|
Flip Flop (electronics)
In electronics, a flip-flop or latch is a circuit that has two stable states and can be used to store state information – a bistable multivibrator. The circuit can be made to change state by signals applied to one or more control inputs and will have one or two outputs. It is the basic storage element in sequential logic. Flip-flops and latches are fundamental building blocks of digital electronics systems used in computers, communications, and many other types of systems. Flip-flops and latches are used as data storage elements. A flip-flop is a device which stores a single ''bit'' (binary digit) of data; one of its two states represents a "one" and the other represents a "zero". Such data storage can be used for storage of ''state'', and such a circuit is described as sequential logic in electronics. When used in a finite-state machine, the output and next state depend not only on its current input, but also on its current state (and hence, previous inputs). It can also be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transistor Bistable Interactive Animated-en
file:MOSFET Structure.png, upright=1.4, Metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET), showing Metal gate, gate (G), body (B), source (S) and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an insulating layer (pink). A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch electrical signals and electrical power, power. The transistor is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semiconductor material, usually with at least three Terminal (electronics), terminals for connection to an electronic circuit. A voltage or Electric current, current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals controls the current through another pair of terminals. Because the controlled (output) power can be higher than the controlling (input) power, a transistor can amplify a signal. Some transistors are packaged individually, but many more are found embedded in integrated circuits. Austria- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multivibrator
A multivibrator is an electronic circuit used to implement a variety of simple two-state devices such as relaxation oscillators, timers, and flip-flops. The first multivibrator circuit, the astable multivibrator oscillator, was invented by Henri Abraham and Eugene Bloch during World War I. It consisted of two vacuum tube amplifiers cross-coupled by a resistor-capacitor network. They called their circuit a "multivibrator" because its output waveform was rich in harmonics. A variety of active devices can be used to implement multivibrators that produce similar harmonic-rich wave forms; these include transistors, neon lamps, tunnel diodes and others. Although cross-coupled devices are a common form, single-element multivibrator oscillators are also common. The three types of multivibrator circuits are: * Astable multivibrator, in which the circuit is not stable in either state —it continually switches from one state to the other. It functions as a relaxation oscillator. * Monos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NAND Gate
In digital electronics, a NAND gate (NOT-AND) is a logic gate which produces an output which is false only if all its inputs are true; thus its output is complement to that of an AND gate. A LOW (0) output results only if all the inputs to the gate are HIGH (1); if any input is LOW (0), a HIGH (1) output results. A NAND gate is made using transistors and junction diodes. By De Morgan's laws, a two-input NAND gate's logic may be expressed as =+, making a NAND gate equivalent to inverters followed by an OR gate. The NAND gate is significant because any boolean function can be implemented by using a combination of NAND gates. This property is called functional completeness. It shares this property with the NOR gate. Digital systems employing certain logic circuits take advantage of NAND's functional completeness. The function is logically equivalent to One way of expressing A NAND B is \overline, where the symbol signifies AND and the bar signifies the negation of the express ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NOR Gate
The NOR gate is a digital logic gate that implements logical NOR - it behaves according to the truth table to the right. A HIGH output (1) results if both the inputs to the gate are LOW (0); if one or both input is HIGH (1), a LOW output (0) results. NOR is the result of the negation of the OR operator. It can also in some senses be seen as the inverse of an AND gate. NOR is a functionally complete operation—NOR gates can be combined to generate any other logical function. It shares this property with the NAND gate. By contrast, the OR operator is ''monotonic'' as it can only change LOW to HIGH but not vice versa. In most, but not all, circuit implementations, the negation comes for free—including CMOS and TTL. In such logic families, OR is the more complicated operation; it may use a NOR followed by a NOT. A significant exception is some forms of the domino logic family. The original Apollo Guidance Computer used 4,100 integrated circuits (IC), each one containing o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal Edge
In electronics, a signal edge is a transition of a digital signal from low to high or from high to low: * A rising edge (or positive edge) is the low-to-high transition. * A falling edge (or negative edge) is the high-to-low transition. In the case of a pulse, which consists of two edges: * The leading edge (or front edge) is the first edge of the pulse. * The trailing edge (or back edge) is the second edge of the pulse. See also *Flip-flop (electronics), an edge-triggered circuit *Rise time In electronics, when describing a voltage or current step function, rise time is the time taken by a signal to change from a specified low value to a specified high value. These values may be expressed as ratiosSee for example , and . or, equivale ..., for a signal transition References Digital electronics {{Electronics-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inverter (logic Gate)
In digital logic, an inverter or NOT gate is a logic gate which implements logical negation. It outputs a bit opposite of the bit that is put into it. The bits are typically implemented as two differing voltage levels. Description The NOT gate outputs a zero when given a one, and a one when given a zero. Hence, it inverts its inputs. Colloquially, this inversion of bits is called "flipping" bits. As with all binary logic gates, other pairs of symbols such as true and false, or high and low may be used in lieu of one and zero. It is equivalent to the logical negation operator (¬) in mathematical logic. Because it has only one input, it is a unary operation and has the simplest type of truth table. It is also called the complement gate because it produces the ones' complement of a binary number, swapping 0s and 1s. The NOT gate is one of three basic logic gates from which any Boolean circuit may be built up. Together with the AND gate and the OR gate, any function in binary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
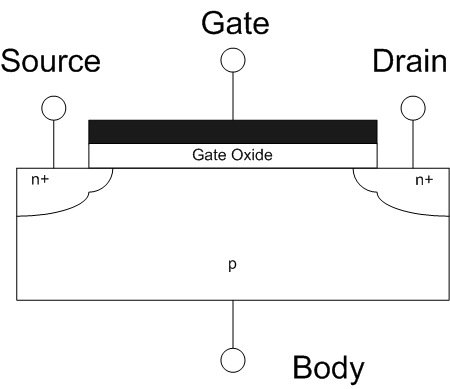
Field Effect Transistor
The field-effect transistor (FET) is a type of transistor that uses an electric field to control the flow of current in a semiconductor. FETs (JFETs or MOSFETs) are devices with three terminals: ''source'', ''gate'', and ''drain''. FETs control the flow of current by the application of a voltage to the gate, which in turn alters the conductivity between the drain and source. FETs are also known as unipolar transistors since they involve single-carrier-type operation. That is, FETs use either electrons (n-channel) or holes (p-channel) as charge carriers in their operation, but not both. Many different types of field effect transistors exist. Field effect transistors generally display very high input impedance at low frequencies. The most widely used field-effect transistor is the MOSFET (metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor). History The concept of a field-effect transistor (FET) was first patented by Austro-Hungarian physicist Julius Edgar Lilienfeld in 1925 an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bipolar Transistor
A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a type of transistor that uses both electrons and electron holes as charge carriers. In contrast, a unipolar transistor, such as a field-effect transistor, uses only one kind of charge carrier. A bipolar transistor allows a small current injected at one of its terminals to control a much larger current flowing between the terminals, making the device capable of amplification or switching. BJTs use two p–n junctions between two semiconductor types, n-type and p-type, which are regions in a single crystal of material. The junctions can be made in several different ways, such as changing the doping of the semiconductor material as it is grown, by depositing metal pellets to form alloy junctions, or by such methods as diffusion of n-type and p-type doping substances into the crystal. The superior predictability and performance of junction transistors quickly displaced the original point-contact transistor. Diffused transistors, along wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TTL Flip-flop ", a single by South Korean girl group T-ara and boy band Supernova
{{Disambiguation ...
TTL may refer to: Photography * Through-the-lens metering, a camera feature * Zenit TTL, an SLR film camera named for its TTL metering capability Technology * Time to live, a computer data lifespan-limiting mechanism * Transistor–transistor logic, a family of integrated-circuit digital logic ** Differential TTL, a serial signaling standard based on TTL * Turtle (syntax), a computer data format used in semantic web technologies Other uses * Taiwan Tobacco and Liquor, a state-owned manufacturer * "TTL (Time to Love) ''Absolute First Album'' is the first studio album and debut Korean release by South Korean girl group T-ara. It was released on November 27, 2009, through Core Contents Media. T-ara sought to showcase "two different charms" through ''Absolute Fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hughes Aircraft Co
The Hughes Aircraft Company was a major American aerospace and defense contractor founded on February 14, 1934 by Howard Hughes in Glendale, California, as a division of Hughes Tool Company. The company was known for producing, among other products, the Hughes H-4 Hercules ''Spruce Goose'' aircraft, the atmospheric entry probe carried by the ''Galileo'' spacecraft, and the AIM-4 Falcon guided missile. Hughes Aircraft was founded to construct Hughes' H-1 Racer world speed record aircraft, and it later modified aircraft for his transcontinental and global circumnavigation speed record flights. The company relocated to Culver City, California, in 1940 and began manufacturing aircraft parts as a subcontractor. Hughes attempted to mold it into a major military aircraft manufacturer during World War II; however, its initial military projects ended in failure, with millions of dollars in U.S. government funds expended but only three aircraft actually built, resulting in a highly publi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hughes Aircraft
The Hughes Aircraft Company was a major American aerospace and defense contractor founded on February 14, 1934 by Howard Hughes Howard Robard Hughes Jr. (December 24, 1905 – April 5, 1976) was an American business magnate, record-setting pilot, engineer, film producer, and philanthropist, known during his lifetime as one of the most influential and richest people in th ... in Glendale, California, as a division of Hughes Tool Company. The company was known for producing, among other products, the Hughes H-4 Hercules ''Spruce Goose'' aircraft, the atmospheric entry probe carried by the Galileo (spacecraft), ''Galileo'' spacecraft, and the AIM-4 Falcon guided missile. Hughes Aircraft was founded to construct Hughes' Hughes H-1 Racer, H-1 Racer world speed record aircraft, and it later modified aircraft for his transcontinental and global circumnavigation speed record flights. The company relocated to Culver City, California, in 1940 and began manufacturing aircraft parts as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)