|
Fire-control
A fire-control system (FCS) is a number of components working together, usually a gun data computer, a Director (military), director and radar, which is designed to assist a ranged weapon system to target, track, and hit a target. It performs the same task as a human Crew-served weapon, gunner firing a weapon, but attempts to do so faster and more accurately. Naval fire control Origins The original fire-control systems were developed for ships. The early history of naval fire control was dominated by the engagement of targets within visual range (also referred to as indirect fire, direct fire). In fact, most naval engagements before 1800 were conducted at ranges of . Even during the American Civil War, the Battle of Hampton Roads, famous engagement between and was often conducted at less than range. Rapid technical improvements in the late 19th century greatly increased the range at which gunfire was possible. Rifled guns of much larger size firing explosive shells of lig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Pollen
Arthur Joseph Hungerford Pollen (13 September 1866 – 28 January 1937) was an English journalist, businessman, and commentator on naval affairs who devised a new computerised fire-control system for use on battleships prior to the First World War. His most important technical innovation was one of the world's first electrically-powered analogue computers, patented as the Argo Clock: a differential analyser which enabled big guns to engage with long-range targets when both ships were moving at speed in different directions. Early life Pollen was born on 13 September 1866, the sixth son and eighth child of eight sons and two daughters born to John Hungerford Pollen (senior), John Hungerford Pollen and Maria Margaret Pollen. His father being a leading convert to Catholicism along with Cardinal Newman, Arthur was educated at the school which the latter founded in Birmingham, The Oratory School (1878–1884). He then went up to read Modern History at Trinity College, Oxford where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gun Data Computer
The gun data computer was a series of artillery computers used by the U.S. Army for coastal artillery, field artillery and anti-aircraft artillery applications. For antiaircraft applications they were used in conjunction with a director computer. Variations * M1: This was used by seacoast artillery for major-caliber seacoast guns. It computed continuous firing data for a battery of two guns that were separated by not more than . It utilised the same type of input data furnished by a range section with the then-current (1940) types of position-finding and fire-control equipment. * M3: This was used in conjunction with the M9 and M10 directors to compute all required firing data, i.e. azimuth, elevation and fuze time. The computations were made continuously, so that the gun was at all times correctly pointed and the fuze correctly timed for firing at any instant. The computer was mounted in the M13 or M14 director trailer. * M4: This was identical to the M3 except for some me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Director (military)
A director, also called an auxiliary predictor, is a mechanical or electronic computer that continuously calculates trigonometric firing solutions for use against a moving target, and transmits targeting data to direct the weapon firing crew. Naval warships For warships of the 20th century, the director is part of the fire control system; it passes information to the computer that calculates range and elevation for the guns. Typically, positions on the ship measured range and bearing of the target; these instantaneous measurements are used to calculate rate of change values, and the computer ("fire control table" in Royal Navy terms) then predicts the correct firing solution, taking into account other parameters, such as wind direction, air temperature, and ballistic factors for the guns. The British Royal Navy widely deployed the Pollen and Dreyer Fire Control Tables during the First World War, while in World War II a widely used computer in the US Navy was the electro-mec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analog Computer
An analog computer or analogue computer is a type of computation machine (computer) that uses physical phenomena such as Electrical network, electrical, Mechanics, mechanical, or Hydraulics, hydraulic quantities behaving according to the mathematical principles in question (''analog signals'') to Scientific modelling, model the problem being solved. In contrast, digital computers represent varying quantities symbolically and by discrete values of both time and amplitude (digital signals). Analog computers can have a very wide range of complexity. Slide rules and nomograms are the simplest, while naval gunfire control computers and large hybrid digital/analog computers were among the most complicated. Complex mechanisms for process control and protective relays used analog computation to perform control and protective functions. Analog computers were widely used in scientific and industrial applications even after the advent of digital computers, because at the time they were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rangekeeper
Rangekeepers were electromechanical fire control computers used primarily during the early part of the 20th century. They were sophisticated analog computers whose development reached its zenith following World War II, specifically the Computer Mk 47 in the Mk 68 Gun Fire Control system. During World War II, rangekeepers directed gunfire on land, sea, and in the air. While rangekeepers were widely deployed, the most sophisticated rangekeepers were mounted on warships to direct the fire of long-range guns.Technically, it would be more accurate to use the term "rifle" for long-range ship-board cannon. However, the term "gun" is commonly used and that nomenclature is maintained here. These warship-based computing devices needed to be sophisticated because the problem of calculating gun angles in a naval engagement is very complex. In a naval engagement, both the ship firing the gun and the target are moving with respect to each other. In addition, the ship firing its gun is not a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
880mm Flak D WWII Db
88 may refer to: * 88 (number) * one of the years 88 BC, AD 88, 1988, 2088 * Highway 88, see List of highways numbered 88 * The 88 (San Jose), a residential skyscraper in San Jose, California, USA * The 88, a nickname for the piano A piano is a keyboard instrument that produces sound when its keys are depressed, activating an Action (music), action mechanism where hammers strike String (music), strings. Modern pianos have a row of 88 black and white keys, tuned to a c ... derived from the number of keys it typically has * A Morse code abbreviation meaning "Love and kisses" * ''88'' (film), a 2015 film directed by April Mullen, starring Katharine Isabelle * Atomic number 88: radium * The butterfly genus '' Diaethria'', which has an 88-like pattern on its wings * The butterfly genus '' Callicore'', which has an 88-like pattern on its wings * 88, a neo-Nazi symbol and code number for "Heil Hitler," based on "H" being the eighth letter of the alphabet * 88 Thisbe, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yaw Angle
The Euler angles are three angles introduced by Leonhard Euler to describe the Orientation (geometry), orientation of a rigid body with respect to a fixed coordinate system.Novi Commentarii academiae scientiarum Petropolitanae 20, 1776, pp. 189–207 (E478PDF/ref> They can also represent the orientation of a mobile frame of reference in physics or the orientation of a general Basis (linear algebra), basis in three dimensional linear algebra. Classic Euler angles usually take the inclination angle in such a way that zero degrees represent the vertical orientation. Alternative forms were later introduced by Peter Guthrie Tait and George H. Bryan intended for use in aeronautics and engineering in which zero degrees represent the horizontal position. Chained rotations equivalence Euler angles can be defined by elemental geometry or by composition of rotations (i.e. chained rotations). The geometrical definition demonstrates that three consecutive ''elemental rotations'' (rotatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
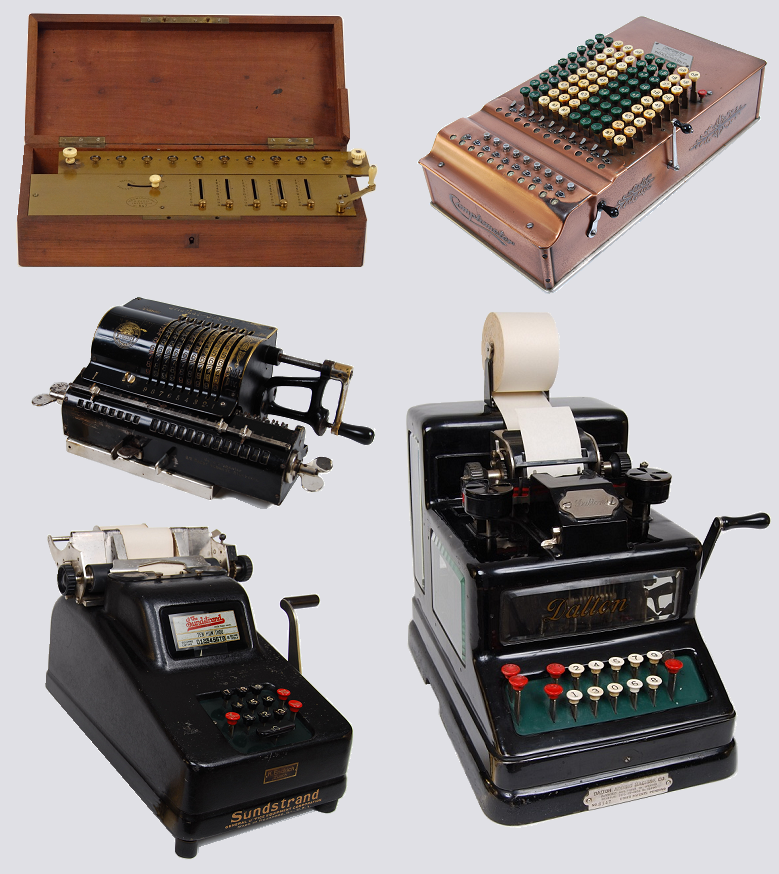
Calculating Machine
A mechanical calculator, or calculating machine, is a mechanical device used to perform the basic operations of arithmetic automatically, or a simulation like an analog computer or a slide rule. Most mechanical calculators were comparable in size to small desktop computers and have been rendered obsolete by the advent of the electronic calculator and the digital computer. Surviving notes from Wilhelm Schickard in 1623 reveal that he designed and had built the earliest known apparatus fulfilling the widely accepted definition of a mechanical calculator (a counting machine with an automated tens-carry). His machine was composed of two sets of technologies: first an abacus made of Napier's bones, to simplify multiplications and divisions first described six years earlier in 1617, and for the mechanical part, it had a dialed pedometer to perform additions and subtractions. A study of the surviving notes shows a machine that could have jammed after a few entries on the same dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin
William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin (26 June 182417 December 1907), was a British mathematician, Mathematical physics, mathematical physicist and engineer. Born in Belfast, he was the Professor of Natural Philosophy (Glasgow), professor of Natural Philosophy at the University of Glasgow for 53 years, where he undertook significant research on the mathematical analysis of electricity, was instrumental in the formulation of the first and second laws of thermodynamics, and contributed significantly to unifying physics, which was then in its infancy of development as an emerging academic discipline. He received the Royal Society's Copley Medal in 1883 and served as its President of the Royal Society, president from 1890 to 1895. In 1892, he became the first scientist to be elevated to the House of Lords. Absolute temperatures are stated in units of kelvin in Lord Kelvin's honour. While the existence of a coldest possible temperature, absolute zero, was known before his work, Kelvin d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malta
Malta, officially the Republic of Malta, is an island country in Southern Europe located in the Mediterranean Sea, between Sicily and North Africa. It consists of an archipelago south of Italy, east of Tunisia, and north of Libya. The two official languages are Maltese language, Maltese and English language, English. The country's capital is Valletta, which is the smallest capital city in the EU by both area and population. It was also the first World Heritage Site, World Heritage City in Europe to become a European Capital of Culture in 2018. With a population of about 542,000 over an area of , Malta is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, tenth-smallest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population density, ninth-most densely populated. Various sources consider the country to consist of a single urban region, for which it is often described as a city-state. Malta has been inhabited since at least 6500 BC, during the Mesolith ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
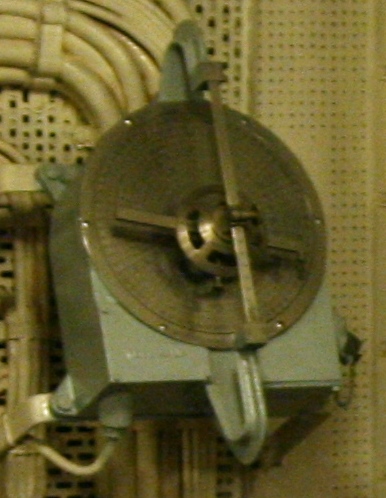
Dumaresq
The Dumaresq is a mechanical calculating device invented around 1902 by Lieutenant John Dumaresq of the Royal Navy. It is an analog computer that relates vital variables of the fire control problem to the movement of one's own ship and that of a target ship. It was often used with other devices, such as a Vickers range clock, to generate range and deflection data so the gun sights of the ship could be continuously set. A number of versions of the Dumaresq were produced of increasing complexity as development proceeded. Geometric principle The dumaresq relies on sliding and rotating bars and dials to represent the motion of the two ships. Normally the motion of the ship carrying the dumaresq is represented by a metal bar running above the instrument. Below the bar is a round metal plate inscribed with a coordinate plot, and an angle scale around its outer rim. The fixed bar is mounted on a bearing that allows it to be turned to represent the direction of motion of the ship, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederic Charles Dreyer
Admiral Sir Frederic Charles Dreyer (8 January 1878 – 11 December 1956) was an officer of the Royal Navy. A gunnery expert, he developed a fire control system for British warships, and served as flag captain to Admiral Sir John Jellicoe at the Battle of Jutland. He retired with the rank of admiral in 1943, having served through two world wars and having already retired once. Background and early life Frederic Dreyer was born on 8 January 1878 in the Irish town of Parsonstown (now Birr) in King's County (now County Offaly), the second son of the Danish-born astronomer John Louis Emil Dreyer who was director of the Armagh Observatory. Educated at The Royal School, Armagh, in 1891 Dreyer joined the Royal Navy and entered the Royal Naval College, Dartmouth. Royal Navy career Early years At Dartmouth Dreyer performed well in his examinations and was placed fifth in his term. He then served as a midshipman in HMS ''Anson'' (1893–1896) and HMS ''Barfleur'' (1896–1897). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |