|
Fighting Withdrawal
A tactical withdrawal or retreating defensive action is a type of military operation, generally meaning that retreating forces draw back while maintaining contact with the enemy. A withdrawal may be undertaken as part of a general retreat, to consolidate forces, to occupy ground that is more easily defended, force the enemy to overextend to secure a decisive victory, or to lead the enemy into an ambush. It is considered a relatively risky operation, requiring discipline to keep from turning into a disorganized rout or at the very least doing severe damage to the military's morale. Tactical withdrawal A withdrawal may be anticipated, as when a defending force is outmatched or on disadvantageous ground, but must cause as much damage to an enemy as possible. In such a case, the retreating force may employ a number of tactics and strategies to further impede the enemy's progress. This could include setting mines or booby traps during or before withdrawal, leading the enemy into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
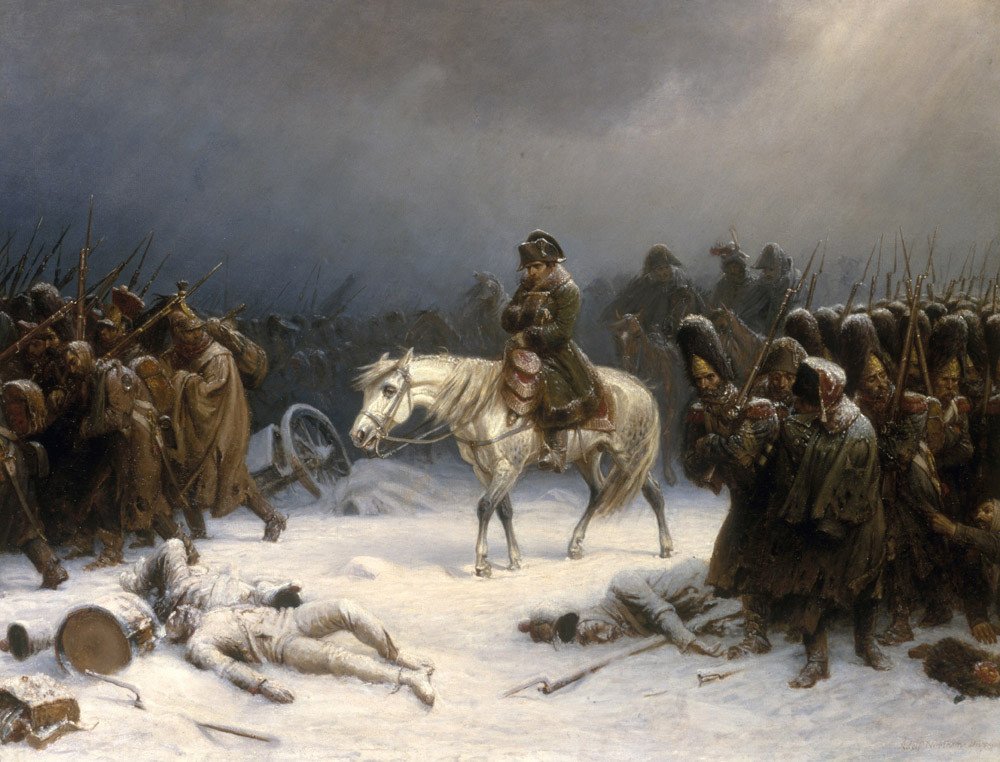
Napoleons Retreat From Moscow
Napoleons is a town in Victoria, Australia in the Golden Plains Shire local government area, west of the state capital, Melbourne Melbourne ( ; Boonwurrung/Woiwurrung: ''Narrm'' or ''Naarm'') is the capital and most populous city of the Australian state of Victoria, and the second-most populous city in both Australia and Oceania. Its name generally refers to a met .... At the , Napoleons had a population of 553. The Post Office opened on 1 September 1862, was known as Napoleon until around 1950, and closed in 1971. A Community Postal Agency opened at the Napoleons store on 17 April 2012. The town is served by Napoleons Primary School, with an enrolment of 102. The current school opened in 2002. The original school, situated nearby, opened in 1870. References Towns in Victoria (Australia) Golden Plains Shire {{GrampiansAU-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member of the large family of Mongolic peoples. The Oirats in Western Mongolia as well as the Buryats and Kalmyks of Russia are classified either as distinct ethno-linguistic groups or subgroups of Mongols. The Mongols are bound together by a common heritage and ethnic identity. Their indigenous dialects are collectively known as the Mongolian language. The ancestors of the modern-day Mongols are referred to as Proto-Mongols. Definition Broadly defined, the term includes the Mongols proper (also known as the Khalkha Mongols), Buryats, Oirats, the Kalmyk people and the Southern Mongols. The latter comprises the Abaga Mongols, Abaganar, Aohans, Baarins, Chahars, Eastern Dorbets, Gorlos Mongols, Jalaids, Jaruud, Kharchins, Khishig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Strategy
Military strategy is a set of ideas implemented by military organizations to pursue desired strategic goals. Derived from the Greek word '' strategos'', the term strategy, when it appeared in use during the 18th century, was seen in its narrow sense as the "art of the general", or "'the art of arrangement" of troops. Military strategy deals with the planning and conduct of campaigns, the movement and disposition of forces, and the deception of the enemy. The father of Western modern strategic studies, Carl von Clausewitz (1780–1831), defined military strategy as "the employment of battles to gain the end of war." B. H. Liddell Hart's definition put less emphasis on battles, defining strategy as "the art of distributing and applying military means to fulfill the ends of policy". Hence, both gave the pre-eminence to political aims over military goals. Sun Tzu (544–496 BC) is often considered as the father of Eastern military strategy and greatly influenced Chinese, Japanese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maneuver Tactics
Maneuver (American English), manoeuvre (British English), manoeuver, manœuver (also spelled, directly from the French, as manœuvre) denotes one's tactical move, or series of moves, that improves or maintains one's strategic situation in a competitive environment or avoids a worse situation. Military or naval * Military exercise * Maneuver warfare * Military tactics * Military strategy Controlled change in movement * Aerobatic maneuver * Orbital maneuver Skilled movement or procedure * Credé's maneuver * Gowers's maneuver * Heimlich maneuver, abdominal thrusts to relieve choking * Kocher maneuver * Leopold's maneuvers * McRoberts maneuver * Müller's maneuver * Phalen's maneuver * Pringle maneuver * Sellick maneuver * Valsalva's maneuver Other * Moose test The evasive manoeuvre test ( Swedish: ''Undanmanöverprov''; colloquial: moose test or elk test; Swedish: ''Älgtest'', German: ''Elchtest'') is performed to determine how well a certain vehicle evades a suddenly a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German 21st Panzer Division
The 21st Panzer Division was a German armoured division best known for its role in the battles of the North African Campaign from 1941–1943 during World War II when it was one of the two armoured divisions making up the Deutsches Afrikakorps (DAK). 1941–1942 The Italian army group in North Africa was routed by the British Commonwealth Western Desert Force in Operation Compass 9 December 1940 – 9 February 1941 under General Wavell. The German Armed Forces High Command ('' Oberkommando der Wehrmacht'') decided to send a "blocking force" to Libya to support the Italian army, commanded by the future Field Marshal Erwin Rommel. The German blocking force at first was based only on Panzer Regiment 5, which was put together from the second regiment of the 3rd Panzer Division. These elements were organized into the 5th Light Division when they arrived in Africa from 10 February – 12 March 1941. On 2 March 1941, the first 8.8 cm "88" dual purpose anti-aircraft/anti-tank guns ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1st Armored Division (United States)
The 1st Armored Division, nicknamed "Old Ironsides," is a combined arms division of the United States Army. The division is part of III Armored Corps and operates out of Fort Bliss in El Paso, Texas. It was the first armored division of the United States' Army to see battle in World War II. Since World War II, the division has been involved in the Korean War, Cuban Missile Crisis, Persian Gulf War, Iraq, Afghanistan, and several other operations. The division has also received numerous awards and recognition. Insignia The division was nicknamed "Old Ironsides" by its first commander, Major General Bruce Magruder, after he saw a picture of the frigate USS ''Constitution'', also nicknamed "Old Ironsides". The large "1" at the top represents the numerical designation of the division and the insignia is used as a basis for most of the other sub-unit insignias. In January 1918, the Tank Corps of the United States Army was established under Colonel Samuel Rockenbach. At his dir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Kasserine Pass
The Battle of Kasserine Pass was a series of battles of the Tunisian campaign of World War II that took place in February 1943 at Kasserine Pass, a gap in the Grand Dorsal chain of the Atlas Mountains in west central Tunisia. The Axis forces, led by ''Generalfeldmarschall'' Erwin Rommel, were primarily from the ''Afrika Korps'' Assault Group, the Italian ''Centauro'' Armored Division and two Panzer divisions detached from the 5th Panzer Army, while the Allied forces consisted of the U.S. II Corps (Major General Lloyd Fredendall), the British 6th Armoured Division (Major-General Charles Keightley) and other parts of the First Army (Lieutenant-General Kenneth Anderson). The battle was the first major engagement between U.S. and Axis forces in Africa. The American troops were numerically superior, but inexperienced and poorly led; they suffered many casualties and were quickly pushed back over from their original positions west of Faïd Pass. After the early defeat, elem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Defeat In Detail
Defeat in detail, or divide and conquer, is a military tactic of bringing a large portion of one's own force to bear on small enemy units in sequence, rather than engaging the bulk of the enemy force all at once. This exposes one's own units to many small risks but allows for the eventual destruction of an entire enemy force. Use In military strategy and tactics, a recurring theme is that units are strengthened by proximity to supporting units. Nearby units can fire on an attacker's flank, lend indirect fire support such as artillery or maneuver to counterattack. ''Defeat in detail'' is the tactic of exploiting failures of an enemy force to co-ordinate and support the various smaller units that make up the force. An overwhelming attack on one defending subunit minimizes casualties on the attacking side and can be repeated a number of times against the defending subunits until all are eliminated. An attacker can successfully conduct the tactic of defeat in detail by exploiting the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
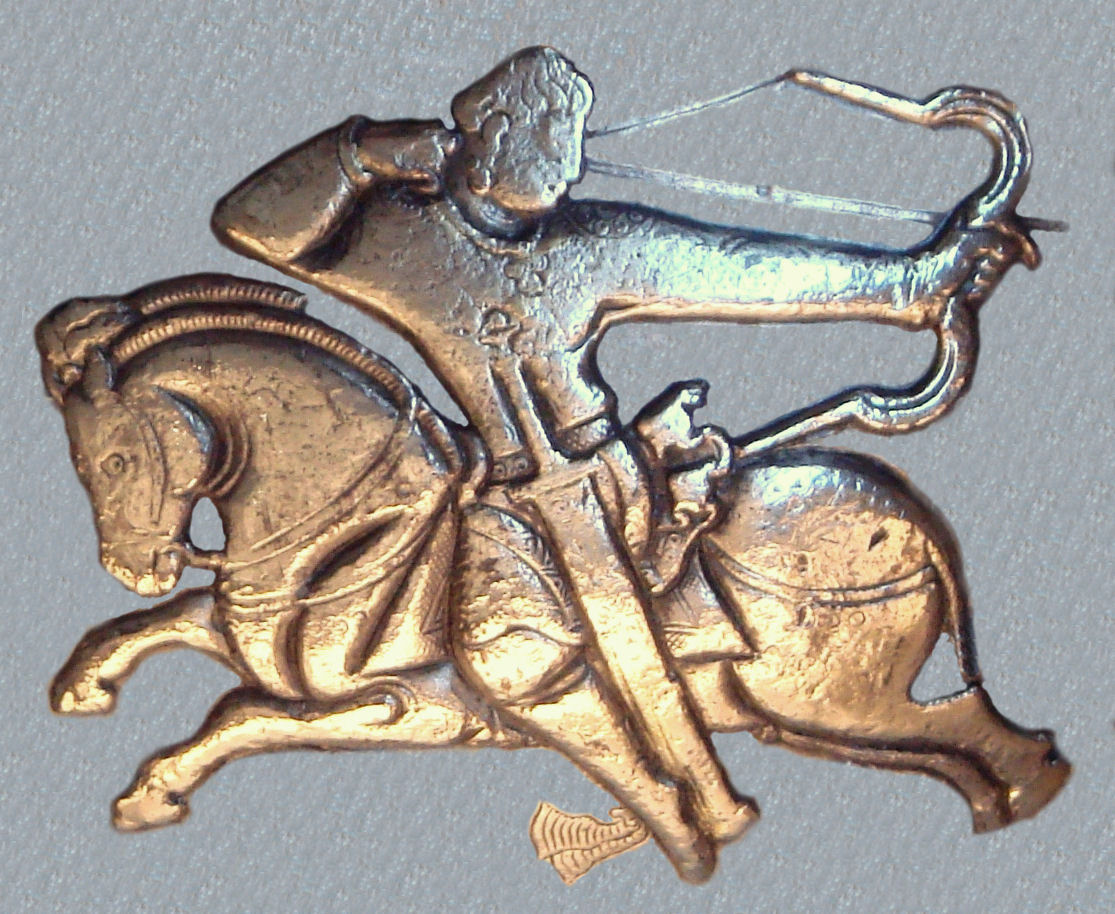
Parthian Shot
The Parthian shot is a light cavalry hit-and-run tactic made famous by the Parthians, an ancient Iranian people. While performing a real or feigned retreat at full gallop, the horse archers would turn their bodies back to shoot at the pursuing enemy. The maneuver required superb equestrian skills, since the rider's hands were occupied by his composite bow and his body was twisted around. As the stirrup had not been invented at the time of the Parthians, the rider relied solely on squeezing pressure from his legs to stay mounted and guide his horse. History In addition to the Parthians and their successors, the Sasanians, this tactic was used by most nomads of the Eurasian Steppe, including the Scythians, Huns, Turks, Magyars, Mongols, Koreans, as well as the Urartians and the Comanche. The Parthians used the tactic to great effect in their victory over the Roman general Crassus in the Battle of Carrhae. A tactic similar to the Parthian shot was attributed to the Phoenicia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cavalry
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from "cheval" meaning "horse") are soldiers or warriors who fight mounted on horseback. Cavalry were the most mobile of the combat arms, operating as light cavalry in the roles of reconnaissance, screening, and skirmishing in many armies, or as heavy cavalry for decisive shock attacks in other armies. An individual soldier in the cavalry is known by a number of designations depending on era and tactics, such as cavalryman, horseman, trooper, cataphract, knight, hussar, uhlan, mamluk, cuirassier, lancer, dragoon, or horse archer. The designation of ''cavalry'' was not usually given to any military forces that used other animals for mounts, such as camels or elephants. Infantry who moved on horseback, but dismounted to fight on foot, were known in the early 17th to the early 18th century as '' dragoons'', a class of mounted infantry which in most armies later evolved into standard cavalry while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Hastings
The Battle of Hastings nrf, Batâle dé Hastings was fought on 14 October 1066 between the Norman-French army of William the Conqueror, William, the Duke of Normandy, and an English army under the Anglo-Saxons, Anglo-Saxon King Harold Godwinson, beginning the Norman Conquest of England. It took place approximately northwest of Hastings, close to the present-day town of Battle, East Sussex, and was a decisive Normans, Norman victory. The background to the battle was the death of the childless King Edward the Confessor in January 1066, which set up a succession struggle between several claimants to his throne. Harold was crowned king shortly after Edward's death, but faced invasions by William, his own brother Tostig Godwinson, Tostig, and the Norwegian King Harald Hardrada (Harold III of Norway). Hardrada and Tostig defeated a hastily gathered army of Englishmen at the Battle of Fulford on 20 September 1066, and were in turn defeated by Harold at the Battle of Stamford Brid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Museum In Poznan - Przejście Przez Berezynę
National may refer to: Common uses * Nation or country ** Nationality – a ''national'' is a person who is subject to a nation, regardless of whether the person has full rights as a citizen Places in the United States * National, Maryland, census-designated place * National, Nevada, ghost town * National, Utah, ghost town * National, West Virginia, unincorporated community Commerce * National (brand), a brand name of electronic goods from Panasonic * National Benzole (or simply known as National), former petrol station chain in the UK, merged with BP * National Car Rental, an American rental car company * National Energy Systems, a former name of Eco Marine Power * National Entertainment Commission, a former name of the Media Rating Council * National Motor Vehicle Company, Indianapolis, Indiana, USA 1900-1924 * National Supermarkets, a defunct American grocery store chain * National String Instrument Corporation, a guitar company formed to manufacture the first resonator g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |