|
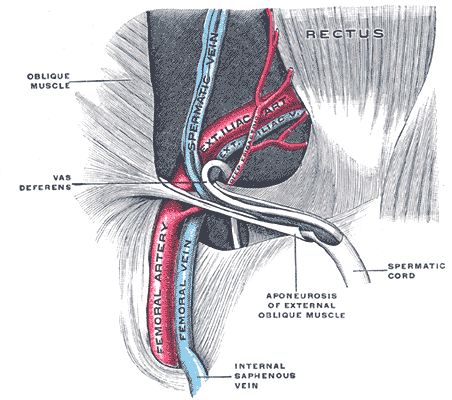
Femoral Vessels
The femoral vessels are those blood vessels passing through the femoral ring into the femoral canal thereby passing down the length of the thigh until behind the knee. These large vessel are the: * Femoral artery (also known in this location as the common femoral artery) and * Femoral vein Lymphatic vessels found in the thigh aren’t usually included in this collective noun. As the blood vessels pass along the thigh, they branch, with their main branches remaining closely associated, where they are still referred to collectively as femoral vessels. The adjective femoral, in this case, relates to the thigh, which contains the femur. The relative position of these two large vessels is very important in medicine and surgery, because several medical interventions involve puncturing one or the other of them. Reliably distinguishing between them is therefore important. The location of the vessel is also used as an anatomical landmark for the femoral nerve The femoral nerve is a n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Femoral Ring
The femoral ring is the opening at the proximal, abdominal end of the femoral canal, and represents the (superiorly directed/oriented) base of the conically-shaped femoral canal. The femoral ring is oval-shaped, with its long diameter being directed transversely and measuring about 1.25 cm.'''' The opening of the femoral ring is filled in by extraperitoneal fat, forming the femoral septum. Part of the intestine can sometimes pass through the femoral ring into the femoral canal causing a femoral hernia. Boundaries The femoral ring is bounded as follows:'''' * anteriorly by the inguinal ligament. * posteriorly by the pectineal ligament. * medially by the crescentic base of the lacunar ligament. * laterally by the fibrous septum on the medial side of the femoral vein. Additional images File:Gray1227.png, Front of abdomen, showing surface markings for arteries and inguinal canal. See also * Femoral canal * Femoral hernia * Inguinal canal The inguinal canals are the tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Femoral Canal
The femoral canal is the medial (and smallest) compartment of the three compartments of the femoral sheath. It is conical in shape. The femoral canal contains lymphatic vessels, and adipose and loose connective tissue, as well as - sometimes - a deep inguinal lymph node. The function of the femoral canal is to accommodate the distension of the femoral vein when venous return from the leg is increased or temporarily restricted (e.g. during a Valsalva maneuver). The proximal, abdominal end of the femoral canal forms the femoral ring. The femoral canal should not be confused with the nearby adductor canal. Anatomy The femoral canal is bordered: * anterosuperiorly by the inguinal ligament * posteriorly by the pectineal ligament lying anterior to the superior pubic ramus * Medially by the lacunar ligament * Laterally by the femoral vein Physiological significance The position of the femoral canal medially to the femoral vein is of physiologic importance. The space of the canal all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Popliteal Fossa
The popliteal fossa (also referred to as hough, .html" ;"title="/sup>">/sup> or kneepit in analogy to the cubital fossa) is a shallow depression located at the back of the knee joint. The bones of the popliteal fossa are the femur and the tibia. Like other flexion surfaces of large joints (groin, armpit, cubital fossa and essentially the anterior part of the neck), it is an area where blood vessels and nerves pass relatively superficially, and with an increased number of lymph nodes. Structure Boundaries The boundaries of the fossa are: Roof Moving from superficial to deep structures, the roof is formed by: # the skin. # the superficial fascia. This contains the small saphenous vein, the terminal branch of the posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh, posterior division of the medial cutaneous nerve, lateral sural cutaneous nerve, and medial sural cutaneous nerve. # the popliteal fascia. Floor The floor is formed by: # the popliteal surface of the femur. # the capsule of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Femoral Artery
The femoral artery is a large artery in the thigh and the main arterial supply to the thigh and leg. The femoral artery gives off the deep femoral artery or profunda femoris artery and descends along the anteromedial part of the thigh in the femoral triangle. It enters and passes through the adductor canal, and becomes the popliteal artery as it passes through the adductor hiatus in the adductor magnus near the junction of the middle and distal thirds of the thigh. Structure The femoral artery enters the thigh from behind the inguinal ligament as the continuation of the external iliac artery. Here, it lies midway between the anterior superior iliac spine and the symphysis pubis (Mid-inguinal point). Segments In clinical parlance, the femoral artery has the following segments: *The common femoral artery (CFA) is the segment of the femoral artery between the inferior margin of the inguinal ligament and the branching point of the deep femoral artery/profunda femoris artery. Its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Femoral Vein
In the human body, the femoral vein is a blood vessel that accompanies the femoral artery in the femoral sheath. It begins at the adductor hiatus (an opening in the adductor magnus muscle) as the continuation of the popliteal vein. It ends at the inferior margin of the inguinal ligament where it becomes the external iliac vein. The femoral vein bears valves which are mostly bicuspid and whose number is variable between individuals and often between left and right leg. Structure Segments *The common femoral vein is the segment of the femoral vein between the branching point of the deep femoral vein and the inferior margin of the inguinal ligament.Page 590 in: *The subsartorial vein or superficial femoral vein are designations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphatic Vessels
The lymphatic vessels (or lymph vessels or lymphatics) are thin-walled vessels (tubes), structured like blood vessels, that carry lymph. As part of the lymphatic system, lymph vessels are complementary to the cardiovascular system. Lymph vessels are lined by endothelial cells, and have a thin layer of smooth muscle, and adventitia that binds the lymph vessels to the surrounding tissue. Lymph vessels are devoted to the propulsion of the lymph from the lymph capillaries, which are mainly concerned with the absorption of interstitial fluid from the tissues. Lymph capillaries are slightly bigger than their counterpart capillaries of the vascular system. Lymph vessels that carry lymph to a lymph node are called afferent lymph vessels, and those that carry it from a lymph node are called efferent lymph vessels, from where the lymph may travel to another lymph node, may be returned to a vein, or may travel to a larger lymph duct. Lymph ducts drain the lymph into one of the subclavian ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Femur
The femur (; ), or thigh bone, is the proximal bone of the hindlimb in tetrapod vertebrates. The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum in the pelvic bone forming the hip joint, while the distal part of the femur articulates with the tibia (shinbone) and patella (kneecap), forming the knee joint. By most measures the two (left and right) femurs are the strongest bones of the body, and in humans, the largest and thickest. Structure The femur is the only bone in the upper leg. The two femurs converge medially toward the knees, where they articulate with the proximal ends of the tibiae. The angle of convergence of the femora is a major factor in determining the femoral-tibial angle. Human females have thicker pelvic bones, causing their femora to converge more than in males. In the condition ''genu valgum'' (knock knee) the femurs converge so much that the knees touch one another. The opposite extreme is ''genu varum'' (bow-leggedness). In the general populatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Femoral Nerve
The femoral nerve is a nerve in the thigh that supplies skin on the upper thigh and inner leg, and the muscles that extend the knee. Structure The femoral nerve is the major nerve supplying the anterior compartment of the thigh. It is the largest branch of the lumbar plexus, and arises from the dorsal divisions of the ventral rami of the second, third, and fourth lumbar nerves (L2, L3, and L4). The nerve enters Scarpa's triangle by passing beneath the inguinal ligament, just lateral to the femoral artery. In the thigh, the nerve lies in a groove between iliacus muscle and psoas major muscle, outside the femoral sheath, and lateral to the femoral artery. After a short course of about 4 cm in the thigh, the nerve is divided into anterior and posterior divisions, separated by lateral femoral circumflex artery. The branches are shown below: Muscular branches * The nerve to the pectineus muscle arises immediately above the inguinal ligament from the medial side of the femoral n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arteries Of The Lower Limb
An artery (plural arteries) () is a blood vessel in humans and most animals that takes blood away from the heart to one or more parts of the body (tissues, lungs, brain etc.). Most arteries carry oxygenated blood; the two exceptions are the pulmonary and the umbilical arteries, which carry deoxygenated blood to the organs that oxygenate it (lungs and placenta, respectively). The effective arterial blood volume is that extracellular fluid which fills the arterial system. The arteries are part of the circulatory system, that is responsible for the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all cells, as well as the removal of carbon dioxide and waste products, the maintenance of optimum blood pH, and the circulation of proteins and cells of the immune system. Arteries contrast with veins, which carry blood back towards the heart. Structure The anatomy of arteries can be separated into gross anatomy, at the macroscopic level, and microanatomy, which must be studied with a microscop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |