|
Flotation Process
Froth flotation is a process for selectively separating hydrophobic materials from hydrophilic. This is used in mineral processing, paper recycling and waste-water treatment industries. Historically this was first used in the mining industry, where it was one of the great enabling technologies of the 20th century. It has been described as "the single most important operation used for the recovery and upgrading of sulfide ores". The development of froth flotation has improved the recovery of valuable minerals, such as copper- and lead-bearing minerals. Along with mechanized mining, it has allowed the economic recovery of valuable metals from much lower grade ore than previously. Industries Froth flotation is applied to a wide range of separations. An estimated 1B tons of materials are processed in this manner annually. Mineral processing Froth flotation is a process for separating minerals from gangue by exploiting differences in their hydrophobicity. Hydrophobicity differenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flotation Cell
Flotation (also spelled floatation) involves phenomena related to the relative buoyancy of objects. The term may also refer to: *Flotation (archaeology), a method for recovering very small artefacts from excavated sediments *Flotation (shares), an initial public offering of stocks or shares in a company *Flotation, any material added to the hull of a watercraft to keep the hull afloat *Flotation, the ability (as of a tire or snowshoes) to stay on the surface of soft ground or snow *"Floatation", a 1990 electronic music song by The Grid *Flotation process, in process engineering, a method for the separation of mixtures **Dissolved air flotation (DAF), a water treatment process **Froth flotation, a process for separating hydrophobic from hydrophilic materials ** Induced gas flotation, a water treatment process that clarifies wastewaters (or other waters) by the removal of suspended matter such as oil or solids *Flotation therapy, a technique whereby users 'float' in an isolation t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continuous Foam Separation
Continuous foam separation is a chemical process closely related to foam fractionation in which foam is used to separate components of a solution when they differ in surface activity. In any solution, surface active components tend to adsorb to gas-liquid interfaces while surface inactive components stay within the bulk solution. When a solution is foamed, the most surface active components collect in the foam and the foam can be easily extracted. This process is commonly used in large-scale projects such as water waste treatment due to a continuous gas flow in the solution. There are two types of foam that can form from this process. They are wet foam (or ''kugelschaum'') and dry foam (or ''polyederschaum''). Wet foam tends to form at the lower portion of the foam column, while dry foam tends to form at the upper portion. The wet foam is more spherical and viscous, and the dry foam tends to be larger in diameter and less viscous. Wet foam forms closer to the originating liquid, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adsorb
Adsorption is the adhesion of atoms, ions or molecules from a gas, liquid or dissolved solid to a surface. This process creates a film of the ''adsorbate'' on the surface of the ''adsorbent''. This process differs from absorption, in which a fluid (the ''absorbate'') is dissolved by or permeates a liquid or solid (the ''absorbent''). Adsorption is a '' surface phenomenon'', while absorption involves the whole volume of the material, although adsorption does often precede absorption. The term ''sorption'' encompasses both processes, while ''desorption'' is the reverse of it. Like surface tension, adsorption is a consequence of surface energy. In a bulk material, all the bonding requirements (be they ionic, covalent or metallic) of the constituent atoms of the material are fulfilled by other atoms in the material. However, atoms on the surface of the adsorbent are not wholly surrounded by other adsorbent atoms and therefore can attract adsorbates. The exact nature of the bond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wetting
Wetting is the ability of a liquid to maintain contact with a solid surface, resulting from intermolecular interactions when the two are brought together. This happens in presence of a gaseous phase or another liquid phase not miscible with the first one. The degree of wetting (wettability) is determined by a force balance between adhesive and cohesive forces. Wetting is important in the bonding or adherence of two materials. Wetting and the surface forces that control wetting are also responsible for other related effects, including capillary effects. There are two types of wetting: non-reactive wetting and reactive wetting. Wetting deals with three phases of matter: gas, liquid, and solid. It is now a center of attention in nanotechnology and nanoscience studies due to the advent of many nanomaterials in the past two decades (e.g. graphene, Carbon nano tube, carbon nanotube, boron nitride nanomesh). Explanation Adhesive forces between a liquid and solid cause a liquid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IsaMill
The IsaMill is an energy-efficient mineral industry grinding mill that was jointly developed in the 1990s by Mount Isa Mines Limited ("MIM", a subsidiary of MIM Holdings Limited and now part of the Glencore Xstrata group of companies) and Netzsch Feinmahltechnik ("Netzsch"), a German manufacturer of bead mills.C R Fountain, ‘Isasmelt and IsaMills—models of successful R&D,’ in: ''Young Leaders’ Conference, Kalgoorlie, Western Australia, 19–21 March 2002'' (The Australasian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy: Melbourne, 2002), 1–12. The IsaMill is primarily known for its ultrafine grinding applications in the mining industry, but is also being used as a more efficient means of coarse grinding.G S Anderson and B D Burford, "IsaMill—the crossover from ultrafine to coarse grinding," in: ''Metallurgical Plant Design and Operating Strategies (MetPlant 2006), 18–19 September 2006, Perth, Western Australia'' (The Australasian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy: Melbourne, 2006 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
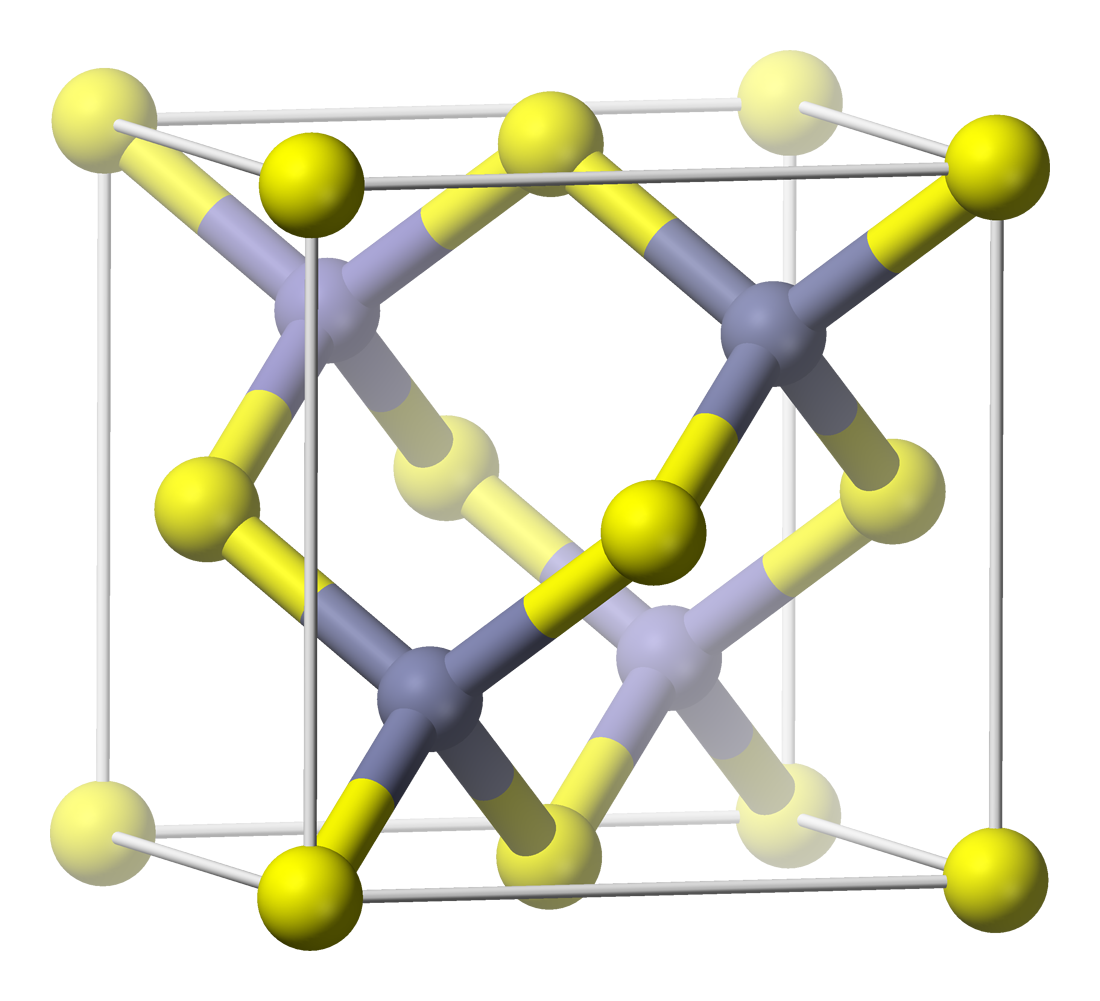
Sphalerite
Sphalerite (sometimes spelled sphaelerite) is a sulfide mineral with the chemical formula . It is the most important ore of zinc. Sphalerite is found in a variety of deposit types, but it is primarily in Sedimentary exhalative deposits, sedimentary exhalative, Carbonate-hosted lead-zinc ore deposits, Mississippi-Valley type, and Volcanogenic massive sulfide ore deposit, volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits. It is found in association with galena, chalcopyrite, pyrite (and other sulfide mineral, sulfides), calcite, dolomite (mineral), dolomite, quartz, rhodochrosite, and fluorite. German geologist Ernst Friedrich Glocker discovered sphalerite in 1847, naming it based on the Greek word ''sphaleros'', meaning "deceiving", due to the difficulty of identifying the mineral. In addition to zinc, sphalerite is an ore of cadmium, gallium, germanium, and indium. Miners have been known to refer to sphalerite as ''zinc blende'', ''black-jack'', and ''ruby blende''. Marmatite is an opaque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galena
Galena, also called lead glance, is the natural mineral form of lead(II) sulfide (PbS). It is the most important ore of lead and an important source of silver. Galena is one of the most abundant and widely distributed sulfide minerals. It crystallizes in the cubic crystal system often showing octahedral forms. It is often associated with the minerals sphalerite, calcite and fluorite. Occurrence Galena is the main ore of lead, used since ancient times, since lead can be smelted from galena in an ordinary wood fire. Galena typically is found in hydrothermal veins in association with sphalerite, marcasite, chalcopyrite, cerussite, anglesite, dolomite, calcite, quartz, barite, and fluorite. It is also found in association with sphalerite in low-temperature lead-zinc deposits within limestone beds. Minor amounts are found in contact metamorphic zones, in pegmatites, and disseminated in sedimentary rock. In some deposits the galena contains up to 0.5% silver, a byproduct that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Ethyl Xanthate
Sodium ethyl xanthate (SEX) is an organosulfur compound with the chemical formula . It is a pale yellow powder, which is usually obtained as the dihydrate. Sodium ethyl xanthate is used in the mining industry as a flotation agent. A closely related potassium ethyl xanthate (KEX) is obtained as the anhydrous salt. Production Akin to the preparation of most xanthates, sodium ethyl xanthate can be prepared by treating sodium ethoxide with carbon disulfide: Properties and reactions Sodium ethyl xanthate is a pale yellow powder. Its aqueous solutions are stable at high pH if not heated. It rapidly hydrolyses at pH <9 at 25 °C. It is the conjugate base of the unknown strong acid with p''K''a of 1.6 and p''K''b estimated as 12.4 for the . Sodium ethyl xanthate easily adsorbs on the surface of many sulfide minerals, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comminution
Comminution is the reduction of solid materials from one average particle size to a smaller average particle size, by crushing, grinding, cutting, vibrating, or other processes. In geology, it occurs naturally during faulting in the upper part of the Earth's crust. In industry, it is an important unit operation in mineral processing, ceramics, electronics, and other fields, accomplished with many types of mill. In dentistry, it is the result of mastication of food. In general medicine, it is one of the most traumatic forms of bone fracture. Within industrial uses, the purpose of comminution is to reduce the size and to increase the surface area of solids. It is also used to free useful materials from matrix materials in which they are embedded, and to concentrate minerals. Energy requirements The comminution of solid materials consumes energy, which is being used to break up the solid into smaller pieces. The comminution energy can be estimated by: * Rittinger's law, which assu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Gas Processing
Natural-gas processing is a range of industrial processes designed to purify raw natural gas by removing impurities, contaminants and higher molecular mass hydrocarbons to produce what is known as ''pipeline quality'' dry natural gas. Natural gas has to be processed in order to prepare it for final use and ensure that elimination of contaminants. Natural-gas processing starts underground or at the well-head. If the gas is being produced, for instance, alongside crude oil, the separation process already transpires as the fluid flows through the reservoir rocks until it reaches the well tubing. The process beginning at the wellhead extracts the composition of natural gas according to the type, depth, and location of the underground deposit and the geology of the area. Oil and natural gas are often found together in the same reservoir. The natural gas produced from oil wells is generally classified as ''associated-dissolved gas'' meaning that the gas had been associated with or disso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Plant
A chemical plant is an industrial process plant that manufactures (or otherwise processes) chemicals, usually on a large scale. The general objective of a chemical plant is to create new material wealth via the chemical or biological transformation and or separation of materials. Chemical plants use specialized equipment, units, and technology in the manufacturing process. Other kinds of plants, such as polymer, pharmaceutical, food, and some beverage production facilities, power plants, oil refineries or other refineries, natural gas processing and biochemical plants, water and wastewater treatment, and pollution control equipment use many technologies that have similarities to chemical plant technology such as fluid systems and chemical reactor systems. Some would consider an oil refinery or a pharmaceutical or polymer manufacturer to be effectively a chemical plant. Petrochemical plants (plants using chemicals from petroleum as a raw material or '' feedstock'') are usual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petrochemical
Petrochemicals (sometimes abbreviated as petchems) are the chemical products obtained from petroleum by refining. Some chemical compounds made from petroleum are also obtained from other fossil fuels, such as coal or natural gas, or renewable sources such as maize, palm fruit or sugar cane. The two most common petrochemical classes are olefins (including ethylene and propylene) and aromatics (including benzene, toluene and xylene isomers). Oil refineries produce olefins and aromatics by fluid catalytic cracking of petroleum fractions. Chemical plants produce olefins by steam cracking of natural gas liquids like ethane and propane. Aromatics are produced by catalytic reforming of naphtha. Olefins and aromatics are the building-blocks for a wide range of materials such as solvents, detergents, and adhesives. Olefins are the basis for polymers and oligomers used in plastics, resins, fibers, elastomers, lubricants, and gels. Global ethylene production was 190 million tonnes an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |