|
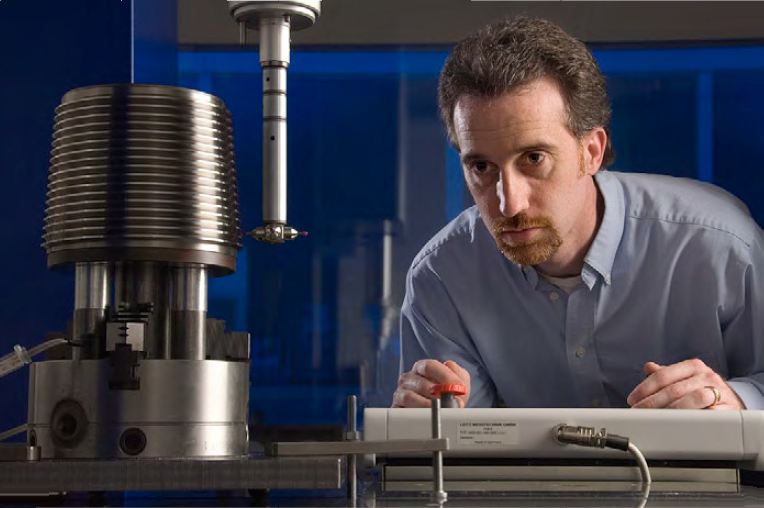
Flexure
A flexure is a flexible element (or combination of elements) engineered to be compliant in specific degrees of freedom. Flexures are a design feature used by design engineers (usually mechanical engineers) for providing adjustment or compliance in a design. Flexure types Most compound flexure designs are composed of 3 fundamental types of flexure: * Pin flexure- a thin bar or cylinder of material, constrains 3 degrees of freedom when geometry matches a notch cutout. * Blade flexure- thin sheet of material, constrains 3 degrees of freedom. * Notch flexure- thin cutout on both sides of a thick piece of material, constrains 5 degrees of freedom Since single flexure features are limited both in travel capability and degrees of freedom available, compound flexure systems are designed using combinations of these component features. Using compound flexures, complex motion profiles with specific degrees of freedom and relatively long travel distances are possible. Design asp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flexure Pivot
A flexure is a flexible element (or combination of elements) engineered to be compliant in specific degrees of freedom. Flexures are a design feature used by design engineers (usually mechanical engineers) for providing adjustment or compliance in a design. Flexure types Most compound flexure designs are composed of 3 fundamental types of flexure: * Pin flexure- a thin bar or cylinder of material, constrains 3 degrees of freedom when geometry matches a notch cutout. * Blade flexure- thin sheet of material, constrains 3 degrees of freedom. * Notch flexure- thin cutout on both sides of a thick piece of material, constrains 5 degrees of freedom Since single flexure features are limited both in travel capability and degrees of freedom available, compound flexure systems are designed using combinations of these component features. Using compound flexures, complex motion profiles with specific degrees of freedom and relatively long travel distances are possible. Design asp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bearing (mechanical)
A bearing is a machine element that constrains relative motion to only the desired motion, and reduces friction between moving parts. The design of the bearing may, for example, provide for free linear movement of the moving part or for free rotation around a fixed axis; or, it may ''prevent'' a motion by controlling the vectors of normal forces that bear on the moving parts. Most bearings facilitate the desired motion by minimizing friction. Bearings are classified broadly according to the type of operation, the motions allowed, or to the directions of the loads (forces) applied to the parts. Rotary bearings hold rotating components such as shafts or axles within mechanical systems, and transfer axial and radial loads from the source of the load to the structure supporting it. The simplest form of bearing, the ''plain bearing'', consists of a shaft rotating in a hole. Lubrication is used to reduce friction. In the ''ball bearing'' and ''roller bearing'', to reduce sliding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bending
In applied mechanics, bending (also known as flexure) characterizes the behavior of a slender structural element subjected to an external load applied perpendicularly to a longitudinal axis of the element. The structural element is assumed to be such that at least one of its dimensions is a small fraction, typically 1/10 or less, of the other two.Boresi, A. P. and Schmidt, R. J. and Sidebottom, O. M., 1993, Advanced mechanics of materials, John Wiley and Sons, New York. When the length is considerably longer than the width and the thickness, the element is called a beam. For example, a closet rod sagging under the weight of clothes on clothes hangers is an example of a beam experiencing bending. On the other hand, a shell is a structure of any geometric form where the length and the width are of the same order of magnitude but the thickness of the structure (known as the 'wall') is considerably smaller. A large diameter, but thin-walled, short tube supported at its ends and loa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precision Engineering
Precision engineering is a subdiscipline of electrical engineering, software engineering, electronics engineering, mechanical engineering, and optical engineering concerned with designing machines, fixtures, and other structures that have exceptionally low tolerances, are repeatable, and are stable over time. These approaches have applications in machine tools, MEMS, NEMS, optoelectronics design, and many other fields. Overview Professors Hiromu Nakazawa and Pat McKeown provide the following list of goals for precision engineering: # Create a highly precise movement. # Reduce the dispersion of the product's or part's function. # Eliminate fitting and promote assembly, especially automatic assembly. # Reduce the initial cost. # Reduce the running cost. # Extend the life span. # Enable the design safety factor to be lowered. # Improve interchangeability of components so that corresponding parts made by other factories or firms can be used in their place. # Improve quality contro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Living Hinge
A living hinge or integral hinge is a thin flexible hinge (flexure bearing) made from the same material as the two rigid pieces it connects. It is typically thinned or cut to allow the rigid pieces to bend along the line of the hinge. The minimal friction and very little wear in such a hinge makes it useful in the design of microelectromechanical systems, and the low cost and ease of manufacturing makes them quite common in clamshell containers and other disposable, recyclable packaging. Plastic Plastic living hinges are typically manufactured in an injection molding operation that creates all three parts at one time as a single piece, and if correctly designed and constructed, it can remain functional over the life of the part. Thermoforming can also produce hinged products. Polyethylene and polypropylene are considered to be the best resins for living hinges, due to their excellent fatigue resistance. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is also common. Wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tic Tac
Tic Tac (stylized as "tic tac") is a brand of small, hard mint manufactured by the Italian company Ferrero. They were first produced in 1969 and are now available in a variety of flavours in over 100 countries. Tic Tacs are usually sold in small transparent plastic boxes with a flip-action living hinge lid. Originally, Tic Tacs were dyed specific colours for different flavours, although in many countries the transparent plastic boxes are now coloured and the actual Tic Tacs are white. Tic Tac has featured advertising that emphasizes the low calorie count of the mints. Most flavours have approximately 1.9 calories per mint. History Tic Tac were first introduced by Ferrero in 1969, under the name "Refreshing Mints". In 1970, the name was changed to Tic Tac, after the distinctive clicking sound made by the pack being opened and closed. Besides the original mint and orange flavours, several new varieties were added, including aniseed, cinnamon (or "Winter Warmer"), an orange and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA MSL FLEXURE WHEEL
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research. NASA was established in 1958, succeeding the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), to give the U.S. space development effort a distinctly civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. NASA has since led most American space exploration, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968-1972 Apollo Moon landing missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. NASA supports the International Space Station and oversees the development of the Orion spacecraft and the Space Launch System for the crewed lunar Artemis program, Commercial Crew spacecraft, and the planned Lunar Gateway space station. The agency is also responsible for the Launch Services Program, which provides oversight of launch operations and countdown management f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA MER FLEXURE WHEEL
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research. NASA was established in 1958, succeeding the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), to give the U.S. space development effort a distinctly civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. NASA has since led most American space exploration, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968-1972 Apollo Moon landing missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. NASA supports the International Space Station and oversees the development of the Orion spacecraft and the Space Launch System for the crewed lunar Artemis program, Commercial Crew spacecraft, and the planned Lunar Gateway space station. The agency is also responsible for the Launch Services Program, which provides oversight of launch operations and countdown management for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Failure Cause
Failure causes are defects in design, process, quality, or part application, which are the underlying cause of a failure or which initiate a process which leads to failure. Where failure depends on the user of the product or process, then human error must be considered. Component failure / failure modes A part failure mode is the way in which a component failed "functionally" on the component level. Often a part has only a few failure modes. For example, a relay may fail to open or close contacts on demand. The failure mechanism that caused this can be of many different kinds, and often multiple factors play a role at the same time. They include corrosion, welding of contacts due to an abnormal electric current, return spring fatigue failure, unintended command failure, dust accumulation and blockage of mechanism, etc. Seldom only one cause (hazard) can be identified that creates system failures. The real root causes can in theory in most cases be traced back to some kind of huma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatigue (material)
In materials science, fatigue is the initiation and propagation of cracks in a material due to cyclic loading. Once a fatigue crack has initiated, it grows a small amount with each loading cycle, typically producing striations on some parts of the fracture surface. The crack will continue to grow until it reaches a critical size, which occurs when the stress intensity factor of the crack exceeds the fracture toughness of the material, producing rapid propagation and typically complete fracture of the structure. Fatigue has traditionally been associated with the failure of metal components which led to the term metal fatigue. In the nineteenth century, the sudden failing of metal railway axles was thought to be caused by the metal ''crystallising'' because of the brittle appearance of the fracture surface, but this has since been disproved. Most materials, such as composites, plastics and ceramics, seem to experience some sort of fatigue-related failure. To aid in predicting t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yield (engineering)
In materials science and engineering, the yield point is the point on a stress-strain curve that indicates the limit of elastic behavior and the beginning of plastic behavior. Below the yield point, a material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the applied stress is removed. Once the yield point is passed, some fraction of the deformation will be permanent and non-reversible and is known as plastic deformation. The yield strength or yield stress is a material property and is the stress corresponding to the yield point at which the material begins to deform plastically. The yield strength is often used to determine the maximum allowable load in a mechanical component, since it represents the upper limit to forces that can be applied without producing permanent deformation. In some materials, such as aluminium, there is a gradual onset of non-linear behavior, making the precise yield point difficult to determine. In such a case, the offset yiel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |