|
Fluoroacetic Acid
Fluoroacetic acid is a organofluorine compound with formula CH2FCO2H. It is a colorless solid that is noted for its relatively high toxicity. The conjugate base, fluoroacetate occurs naturally in at least 40 plants in Australia, Brazil, and Africa. It is one of only five known organic fluorine-containing natural products. Toxicity Fluoroacetic acid is a harmful metabolite of some fluorine-containing drugs (median lethal dose, LD50 = 10 mg/kg in humans). The most common metabolic sources of fluoroacetic acid are fluoroamines and fluoroethers. Fluoroacetic acid can disrupt the Krebs cycle. In contrast with monofluoroacetic acid, difluoroacetic acid and trifluoroacetic acid are far less toxic. Its pKa is 2.66, in contrast to 1.24 and 0.23 for the respective di- and trifluorinated acids. Uses Fluoroacetic acid is used to manufacture pesticides especially rodenticides (see sodium fluoroacetate Sodium fluoroacetate is an organofluorine chemical compound with the formula FCH2CO2Na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trifluoroacetic Acid
Trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) is an organofluorine compound with the chemical formula CF3CO2H. It is a structural analogue of acetic acid with all three of the acetyl group's hydrogen atoms replaced by fluorine atoms and is a colorless liquid with a vinegar-like odor. TFA is a stronger acid than acetic acid, having an acid ionisation constant, ''K''a, that is approximately 34,000 times higher, as the highly electronegative fluorine atoms and consequent electron-withdrawing nature of the trifluoromethyl group weakens the oxygen-hydrogen bond (allowing for greater acidity) and stabilises the anionic conjugate base. TFA is widely used in organic chemistry for various purposes. Synthesis TFA is prepared industrially by the electrofluorination of acetyl chloride or acetic anhydride, followed by hydrolysis of the resulting trifluoroacetyl fluoride: : + 4 → + 3 + : + → + Where desired, this compound may be dried by addition of trifluoroacetic anhydride. An older route to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organofluorine Compound
Organofluorine chemistry describes the chemistry of the organofluorines, organic compounds that contain the carbon–fluorine bond. Organofluorine compounds find diverse applications ranging from oil and water repellents to pharmaceuticals, refrigerants, and reagents in catalysis. In addition to these applications, some organofluorine compounds are pollutants because of their contributions to ozone depletion, global warming, bioaccumulation, and toxicity. The area of organofluorine chemistry often requires special techniques associated with the handling of fluorinating agents. The carbon–fluorine bond Fluorine has several distinctive differences from all other substituents encountered in organic molecules. As a result, the physical and chemical properties of organofluorines can be distinctive in comparison to other organohalogens. # The carbon–fluorine bond is one of the strongest in organic chemistry (an average bond energy around 480 kJ/molKirsch, Peer ''Modern fluoroorga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
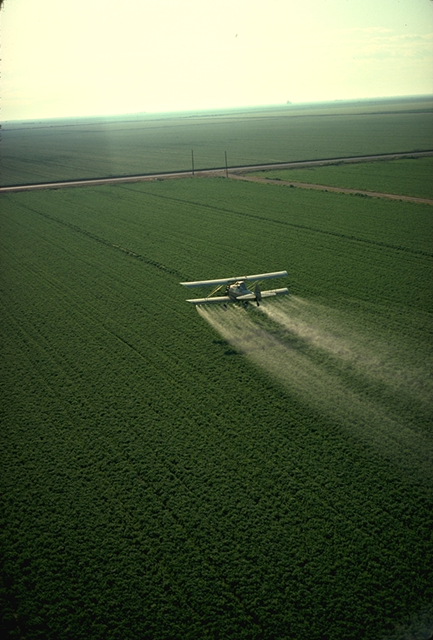
Rodenticides
Rodenticides are chemicals made and sold for the purpose of killing rodents. While commonly referred to as "rat poison", rodenticides are also used to kill mice, squirrels, woodchucks, chipmunks, porcupines, nutria, beavers, and voles. Despite the crucial roles that rodents play in nature, there are times when they need to be controlled. Some rodenticides are lethal after one exposure while others require more than one. Rodents are disinclined to gorge on an unknown food (perhaps reflecting an adaptation to their inability to vomit), preferring to sample, wait and observe whether it makes them or other rats sick. This phenomenon of poison shyness is the rationale for poisons that kill only after multiple doses. Besides being directly toxic to the mammals that ingest them, including dogs, cats, and humans, many rodenticides present a secondary poisoning risk to animals that hunt or scavenge the dead corpses of rats. Classes of rodenticides Anticoagulants Anticoagulants ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluoroacetates
Fluoroacetic acid is a organofluorine compound with formula CH2FCO2H. It is a colorless solid that is noted for its relatively high toxicity. The conjugate base, fluoroacetate occurs naturally in at least 40 plants in Australia, Brazil, and Africa. It is one of only five known organic fluorine-containing natural products. Toxicity Fluoroacetic acid is a harmful metabolite of some fluorine-containing drugs (median lethal dose, LD50 = 10 mg/kg in humans). The most common metabolic sources of fluoroacetic acid are fluoroamines and fluoroethers. Fluoroacetic acid can disrupt the Krebs cycle. In contrast with monofluoroacetic acid, difluoroacetic acid and trifluoroacetic acid are far less toxic. Its pKa is 2.66, in contrast to 1.24 and 0.23 for the respective di- and trifluorinated acids. Uses Fluoroacetic acid is used to manufacture pesticides especially rodenticides (see sodium fluoroacetate Sodium fluoroacetate is an organofluorine chemical compound with the formula FCH2CO ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
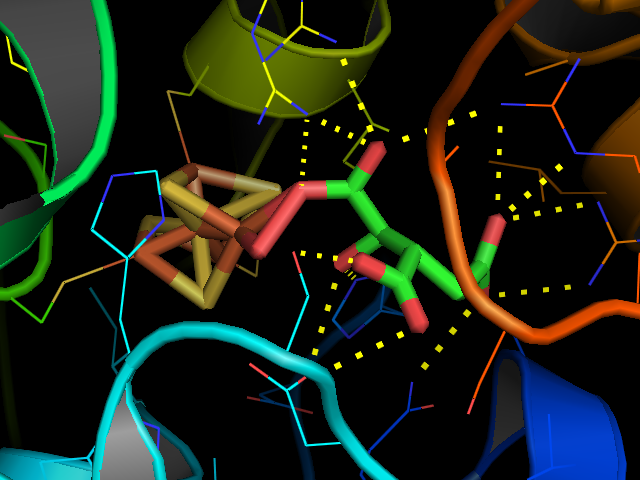
Aconitase Inhibitors
Aconitase (aconitate hydratase; ) is an enzyme that catalyses the stereo-specific isomerization of citrate to isocitrate via ''cis''-aconitate in the tricarboxylic acid cycle, a non-redox-active process. Image:Citrate wpmp.png, Image:Cis-Aconitate wpmp.png, Image:isocitric acid.svg, Structure Aconitase, displayed in the structures in the right margin of this page, has two slightly different structures, depending on whether it is activated or inactivated. In the inactive form, its structure is divided into four domains. Counting from the N-terminus, only the first three of these domains are involved in close interactions with the Fe-4Scluster, but the active site consists of residues from all four domains, including the larger C-terminal domain. The Fe-S cluster and a anion also reside in the active site. When the enzyme is activated, it gains an additional iron atom, creating a Fe-4Scluster. However, the structure of the rest of the enzyme is nearly unchanged; the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Respiratory Toxins
The respiratory system (also respiratory apparatus, ventilatory system) is a biological system consisting of specific organs and structures used for gas exchange in animals and plants. The anatomy and physiology that make this happen varies greatly, depending on the size of the organism, the environment in which it lives and its evolutionary history. In land animals the respiratory surface is internalized as linings of the lungs. Gas exchange in the lungs occurs in millions of small air sacs; in mammals and reptiles these are called alveoli, and in birds they are known as atria. These microscopic air sacs have a very rich blood supply, thus bringing the air into close contact with the blood. These air sacs communicate with the external environment via a system of airways, or hollow tubes, of which the largest is the trachea, which branches in the middle of the chest into the two main bronchi. These enter the lungs where they branch into progressively narrower secondary and terti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organofluorides
Organofluorine chemistry describes the chemistry of the organofluorines, organic compounds that contain the carbon–fluorine bond. Organofluorine compounds find diverse applications ranging from Lipophobicity, oil and hydrophobe, water repellents to pharmaceuticals, refrigerants, and reagents in catalysis. In addition to these applications, some organofluorine compounds are pollutants because of their contributions to ozone depletion, global warming, bioaccumulation, and toxicity. The area of organofluorine chemistry often requires special techniques associated with the handling of fluorinating agents. The carbon–fluorine bond Fluorine has several distinctive differences from all other substituents encountered in organic molecules. As a result, the physical and chemical properties of organofluorines can be distinctive in comparison to other organohalogens. # The carbon–fluorine bond is one of the strongest in organic chemistry (an average bond energy around 480 kJ/molKirsch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboxylic Acids
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is or , with R referring to the alkyl, alkenyl, aryl, or other group. Carboxylic acids occur widely. Important examples include the amino acids and fatty acids. Deprotonation of a carboxylic acid gives a carboxylate anion. Examples and nomenclature Carboxylic acids are commonly identified by their trivial names. They at oftentimes have the suffix ''-ic acid''. IUPAC-recommended names also exist; in this system, carboxylic acids have an ''-oic acid'' suffix. For example, butyric acid (C3H7CO2H) is butanoic acid by IUPAC guidelines. For nomenclature of complex molecules containing a carboxylic acid, the carboxyl can be considered position one of the parent chain even if there are other substituents, such as 3-chloropropanoic acid. Alternately, it can be named as a "carboxy" or "carboxylic acid" substituent on another ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Fluoroacetate
Sodium fluoroacetate is an organofluorine chemical compound with the formula FCH2CO2Na. This colourless salt has a taste similar to that of sodium chloride and is used as a rodenticide. History and production The effectiveness of sodium fluoroacetate as a rodenticide was reported in 1942. The name "1080" refers to the catalogue number of the poison, which became its brand name. The salt is synthesized by treating sodium chloroacetate with potassium fluoride. Both sodium and potassium salts are derivatives of fluoroacetic acid. Natural occurrence Fluoroacetate occurs naturally in at least 40 plants in Australia, Brazil, and Africa. It is one of only five known organic fluorine-containing natural products. Fluoroacetate occurrence in ''Gastrolobium'' species ''Gastrolobium'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Fabaceae. This genus consists of over 100 species, and all but two are native to the southwest region of Western Australia, where they are known as "poison peas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pesticides
Pesticides are substances that are meant to control pests. This includes herbicide, insecticide, nematicide, molluscicide, piscicide, avicide, rodenticide, bactericide, insect repellent, animal repellent, microbicide, fungicide, and lampricide. The most common of these are herbicides which account for approximately 80% of all pesticide use. Most pesticides are intended to serve as plant protection products (also known as crop protection products), which in general, protect plants from weeds, fungi, or insects. As an example, the fungus ''Alternaria solani'' is used to combat the aquatic weed ''Salvinia''. In general, a pesticide is a chemical (such as carbamate) or biological agent (such as a virus, bacterium, or fungus) that deters, incapacitates, kills, or otherwise discourages pests. Target pests can include insects, plant pathogens, weeds, molluscs, birds, mammals, fish, nematodes (roundworms), and microbes that destroy property, cause nuisance, or spread disease, or ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |