|
Function Composition Operator
In computer science, function composition is an act or mechanism to combine simple functions to build more complicated ones. Like the usual composition of functions in mathematics, the result of each function is passed as the argument of the next, and the result of the last one is the result of the whole. Programmers frequently apply functions to results of other functions, and almost all programming languages allow it. In some cases, the composition of functions is interesting as a function in its own right, to be used later. Such a function can always be defined but languages with first-class functions make it easier. The ability to easily compose functions encourages factoring (breaking apart) functions for maintainability and code reuse. More generally, big systems might be built by composing whole programs. Narrowly speaking, function composition applies to functions that operate on a finite amount of data, each step sequentially processing it before handing it to the next ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Science
Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans Theoretical computer science, theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, and information theory) to Applied science, applied disciplines (including the design and implementation of Computer architecture, hardware and Software engineering, software). Algorithms and data structures are central to computer science. The theory of computation concerns abstract models of computation and general classes of computational problem, problems that can be solved using them. The fields of cryptography and computer security involve studying the means for secure communication and preventing security vulnerabilities. Computer graphics (computer science), Computer graphics and computational geometry address the generation of images. Programming language theory considers different ways to describe computational processes, and database theory concerns the management of re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
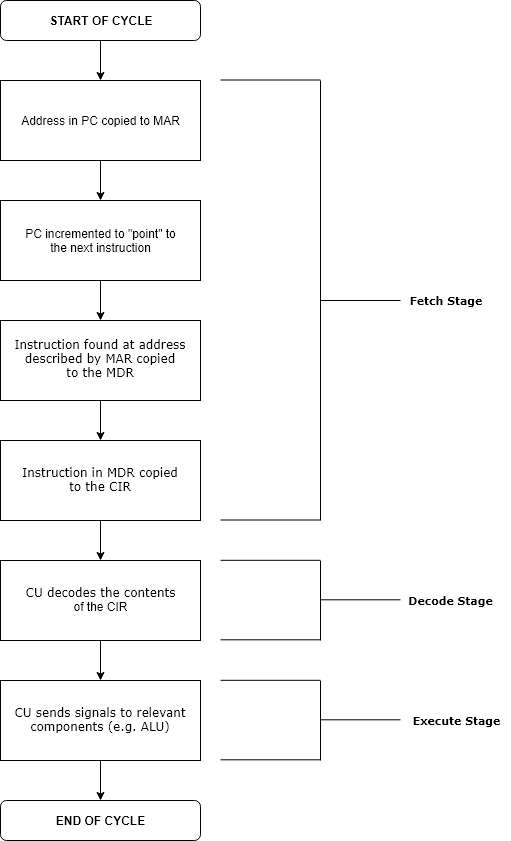
Run Time (program Lifecycle Phase)
Execution in computer and software engineering is the process by which a computer or virtual machine interprets and acts on the instructions of a computer program. Each instruction of a program is a description of a particular action which must be carried out, in order for a specific problem to be solved. Execution involves repeatedly following a " fetch–decode–execute" cycle for each instruction done by the control unit. As the executing machine follows the instructions, specific effects are produced in accordance with the semantics of those instructions. Programs for a computer may be executed in a batch process without human interaction or a user may type commands in an interactive session of an interpreter. In this case, the "commands" are simply program instructions, whose execution is chained together. The term run is used almost synonymously. A related meaning of both "to run" and "to execute" refers to the specific action of a user starting (or ''launching'' o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rakudo
Rakudo is a Raku compiler targeting MoarVM, and the Java Virtual Machine, that implements the Raku specification. It is currently the only major Raku compiler in active development. Originally developed within the Parrot Parrots (Psittaciformes), also known as psittacines (), are birds with a strong curved beak, upright stance, and clawed feet. They are classified in four families that contain roughly 410 species in 101 genus (biology), genera, found mostly in ... project, the Rakudo source code repository was split from the project in February 2009 so that it could be developed independently, although there were still many dependencies at the time. Rakudo is written in C, Raku, and the lightweight Raku subset NQP (Not Quite Perl). Rakudo Perl #14 was released in February 2009, codenamed ''Vienna'' after the Perl mongers group that had sponsored one of its developers since April 2008. Subsequent releases have used codenames based on Perl mongers groups. The first ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raku (programming Language)
Raku is a member of the Perl family of programming languages. Formerly named Perl 6, it was renamed in October 2019. Raku introduces elements of many modern and historical languages. Compatibility with Perl was not a goal, though a compatibility mode is part of the specification. The design process for Raku began in 2000. History The Raku design process was first announced on 19 July 2000, on the fourth day of that year's O'Reilly Open Source Convention, Perl Conference, by Larry Wall in his ''Perl#State of the Onion, State of the Onion 2000'' talk. At that time, the primary goals were to remove "historical warts" from the language; "easy things should stay easy, hard things should get easier, and impossible things should get hard"; and a general cleanup of the internal design and application programming interfaces (APIs). The process began with a series of Request for Comments (RFCs). This process was open to all contributors, and left no aspect of the language closed to chang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arity
In logic, mathematics, and computer science, arity () is the number of arguments or operands taken by a function, operation or relation. In mathematics, arity may also be called rank, but this word can have many other meanings. In logic and philosophy, arity may also be called adicity and degree. In linguistics, it is usually named valency. Examples In general, functions or operators with a given arity follow the naming conventions of ''n''-based numeral systems, such as binary and hexadecimal. A Latin prefix is combined with the -ary suffix. For example: * A nullary function takes no arguments. ** Example: f()=2 * A unary function takes one argument. ** Example: f(x)=2x * A binary function takes two arguments. ** Example: f(x,y)=2xy * A ternary function takes three arguments. ** Example: f(x,y,z)=2xyz * An ''n''-ary function takes ''n'' arguments. ** Example: f(x_1, x_2, \ldots, x_n)=2\prod_^n x_i Nullary A constant can be treated as the output of an operation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
APL (programming Language)
APL (named after the book ''A Programming Language'') is a programming language developed in the 1960s by Kenneth E. Iverson. Its central datatype is the multidimensional array. It uses a large range of special graphic symbols to represent most functions and operators, leading to very concise code. It has been an important influence on the development of concept modeling, spreadsheets, functional programming, and computer math packages. It has also inspired several other programming languages. History Mathematical notation A mathematical notation for manipulating arrays was developed by Kenneth E. Iverson, starting in 1957 at Harvard University. In 1960, he began work for IBM where he developed this notation with Adin Falkoff and published it in his book ''A Programming Language'' in 1962. The preface states its premise: This notation was used inside IBM for short research reports on computer systems, such as the Burroughs B5000 and its stack mechanism when stack m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variadic
In computer science, an operator or function is variadic if it can take a varying number of arguments; that is, if its arity is not fixed. For specific articles, see: * Variadic function * Variadic macro in the C preprocessor * Variadic template In computer programming, variadic templates are templates that take a variable number of arguments. Variadic templates are supported by C++ (since the C++11 standard), and the D programming language. C++ The variadic template feature of C++ wa ... Programming language theory {{Comp-sci-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homoiconic
In computer programming, homoiconicity (from the Greek words ''homo-'' meaning "the same" and ''icon'' meaning "representation") is an informal property of some programming languages. A language is homoiconic if a program written in it can be manipulated as data using the language. The program's internal representation can thus be inferred just by reading the program itself. This property is often summarized by saying that the language treats code as data. The informality of the property arises from the fact that, strictly, this applies to almost all programming languages. No consensus exists on a precise definition of the property. In a homoiconic language, the primary representation of programs is also a data structure in a primitive type of the language itself. This makes metaprogramming easier than in a language without this property: reflection in the language (examining the program's entities at runtime) depends on a single, homogeneous structure, and it does not have to ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scheme (programming Language)
Scheme is a dialect of the Lisp family of programming languages. Scheme was created during the 1970s at the MIT Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (MIT CSAIL) and released by its developers, Guy L. Steele and Gerald Jay Sussman, via a series of memos now known as the Lambda Papers. It was the first dialect of Lisp to choose lexical scope and the first to require implementations to perform tail-call optimization, giving stronger support for functional programming and associated techniques such as recursive algorithms. It was also one of the first programming languages to support first-class continuations. It had a significant influence on the effort that led to the development of Common Lisp.Common LISP: The Language, 2nd Ed., Guy L. Steele Jr. Digital Press; 1981. . "Common Lisp is a new dialect of Lisp, a successor to MacLisp, influenced strongly by ZetaLisp and to some extent by Scheme and InterLisp." The Scheme language is standardized in the offic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lisp (programming Language)
Lisp (historically LISP, an abbreviation of "list processing") is a family of programming languages with a long history and a distinctive, fully parenthesized prefix notation. Originally specified in the late 1950s, it is the second-oldest high-level programming language still in common use, after Fortran. Lisp has changed since its early days, and many dialects have existed over its history. Today, the best-known general-purpose Lisp dialects are Common Lisp, Scheme, Racket, and Clojure. Lisp was originally created as a practical mathematical notation for computer programs, influenced by (though not originally derived from) the notation of Alonzo Church's lambda calculus. It quickly became a favored programming language for artificial intelligence (AI) research. As one of the earliest programming languages, Lisp pioneered many ideas in computer science, including tree data structures, automatic storage management, dynamic typing, conditionals, higher-order function ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymorphism (computer Science)
In programming language theory and type theory, polymorphism is the use of one symbol to represent multiple different types.: "Polymorphic types are types whose operations are applicable to values of more than one type." In object-oriented programming, polymorphism is the provision of one Interface (object-oriented programming), interface to entities of different data types. The concept is borrowed from a principle in biology where an organism or species can have many different forms or stages. The most commonly recognized major forms of polymorphism are: * ''Ad hoc polymorphism'': defines a common interface for an arbitrary set of individually specified types. * ''Parametric polymorphism'': not specifying concrete types and instead use abstract symbols that can substitute for any type. * ''Subtyping'' (also called ''subtype polymorphism'' or ''inclusion polymorphism''): when a name denotes instances of many different classes related by some common superclass. History Interest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lambda Calculus
In mathematical logic, the lambda calculus (also written as ''λ''-calculus) is a formal system for expressing computability, computation based on function Abstraction (computer science), abstraction and function application, application using variable Name binding, binding and Substitution (algebra), substitution. Untyped lambda calculus, the topic of this article, is a universal machine, a model of computation that can be used to simulate any Turing machine (and vice versa). It was introduced by the mathematician Alonzo Church in the 1930s as part of his research into the foundations of mathematics. In 1936, Church found a formulation which was #History, logically consistent, and documented it in 1940. Lambda calculus consists of constructing #Lambda terms, lambda terms and performing #Reduction, reduction operations on them. A term is defined as any valid lambda calculus expression. In the simplest form of lambda calculus, terms are built using only the following rules: # x: A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |