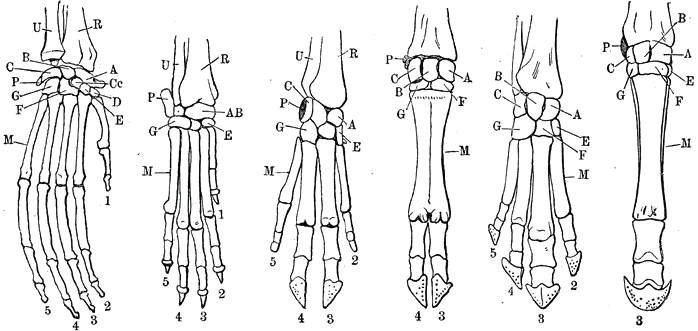|
Forelimbs
A forelimb or front limb is one of the paired articulated appendages (limbs) attached on the cranial (anterior) end of a terrestrial tetrapod vertebrate's torso. With reference to quadrupeds, the term foreleg or front leg is often used instead. In bipedal animals with an upright posture (e.g. humans and some primates), the term upper limb is often used. A forelimb is not to be confused with a forearm, which is a distal portion of the human upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. All vertebrate forelimbs are homologous, meaning that they all evolved from the same structures. For example, the flipper of a turtle or of a dolphin, the arm of a human, the foreleg of a horse, and the wings of both bats and birds are ultimately homologous, despite the large differences between them. Specific uses of the forelimbs may be analogous if they evolved from different sub-structures of the forelimb, such as the flippers of turtles and dolphins, and the wings of birds and bats. Evolut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bipedal
Bipedalism is a form of terrestrial locomotion where an organism moves by means of its two rear limbs or legs. An animal or machine that usually moves in a bipedal manner is known as a biped , meaning 'two feet' (from Latin ''bis'' 'double' and ''pes'' 'foot'). Types of bipedal movement include walking, running, and hopping. Several groups of modern species are habitual bipeds whose normal method of locomotion is two-legged. In the Triassic period some groups of archosaurs (a group that includes crocodiles and dinosaurs) developed bipedalism; among the dinosaurs, all the early forms and many later groups were habitual or exclusive bipeds; the birds are members of a clade of exclusively bipedal dinosaurs, the theropods. Within mammals, habitual bipedalism has evolved multiple times, with the macropods, kangaroo rats and mice, springhare, hopping mice, pangolins and hominin apes ( australopithecines, including humans) as well as various other extinct groups evolving the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limb (anatomy)
A limb (from the Old English ''lim'', meaning "body part") or leg is a jointed, muscled appendage that tetrapod vertebrates use for weight-bearing and terrestrial locomotion such as walking, running and jumping, for paddle-swimming, or for grasping and climbing. The distalmost portion of a limb is known as its extremity. The limbs' bony endoskeleton, known as the appendicular skeleton, is homologous among all tetrapods. All tetrapods have four limbs that are organized into two bilaterally symmetrical pairs, with one pair at each end of the torso. The cranial pair are known as the forelimbs or ''front legs'', and the caudal pair the hindlimbs or ''back legs''. In animals with more upright posture (mainly hominid primates, particularly humans), the forelimbs and hindlimbs are often called upper and lower limbs, respectively. The fore-/upper limbs are connected to the thoracic cage via the shoulder girdles, and the hind-/lower limbs are connected to the pelvis via the hip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homology (biology)
In biology, homology is similarity due to shared ancestry between a pair of structures or genes in different taxa. A common example of homologous structures is the forelimbs of vertebrates, where the wings of bats and birds, the arms of primates, the front flippers of whales and the forelegs of four-legged vertebrates like dogs and crocodiles are all derived from the same ancestral tetrapod structure. Evolutionary biology explains homologous structures adapted to different purposes as the result of descent with modification from a common ancestor. The term was first applied to biology in a non-evolutionary context by the anatomist Richard Owen in 1843. Homology was later explained by Charles Darwin's theory of evolution in 1859, but had been observed before this, from Aristotle onwards, and it was explicitly analysed by Pierre Belon in 1555. In developmental biology, organs that developed in the embryo in the same manner and from similar origins, such as from matching p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Limb
The upper limbs or upper extremities are the forelimbs of an upright-postured tetrapod vertebrate, extending from the scapulae and clavicles down to and including the digits, including all the musculatures and ligaments involved with the shoulder, elbow, wrist and knuckle joints. In humans, each upper limb is divided into the arm, forearm and hand, and is primarily used for climbing, lifting and manipulating objects. Definition In formal usage, the term "arm" only refers to the structures from the shoulder to the elbow, explicitly excluding the forearm, and thus "upper limb" and "arm" are not synonymous. However, in casual usage, the terms are often used interchangeably. The term "upper arm" is redundant in anatomy, but in informal usage is used to distinguish between the two terms. Structure In the human body the muscles of the upper limb can be classified by origin, topography, function, or innervation. While a grouping by innervation reveals embryological and phylogenet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrapod
Tetrapods (; ) are four-limbed vertebrate animals constituting the superclass Tetrapoda (). It includes extant and extinct amphibians, sauropsids ( reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids (pelycosaurs, extinct therapsids and all extant mammals). Tetrapods evolved from a clade of primitive semiaquatic animals known as the Tetrapodomorpha which, in turn, evolved from ancient lobe-finned fish (sarcopterygians) around 390 million years ago in the Middle Devonian period; their forms were transitional between lobe-finned fishes and true four-limbed tetrapods. Limbed vertebrates (tetrapods in the broad sense of the word) are first known from Middle Devonian trackways, and body fossils became common near the end of the Late Devonian but these were all aquatic. The first crown-tetrapods (last common ancestors of extant tetrapods capable of terrestrial locomotion) appeared by the very early Carboniferous, 350 million years ago. The specific aquatic ancestors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrapod
Tetrapods (; ) are four-limbed vertebrate animals constituting the superclass Tetrapoda (). It includes extant and extinct amphibians, sauropsids ( reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids (pelycosaurs, extinct therapsids and all extant mammals). Tetrapods evolved from a clade of primitive semiaquatic animals known as the Tetrapodomorpha which, in turn, evolved from ancient lobe-finned fish (sarcopterygians) around 390 million years ago in the Middle Devonian period; their forms were transitional between lobe-finned fishes and true four-limbed tetrapods. Limbed vertebrates (tetrapods in the broad sense of the word) are first known from Middle Devonian trackways, and body fossils became common near the end of the Late Devonian but these were all aquatic. The first crown-tetrapods (last common ancestors of extant tetrapods capable of terrestrial locomotion) appeared by the very early Carboniferous, 350 million years ago. The specific aquatic ancestors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radius (bone)
The radius or radial bone is one of the two large bones of the forearm, the other being the ulna. It extends from the lateral side of the elbow to the thumb side of the wrist and runs parallel to the ulna. The ulna is usually slightly longer than the radius, but the radius is thicker. Therefore the radius is considered to be the larger of the two. It is a long bone, prism-shaped and slightly curved longitudinally. The radius is part of two joints: the elbow and the wrist. At the elbow, it joins with the capitulum of the humerus, and in a separate region, with the ulna at the radial notch. At the wrist, the radius forms a joint with the ulna bone. The corresponding bone in the lower leg is the fibula. Structure The long narrow medullary cavity is enclosed in a strong wall of compact bone. It is thickest along the interosseous border and thinnest at the extremities, same over the cup-shaped articular surface (fovea) of the head. The trabeculae of the spongy tissue are some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dolphin
A dolphin is an aquatic mammal within the infraorder Cetacea. Dolphin species belong to the families Delphinidae (the oceanic dolphins), Platanistidae (the Indian river dolphins), Iniidae (the New World river dolphins), Pontoporiidae (the brackish dolphins), and the extinct Lipotidae (baiji or Chinese river dolphin). There are 40 extant species named as dolphins. Dolphins range in size from the and Maui's dolphin to the and orca. Various species of dolphins exhibit sexual dimorphism where the males are larger than females. They have streamlined bodies and two limbs that are modified into flippers. Though not quite as flexible as seals, some dolphins can briefly travel at speeds of per hour or leap about . Dolphins use their conical teeth to capture fast-moving prey. They have well-developed hearing which is adapted for both air and water. It is so well developed that some can survive even if they are blind. Some species are well adapted for diving to great depths. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flipper (anatomy)
A flipper is a broad, flattened limb adapted for aquatic locomotion. It refers to the fully webbed, swimming appendages of aquatic vertebrates that are not fish. In animals with two flippers, such as whales, the flipper refers solely to the forelimbs. In animals with four flippers, such as pinnipeds and sea turtles, one may distinguish fore- and hind-flippers, or pectoral flippers and pelvic flippers. Animals with flippers include penguins (whose flippers are also called wings), cetaceans (e.g. dolphins and whales), pinnipeds (e.g. walruses, earless and eared seals), sirenians (e.g. manatees and dugongs), and marine reptiles such as the sea turtles and the now-extinct plesiosaurs, mosasaurs, ichthyosaurs, and metriorhynchids. Usage of the terms "fin" and "flipper" is sometimes inconsistent, even in the scientific literature. However, the hydrodynamic control surfaces of fish are always referred to as "fins" and never "flippers". Tetrapod limbs which have evolved into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dactyly
In biology, dactyly is the arrangement of digits (fingers and toes) on the hands, feet, or sometimes wings of a tetrapod animal. It comes from the Greek word δακτυλος (''dáktylos'') = "finger". Sometimes the ending "-dactylia" is used. The derived adjectives end with "-dactyl" or "-dactylous". As a normal feature Pentadactyly Pentadactyly (from Greek "five") is the condition of having five digits on each limb. It is traditionally believed that all living tetrapods are descended from an ancestor with a pentadactyl limb, although many species have now lost or transformed some or all of their digits by the process of evolution. However, this viewpoint was challenged by Stephen Jay Gould in his 1991 essay "Eight (Or Fewer) Little Piggies", where he pointed out polydactyly in early tetrapods and described the specializations of digit reduction. Despite the individual variations listed below, the relationship is to the original five-digit model. In reptiles, the limbs ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torso
The torso or trunk is an anatomical term for the central part, or the core, of the body of many animals (including humans), from which the head, neck, limbs, tail and other appendages extend. The tetrapod torso — including that of a human — is usually divided into the ''thoracic'' segment (also known as the upper torso, where the forelimbs extend), the ''abdominal'' segment (also known as the "mid-section" or "midriff"), and the ''pelvic'' and '' perineal'' segments (sometimes known together with the abdomen as the lower torso, where the hindlimbs extend). Anatomy Major organs In humans, most critical organs, with the notable exception of the brain, are housed within the torso. In the upper chest, the heart and lungs are protected by the rib cage, and the abdomen contains most of the organs responsible for digestion: the stomach, which breaks down partially digested food via gastric acid; the liver, which respectively produces bile necessary for digestion; the large and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior (anatomy)
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and anatomical axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether an organism is bipedal or quadrupedal. Additionally, for some animals such as invertebrates, some terms may not have any meaning at all; for example, an animal that is radially symmetrical will have no anterior surface, but can still have a description that a part is close to the middle ("proximal") or further from the middle ("distal"). International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standard vocabularies for subdisciplines of anatom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |