|
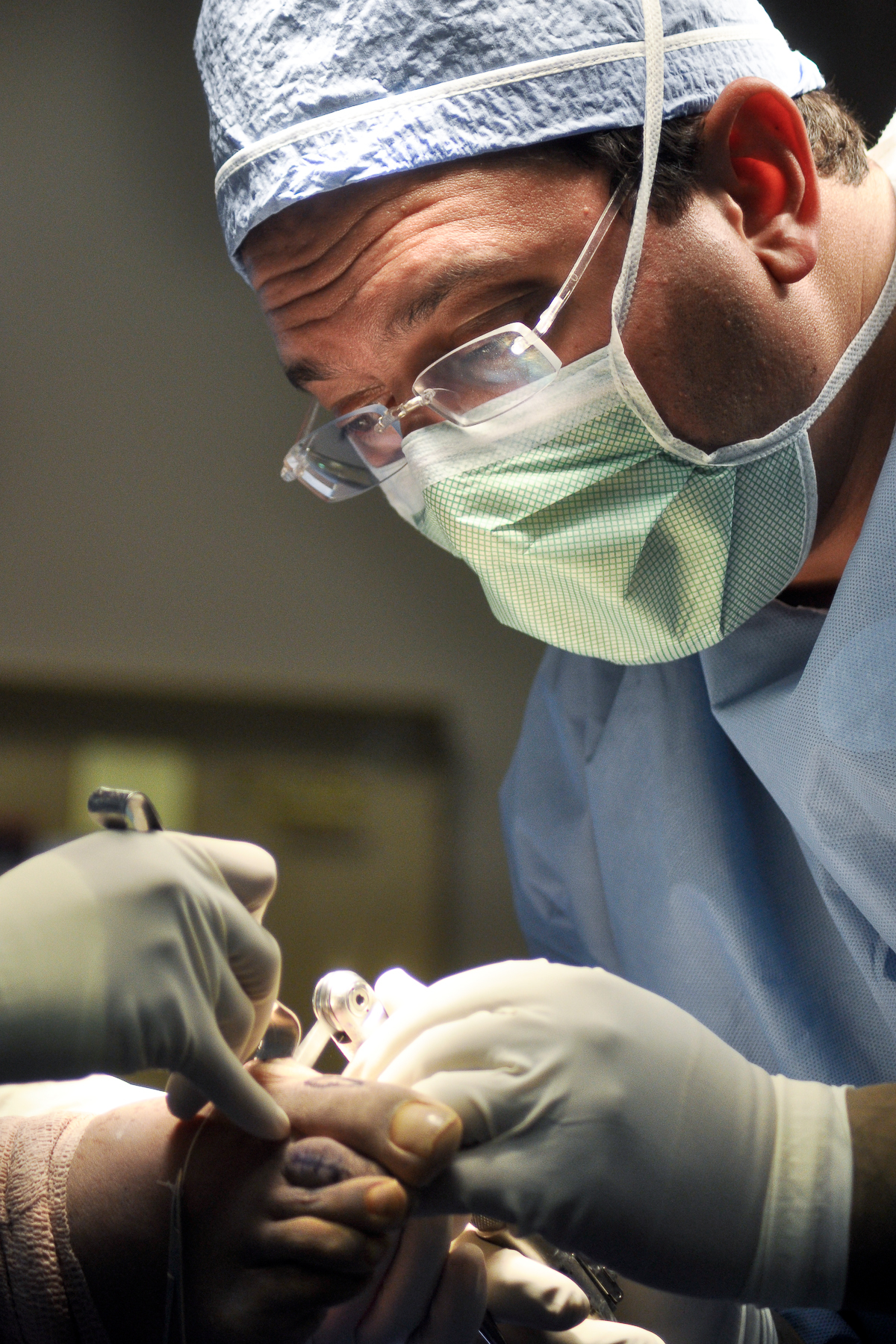
Foot And Ankle Surgery
Foot and ankle surgery is a sub-specialty of orthopedics and podiatry that deals with the treatment, diagnosis and prevention of disorders of the foot and ankle. Orthopaedic surgeons are medically qualified, having been through four years of college, followed by 4 years of medical school or osteopathic medical school to obtain an M.D. or D.O. followed by specialist training as a resident in orthopaedics, and only then do they sub-specialise in foot and ankle surgery. Training for a podiatric foot and ankle surgeon consists of four years of college, four years of podiatric medical school ( D.P.M.), 3–4 years of a surgical residency and an optional 1 year fellowship. The distinction between a podiatric and orthopedic foot and ankle surgeon is: an orthopedic surgeon has a Doctor of Medicine or Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine medical degree or osteopathic medical degree and training that encompasses both orthopedic residency and an optional 6-month to one year of fellowship trainin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physician
A physician (American English), medical practitioner (Commonwealth English), medical doctor, or simply doctor, is a health professional who practices medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring health through the study, diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of disease, injury, and other physical and mental impairments. Physicians may focus their practice on certain disease categories, types of patients, and methods of treatment—known as specialities—or they may assume responsibility for the provision of continuing and comprehensive medical care to individuals, families, and communities—known as general practice. Medical practice properly requires both a detailed knowledge of the academic disciplines, such as anatomy and physiology, underlying diseases and their treatment—the ''science'' of medicine—and also a decent competence in its applied practice—the art or ''craft'' of medicine. Both the role of the physician and the meaning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser Surgery
Laser surgery is a type of surgery that uses a laser (in contrast to using a scalpel) to cut tissue. Examples include the use of a laser scalpel in otherwise conventional surgery, and soft-tissue laser surgery, in which the laser beam vaporizes soft tissue with high water content. Laser surgery is commonly used on the eye. Techniques used include LASIK, which is used to correct near and far-sightedness in vision, and photorefractive keratectomy, a procedure which permanently reshapes the cornea using an excimer laser to remove a small amount of the human tissue. Types of surgical lasers include carbon dioxide, argon, Nd:YAG laser, and potassium titanyl phosphate, among others. Effects # Photochemistry, Photochemical effect: clinically referred to as photodynamic therapy. Photosensitizer (photophrin II) is administered which is taken up by the tumor tissue and later irradiated by laser light resulting in highly toxic substances with resultant necrosis of the tumor. Phot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Podiatry
Podiatry () or podiatric medicine () is a branch of medicine devoted to the study, diagnosis, medical and surgical treatment of disorders of the foot, ankle, and leg. A Doctor of Podiatric Medicine (DPM), or a podiatrist, is a healthcare professional who diagnoses and treats conditions affecting the structures of the foot, ankle, and leg. The US podiatric medical school curriculum includes lower extremity anatomy, general human anatomy, physiology, general medicine, physical assessment, biochemistry, neurobiology, pathophysiology, genetics and embryology, microbiology, histology, pharmacology, women's health, physical rehabilitation, sports medicine, research, ethics and jurisprudence, biomechanics, general principles of orthopedic surgery, and foot and ankle surgery. Podiatry is a high-paying specialization and was listed by ''Forbes'' in 2007 as the 15th-best-paid profession in the United States. The median annual salary of a podiatrist in the US was $124,830 in 2016 acc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Orthopaedic Foot And Ankle Society
The American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society (AOFAS) is a professional medical society based in Rosemont, Illinois. It was founded in 1969 and currently has a membership of around 2,400 foot and ankle orthopaedic surgeons. The society provides education, research, grants, and other services to the general public and orthopaedic doctors, allied health practitioners, and researchers specializing in orthopaedic foot and ankle medicine and surgery. The organization also operates its own peer-reviewed journal, ''Foot & Ankle International''. History Early history The AOFAS was founded in 1969 as the American Orthopaedic Foot Society (AOFS) with around 150 members. Its founding members included doctors Nathaniel Gould, Robert Joplin, Nicholas Giannestras, Melvin Jahss, Hampar Kelikian, Paul Lapidus, and Joseph Milgram. Several of its founding members served as early presidents of the organization including Robert Joplin (1969–70), Nicholas Giannestras (1970–71), Nathaniel Goul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American College Of Foot And Ankle Surgeons
The American College of Foot and Ankle Surgeons (ACFAS) is a professional medical society of foot and ankle surgeons in the United States (US). Each of the over 7,700 members have graduated from one of nine podiatric medical schools in the US with a Doctor of Podiatric Medicine degree. ACFAS publishes the ''Journal of Foot & Ankle Surgery''. Background ACFAS is a professional medical organization of over 7,700 podiatric foot and ankle surgeons practicing in the United States and was formed in 1942. Informing members of the latest techniques and advances of surgical care of the foot, ankle, and related lower extremity are the primary goals of the ACFAS. The college also functions in representing foot and ankle surgeons, helping to advance and improve the standards of education and surgical skill in foot and ankle care in the US. ACFAS members are Doctors of Podiatric Medicine (DPM) and are graduates of one of the nine accredited podiatric medical school ''Podiatric Medical Sch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DMARD
Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) comprise a category of otherwise unrelated disease-modifying drugs defined by their use in rheumatoid arthritis to slow down disease progression. The term is often used in contrast to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (which refers to agents that treat the inflammation, but not the underlying cause) and steroids (which blunt the immune response but are insufficient to slow down the progression of the disease). The term "antirheumatic" can be used in similar contexts, but without making a claim about an effect on the disease course. Other terms that have historically been used to refer to the same group of drugs are "remission-inducing drugs" (RIDs) and "slow-acting antirheumatic drugs" (SAARDs). Terminology Although the use of the term DMARDs was first propagated in rheumatoid arthritis (hence their name), the term has come to pertain to many other diseases, such as Crohn's disease, lupus erythematosus, Sjögren syndrome, immune ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NSAID
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a therapeutic drug class which reduces pain, decreases inflammation, decreases fever, and prevents blood clots. Side effects depend on the specific drug, its dose and duration of use, but largely include an increased risk of gastrointestinal ulcers and bleeds, heart attack, and kidney disease. The term ''non-steroidal'', common from around 1960, distinguishes these drugs from corticosteroids, which during the 1950s had acquired a bad reputation due to overuse and side-effect problems after their initial introduction in 1948. NSAIDs work by inhibiting the activity of cyclooxygenase enzymes (the COX-1 and COX-2 isoenzymes). In cells, these enzymes are involved in the synthesis of key biological mediators, namely prostaglandins, which are involved in inflammation, and thromboxanes, which are involved in blood clotting. There are two general types of NSAIDs available: non-selective, and COX-2 selective. Mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthrodesis
Arthrodesis, also known as artificial ankylosis or syndesis, is the artificial induction of joint ossification between two bones by surgery. This is done to relieve intractable pain in a joint which cannot be managed by pain medication, splints, or other normally indicated treatments. The typical causes of such pain are fractures which disrupt the joint, severe sprains, and arthritis. It is most commonly performed on joints in the spine, hand, ankle, and foot. Historically, knee and hip arthrodeses were also performed as pain-relieving procedures, but with the great successes achieved in hip and knee arthroplasty, arthrodesis of these large joints has fallen out of favour as a primary procedure, and now is only used as a procedure of last resort in some failed arthroplasties. Method Arthrodesis can be done in several ways: * A bone graft can be created between the two bones using a bone from elsewhere in the person's body (autograft) or using donor bone (allograft) from a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X Ray Internal Fixation Leg Fracture
X, or x, is the twenty-fourth and third-to-last letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''"ex"'' (pronounced ), plural ''exes''."X", ''Oxford English Dictionary'', 2nd edition (1989); ''Merriam-Webster's Third New International Dictionary of the English Language, Unabridged'' (1993); "ex", ''op. cit''. X is regularly pronounced as "ks". History In Ancient Greek, ' Χ' and ' Ψ' were among several variants of the same letter, used originally for and later, in western areas such as Arcadia, as a simplification of the digraph 'ΧΣ' for . In the end, more conservative eastern forms became the standard of Classical Greek, and thus 'Χ' ''(Chi)'' stood for (later ; palatalized to in Modern Greek before front vowels). However, the Etruscans had taken over 'Χ' from western Greek, and it therefore stands for in Etruscan and Latin. The letter 'Χ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastrocnemius
The gastrocnemius muscle (plural ''gastrocnemii'') is a superficial two-headed muscle that is in the back part of the lower leg of humans. It runs from its two heads just above the knee to the heel, a three joint muscle (knee, ankle and subtalar joints). The muscle is named via Latin, from Greek γαστήρ (''gaster'') 'belly' or 'stomach' and κνήμη (''knḗmē'') 'leg', meaning 'stomach of the leg' (referring to the bulging shape of the calf). Structure The gastrocnemius is located with the soleus in the posterior (back) compartment of the leg. The lateral head originates from the lateral condyle of the femur, while the medial head originates from the medial condyle of the femur. Its other end forms a common tendon with the soleus muscle; this tendon is known as the calcaneal tendon or Achilles tendon and inserts onto the posterior surface of the calcaneus, or heel bone. It is considered a superficial muscle as it is located directly under skin, and its shape may often b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthotics
Orthotics ( el, Ορθός, translit=ortho, lit=to straighten, to align) is a medical specialty that focuses on the design and application of orthoses, or braces. An is "an externally applied device used to influence the structural and functional characteristics of the Neuromuscular junction, neuromuscular and Skeletal muscle, skeletal system". Orthotists are professionals who specialize in the provision of orthoses. Classification Orthotic devices are classified into four areas of the body according to the international classification system (ICS): orthotics of the Human leg, lower extremities, orthotics of the Upper limb, upper extremities, orthotics for the Torso, trunk, and orthotics for the head. Orthoses are also classified by function: paralysis orthoses, relief orthoses, and soft braces. Under the International standard, International Standard terminology, orthoses are classified by an acronym describing the anatomical joints which they contain. For example, a knee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and hands are involved, with the same joints typically involved on both sides of the body. The disease may also affect other parts of the body, including skin, eyes, lungs, heart, nerves and blood. This may result in a low red blood cell count, inflammation around the lungs, and inflammation around the heart. Fever and low energy may also be present. Often, symptoms come on gradually over weeks to months. While the cause of rheumatoid arthritis is not clear, it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. The underlying mechanism involves the body's immune system attacking the joints. This results in inflammation and thickening of the joint capsule. It also affects the underlying bone and cartilage. The diagnosis is made mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |