|
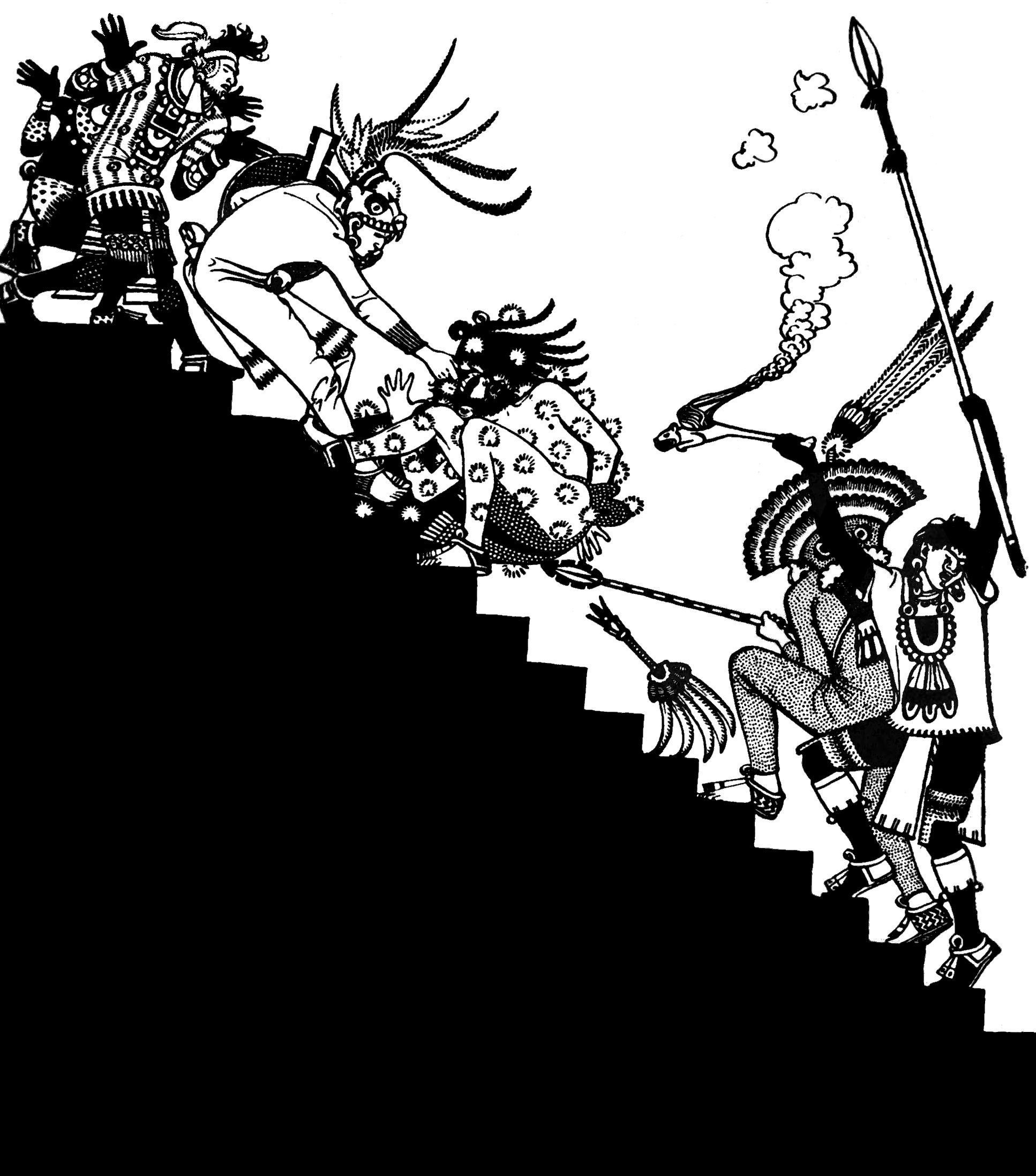
Flower War
A flower war or flowery war ( nah, xōchiyāōyōtl, es, guerra florida) was a ritual war fought intermittently between the Aztec Triple Alliance and its enemies from the "mid-1450s to the arrival of the Spaniards in 1519." Enemies included the city-states of Tlaxcala, Huejotzingo, and Cholula in the Tlaxcala-Pueblan Valley in central Mexico. In these wars, participants would fight according to a set of conventions. During the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, Tlaxcala allied with the Spaniards against the Aztecs, being eager to see their longtime flower war enemies overthrown. Origins Texcocan nobleman Ixtlilxochitl gives the "fullest early statement concerning the origin as well as the initial rationale" of the flower war. From 1450 to 1454, the Aztecs had suffered from crop failure and severe drought; this led to famine and many deaths in the central Mexican highlands. Ixtlilxochitl reports that the flower war began "as a response" to the famine: "the priests ... of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholula (Mesoamerican Site)
Cholula (; nah, Cholōllān) was an important city of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica, dating back to at least the 2nd century BCE, with settlement as a village going back at least some thousand years earlier. The site of Cholula is just west of the modern city of Puebla and served as a trading outpost. Its immense pyramid is the largest such structure in the Americas, and the largest pyramid structure by volume in the world. Cholula was one of the key religious centers of ancient Mexico.McCafferty, Geoffrey G. "Cholula." In Davíd Carrasco (ed). ''The Oxford Encyclopedia of Mesoamerican Cultures''. : Oxford University Press, 2001. Location and environment Cholula is located in the Puebla-Tlaxcala Valley of the central Mexican highlands. It is surrounded to the west by the snow-covered peaks Popocatepetl and Iztaccihuatl, and Malinche to the north. The summer rainy season and the melted snow in winter provide a great environment for irrigation agriculture. There is also a confl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Sacrifice In Aztec Culture
Human sacrifice was common in many parts of Mesoamerica, so the rite was nothing new to the Aztecs when they arrived at the Valley of Mexico, nor was it something unique to pre-Columbian Mexico. Other Mesoamerican cultures, such as the Purépechas and Toltecs, and the Maya performed sacrifices as well and from archaeological evidence, it probably existed since the time of the Olmecs (1200–400 BC), and perhaps even throughout the early farming cultures of the region. However, the extent of human sacrifice is unknown among several Mesoamerican civilizations. What distinguished Aztec practice from Maya human sacrifice was the way in which it was embedded in everyday life. These cultures also notably sacrificed elements of their own population to the gods. In 1519, explorers such as Hernán Cortés conquered the Aztec capital of Tenochtitlan and made observations of and wrote reports about the practice of human sacrifice. Bernal Díaz del Castillo, who participated in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ross Hassig
Ross Hassig (born December 13, 1945) is an American historical anthropologist specializing in Mesoamerican studies, particularly the Aztec culture. His focus is often on the description of practical infrastructure in Mesoamerican societies. He is the author of several influential books, among them: ''Time, History, and Belief in Aztec and Colonial Mexico''; ''Aztec Warfare: Imperial Expansion and Political Control''; and ''Trade, Tribute, and Transportation: The Sixteenth-Century Political Economy of the Valley of Mexico''. Career Hassig began his academic career as an undergraduate at Vanderbilt University, where his studies initially focused on non-Western legal systems. He soon developed an interest in anthropology, later obtaining in 1974 his Master's degree from Vanderbilt in Law and Anthropology, with a thesis on political development among the Puebloan peoples at Acoma Pueblo. He then went on further his graduate studies at Stanford University, obtaining his Ph.D fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diego Muñoz Camargo
Diego Muñoz Camargo (c. 1529 – 1599) was the author of ''History of Tlaxcala'', an illustrated codex that highlights the religious, cultural, and military history of the Tlaxcalan people. Life Diego Muñoz Camargo was born in Spanish colonial Mexico of a Spanish father and Indian mother. He acted as official interpreter for the Spanish, particularly the Franciscans , image = FrancescoCoA PioM.svg , image_size = 200px , caption = A cross, Christ's arm and Saint Francis's arm, a universal symbol of the Franciscans , abbreviation = OFM , predecessor = , .... He was also a chronicler of some note, belonging to a group of mestizo chroniclers with Fernando de Alva Ixtlilxochitl and Fernando Alvarado Tezozomoc. His ''History of Tlaxcala'', one version of a work of various forms stands as an important source for Tlaxcala, in Mexico. Muñoz Camargo was a businessman who entered into lucrative cross-cultural enterprises. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moctezuma II
Moctezuma Xocoyotzin ( – 29 June 1520; oteːkˈsoːmaḁ ʃoːkoˈjoːt͡sĩn̥), nci-IPA, Motēuczōmah Xōcoyōtzin, moteːkʷˈsoːma ʃoːkoˈjoːtsin variant spellings include Motewksomah, Motecuhzomatzin, Montezuma, Moteuczoma, Motecuhzoma, Motēuczōmah, Muteczuma, and referred to retroactively in European sources as Moctezuma II, was the ninth Emperor of the Aztec Empire (also known as Mexica Empire), reigning from 1502 or 1503 to 1520. Through his marriage with queen Tlapalizquixochtzin of Ecatepec, one of his two wives, he was also king consort of that ''altepetl''. The first contact between the indigenous civilizations of Mesoamerica and Europeans took place during his reign, and he was killed during the initial stages of the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, when conquistador Hernán Cortés and his men fought to take over the Aztec capital Tenochtitlan. During his reign, the Aztec Empire reached its greatest size. Through warfare, Moctezuma expanded the ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrés De Tapia Motelchiuh
Don Andrés de Tapia Motelchiuh Huitznahuatlailótlac, also known as Motelchiuhtzin, was the ruler of Tenochtitlan (1525–1530). After the death of Don Juan Velázquez Tlacotzin in Nochixtlan in 1525, Hernán Cortés chose Don Andrés Motelchiuhtzin as the new ruler of Tenochtitlan. Motelchiuhtzin was not of the upper classes; he was born as a " macehualli" or working commoner, but he had gained renown as a warrior captain. He was captured together with Cuauhtémoc, and tortured along with him to reveal the location of the Aztecs' gold. Eventually he was freed and he returned to his lands. Because Tenochtitlan was in ruins, he stayed in Nochixtlan. In the three years of Cortés expeditions, he had been ruling Tenochtitlan as ''cuauhtlatoani''. He would not be tlatoani, but he would stayed as ''cuauhtlatoani'' two years more. During his rule, the Aztec titles and decorations were suppressed by the Spanish rulers. In 1530, Motelchiuhtzin went with the Spaniards to an expedi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hernán Cortés
Hernán Cortés de Monroy y Pizarro Altamirano, 1st Marquess of the Valley of Oaxaca (; ; 1485 – December 2, 1547) was a Spanish '' conquistador'' who led an expedition that caused the fall of the Aztec Empire and brought large portions of what is now mainland Mexico under the rule of the King of Castile in the early 16th century. Cortés was part of the generation of Spanish explorers and conquistadors who began the first phase of the Spanish colonization of the Americas. Born in Medellín, Spain, to a family of lesser nobility, Cortés chose to pursue adventure and riches in the New World. He went to Hispaniola and later to Cuba, where he received an '' encomienda'' (the right to the labor of certain subjects). For a short time, he served as ''alcalde'' (magistrate) of the second Spanish town founded on the island. In 1519, he was elected captain of the third expedition to the mainland, which he partly funded. His enmity with the Governor of Cuba, Diego Velázquez de Cuél ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalco (altépetl)
Chālco was a complex pre-Columbian Nahua ''altepetl'' or confederacy in central Mexico. It was divided into the four sub-altepetl of Tlalmanalco/ Tlacochcalco, Amaquemecan, Tenanco Texopalco Tepopolla and Chimalhuacan-Chalco, which were themselves further subdivided into ''altepetl tlayacatl'', each with its own ''tlatoani'' (king). Its inhabitants were known as the ''Chālcatl'' (singular) or ''Chālcah'' (plural). In the 14th and early 15th centuries, flower wars were fought between the Chalca and the Aztecs. Serious war erupted in 1446. According to the Amaqueme historian Chimalpahin, this was because the Chalca refused a Mexica demand to contribute building materials for the temple of Huitzilopochtli. Chalco was finally conquered by the Aztecs under Moctezuma I in or around 1465, and the kings of Chalco were exiled to Huexotzinco. The rulerships were restored by Tizoc in 1486, who installed new ''tlatoque''. This was achieved, in part, by the diplomacy work carried out ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agriculture In Mesoamerica
Agriculture in Mesoamerica dates to the Archaic period of Mesoamerican chronology (8000–2000 BC). At the beginning of the Archaic period, the Early Hunters of the late Pleistocene era (50,000–10,000 BC) led nomadic lifestyles, relying on hunting and gathering for sustenance. However, the nomadic lifestyle that dominated the late Pleistocene and the early Archaic slowly transitioned into a more sedentary lifestyle as the hunter gatherer micro-bands in the region began to cultivate wild plants. The cultivation of these plants provided security to the Mesoamericans, allowing them to increase surplus of "starvation foods" near seasonal camps; this surplus could be utilized when hunting was bad, during times of drought, and when resources were low. The cultivation of plants could have been started purposefully, or by accident. The former could have been done by bringing a wild plant closer to a camp site, or to a frequented area, so it was easier access and collect. The latter cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macuahuitl
A macuahuitl () is a weapon, a wooden club with several embedded obsidian blades. The name is derived from the Nahuatl language and means "hand-wood". Its sides are embedded with prismatic blades traditionally made from obsidian. Obsidian is capable of producing an edge sharper than high quality steel razor blades. The macuahuitl was a standard close combat weapon. Use of the macuahuitl as a weapon is attested from the first millennium CE. By the time of the Spanish conquest the macuahuitl was widely distributed in Mesoamerica. The weapon was used by different civilisations including the Aztec (Mexicas), Maya, Mixtec and Toltec. One example of this weapon survived the Conquest of the Aztec Empire; it was part of the Royal Armoury of Madrid until it was destroyed by a fire in 1884. Images of the original designs survive in diverse catalogues. The oldest replica is the macuahuitl created by the medievalist Achille Jubinal in the 19th century. Description The maquahui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spear-thrower
A spear-thrower, spear-throwing lever or ''atlatl'' (pronounced or ; Nahuatl ''ahtlatl'' ) is a tool that uses leverage to achieve greater velocity in dart or javelin-throwing, and includes a bearing surface which allows the user to store energy during the throw. It may consist of a shaft with a cup or a spur at the end that supports and propels the butt of the spear. It's usually about as long as the user's arm or forearm. The user holds the spear-thrower in one hand, gripping near the end farthest from the cup. The user puts the butt end of the spear, or dart, in the cup, or grabs the spur with the end of the spear. The spear is much longer than the thrower. The user holds the spear parallel to the spear-thrower and going in the other direction. The user can hold the spear, with the index and thumb, with the same hand as the thrower, with the other fingers. The user reaches back with the spear pointed at the target. Then they make an overhand throwing motion with the thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)