosaurs and a few mammals. A beak is used for eating, preening, manipulating objects, killing prey, fighting, probing for food, courtship, and feeding young. The terms ''beak'' and ''rostrum'' are also used to refer to a similar mouth part in some ornithischians, pterosaurs, cetaceans, dicynodonts, anuran tadpoles, monotremes (i.e. echidnas and platypuses, which have a beak-like structure), sirens, pufferfish, billfishes and cephalopods. Although beaks vary significantly in size, shape, color and texture, they share a similar underlying structure. Two bony projections – the upper and lower mandibles – are covered with a thin keratinized layer of epidermis known as the rhamphotheca. In most species, two holes called ''nares'' lead to the respiratory system. Etymology Although the word "beak" was, in the past, generally restricted to the sharpened bills o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
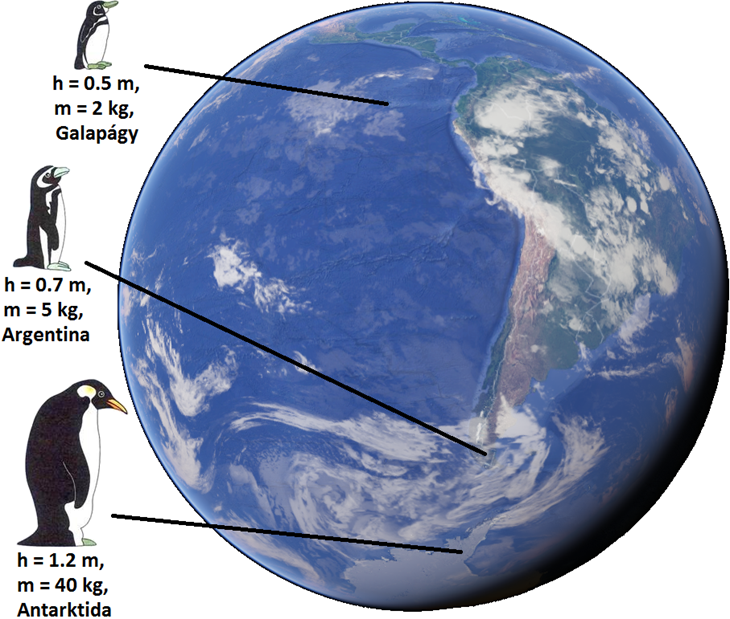
Bergmann's Rule
Bergmann's rule is an ecogeographical rule that states that within a broadly distributed taxonomic clade, populations and species of larger size are found in colder environments, while populations and species of smaller size are found in warmer regions. Bergmann's rule only describes the overall size of the animals, but does not include body parts like Allen's rule does. Although originally formulated in relation to species within a genus, it has often been recast in relation to populations within a species. It is also often cast in relation to latitude. It is possible that the rule also applies to some plants, such as '' Rapicactus''. The rule is named after nineteenth century German biologist Carl Bergmann, who described the pattern in 1847, although he was not the first to notice it. Bergmann's rule is most often applied to mammals and birds which are endotherms, but some researchers have also found evidence for the rule in studies of ectothermic species, such as the ant ''L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexual Dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where the sexes of the same animal and/or plant species exhibit different morphological characteristics, particularly characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most animals and some plants. Differences may include secondary sex characteristics, size, weight, colour, markings, or behavioural or cognitive traits. These differences may be subtle or exaggerated and may be subjected to sexual selection and natural selection. The opposite of dimorphism is ''monomorphism'', which is when both biological sexes are phenotypically indistinguishable from each other. Overview Ornamentation and coloration Common and easily identified types of dimorphism consist of ornamentation and coloration, though not always apparent. A difference in coloration of sexes within a given species is called sexual dichromatism, which is commonly seen in many species of birds and reptiles. Sexual selection leads to the exaggerated dim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old World Oriole
The Old World orioles (Oriolidae) are an Old World family of passerine birds. Taxonomy and systematics The family Oriolidae comprises the piopios, figbirds, pitohuis and the Old World orioles. The piopios were added 2011, having been formerly placed in the family Turnagridae. Several other genera have been proposed to split up the genus ''Oriolus''. For example, the African black-headed species are sometimes placed in a separate genus, ''Baruffius''. The family Oriolidae is not related to the New World orioles, despite their similar size, diet, behaviour and contrasting plumage patterns. Rather, these similarities are an example of convergent evolution. Extant genera There are three extant genera in the family ''Oriolidae'': Extinct genera There are at least two extinct genera in the family ''Oriolidae'': * Genus '' Turnagra'' – piopios (2 extinct species) * Genus '' Longmornis'' – ''Longmornis robustirostrata'' Description The orioles and figbirds are medium-sized pas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Handbook Of The Birds Of The World
The ''Handbook of the Birds of the World'' (HBW) is a multi-volume series produced by the Spanish publishing house Lynx Edicions in partnership with BirdLife International. It is the first handbook to cover every known living species of bird. The series was edited by Josep del Hoyo, Andrew Elliott, Jordi Sargatal and David A. Christie. All 16 volumes have been published. For the first time an animal class will have all the species illustrated and treated in detail in a single work. This has not been done before for any other group in the animal kingdom. Material in each volume is grouped first by family, with an introductory article on each family; this is followed by individual species accounts (taxonomy, subspecies and distribution, descriptive notes, habitat, food and feeding, breeding, movements, status and conservation, bibliography). In addition, all volumes except the first and second contain an essay on a particular ornithological theme. More than 200 renowned speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drongo
The drongos are a family, Dicruridae, of passerine birds of the Old World tropics. The 30 species in the family are placed in a single genus, ''Dicrurus''. Drongos are mostly black or dark grey, short-legged birds, with an upright stance when perched. They have forked tails and some have elaborate tail decorations. They feed on insects and small birds, which they catch in flight or on the ground. Some species are accomplished mimics and have a variety of alarm calls, to which other birds and animals often respond. They are known to utter hoax alarm calls that scare other animals off food, which the drongo then claims. Taxonomy The genus ''Dicrurus'' was introduced by French ornithologist Louis Pierre Vieillot for the drongos in 1816. The type species was subsequently designated as the balicassiao (''Dicrurus balicassius'') by English zoologist George Robert Gray in 1841. The name of the genus combines the Ancient Greek words ''dikros'' "forked" and ''oura'' "tail". "Drongo" i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coenraad Jacob Temminck
Coenraad Jacob Temminck (; 31 March 1778 – 30 January 1858) was a Dutch people, Dutch Aristocracy (class), aristocrat, Zoology, zoologist and museum director. Biography Coenraad Jacob Temminck was born on 31 March 1778 in Amsterdam in the Dutch Republic. From his father, Jacob Temminck, who was treasurer of the Dutch East India Company with links to numerous travellers and collectors, he inherited a large collection of bird specimens. His father was a good friend of Francois Levaillant who also guided Coenraad. Temminck's ''Manuel d'ornithologie, ou Tableau systématique des oiseaux qui se trouvent en Europe'' (1815) was the standard work on European birds for many years. He was also the author of ''Histoire naturelle générale des Pigeons et des Gallinacées'' (1813–1817), ''Nouveau Recueil de Planches coloriées d'Oiseaux'' (1820–1839), and contributed to the mammalian sections of Philipp Franz von Siebold's ''Fauna japonica'' (1844–1850). Temminck was the first dire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plumage
Plumage ( "feather") is a layer of feathers that covers a bird and the pattern, colour, and arrangement of those feathers. The pattern and colours of plumage differ between species and subspecies and may vary with age classes. Within species, there can be different colour morphs. The placement of feathers on a bird is not haphazard, but rather emerge in organized, overlapping rows and groups, and these are known by standardized names. Most birds moult twice a year, resulting in a breeding or ''nuptial plumage'' and a ''basic plumage''. Many ducks and some other species such as the red junglefowl have males wearing a bright nuptial plumage while breeding and a drab ''eclipse plumage'' for some months afterward. The painted bunting's juveniles have two inserted moults in their first autumn, each yielding plumage like an adult female. The first starts a few days after fledging replacing the ''juvenile plumage'' with an ''auxiliary formative plumage''; the second a month or so l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_feeding_on_Peepal_(Ficus_religiosa)_at_Jayanti%2C_Duars%2C_WB_W_Picture_437.jpg)