|
Facilitated Variation
The theory of facilitated variation demonstrates how seemingly complex biological systems can arise through a limited number of regulatory genetic changes, through the differential re-use of pre-existing developmental components. The theory was presented in 2005 by Marc W. Kirschner (a professor and chair at the Department of Systems Biology, Harvard Medical School) and John C. Gerhart (a professor at the Graduate School, University of California, Berkeley). The theory of facilitated variation addresses the nature and function of phenotypic variation in evolution. Recent advances in cellular and evolutionary developmental biology shed light on a number of mechanisms for generating novelty. Most anatomical and physiological traits that have evolved since the Cambrian are, according to Kirschner and Gerhart, the result of regulatory changes in the usage of various conserved core components that function in development and physiology. Novel traits arise as novel packages of modular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heliconius Erato Richard Bartz
''Heliconius'' comprises a colorful and widespread genus of brush-footed butterflies commonly known as the longwings or heliconians. This genus is distributed throughout the tropical and subtropical regions of the New World, from South America as far north as the southern United States. The larvae of these butterflies eat passion flower vines (Passifloraceae). Adults exhibit bright wing color patterns which signal their distastefulness to potential predators. Brought to the forefront of scientific attention by Victorian naturalists, these butterflies exhibit a striking diversity and mimicry, both amongst themselves and with species in other groups of butterflies and moths. The study of ''Heliconius'' and other groups of mimetic butterflies allowed the English naturalist Henry Walter Bates, following his return from Brazil in 1859, to lend support to Charles Darwin, who had found similar diversity amongst the Galápagos finches. Model for evolutionary study ''Heliconius'' bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Developmental Biology
Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop. Developmental biology also encompasses the biology of Regeneration (biology), regeneration, asexual reproduction, metamorphosis, and the growth and differentiation of stem cells in the adult organism. Perspectives The main processes involved in the embryogenesis, embryonic development of animals are: tissue patterning (via regional specification and patterned cellular differentiation, cell differentiation); tissue growth; and tissue morphogenesis. * Regional specification refers to the processes that create the spatial patterns in a ball or sheet of initially similar cells. This generally involves the action of cytoplasmic determinants, located within parts of the fertilized egg, and of inductive signals emitted from signaling centers in the embryo. The early stages of regional specification do not generate functional differentiated cells, but cell populations committed to developing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extended Evolutionary Synthesis
The extended evolutionary synthesis consists of a set of theoretical concepts argued to be more comprehensive than the earlier modern synthesis of evolutionary biology that took place between 1918 and 1942. The extended evolutionary synthesis was called for in the 1950s by C. H. Waddington, argued for on the basis of punctuated equilibrium by Stephen Jay Gould and Niles Eldredge in the 1980s, and was reconceptualized in 2007 by Massimo Pigliucci and Gerd B. Müller. Notably, Dr. Müller concluded from this research that Natural Selection has no way of explaining speciation, saying: “selection has no innovative capacity...the generative and the ordering aspects of morphological evolution are thus absent from evolutionary theory.” The extended evolutionary synthesis revisits the relative importance of different factors at play, examining several assumptions of the earlier synthesis, and augmenting it with additional causative factors. It includes multilevel selection, transgene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constructive Development (biology)
In biology, constructive development refers to the hypothesis that organisms shape their own developmental trajectory by constantly responding to, and causing, changes in both their internal state and their external environment. Constructive development can be contrasted with programmed development, the hypothesis that organisms develop according to a genetic program or blueprint. The constructivist perspective is found in philosophy, most notably developmental systems theory, and in the biological and social sciences, including developmental psychobiology and key themes of the extended evolutionary synthesis. Constructive development may be important to evolution because it enables organisms to produce functional phenotypes in response to genetic or environmental perturbation, and thereby contributes to adaptation and diversification. Key themes of constructive development Responsiveness and flexibility At any point in time, an organism's development depends on both the current sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolvability
Evolvability is defined as the capacity of a system for adaptive evolution. Evolvability is the ability of a population of organisms to not merely generate genetic diversity, but to generate ''adaptive'' genetic diversity, and thereby evolve through natural selection. In order for a biological organism to evolve by natural selection, there must be a certain minimum probability that new, heritable variants are beneficial. Random mutations, unless they occur in DNA sequences with no function, are expected to be mostly detrimental. Beneficial mutations are always rare, but if they are too rare, then adaptation cannot occur. Early failed efforts to evolve computer programs by random mutation and selection showed that evolvability is not a given, but depends on the representation of the program as a data structure, because this determines how changes in the program map to changes in its behavior. Analogously, the evolvability of organisms depends on their genotype–phenotype map. Thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irreducible Complexity
Irreducible complexity (IC) is the argument that certain biological systems with multiple interacting parts would not function if one of the parts was removed, so supposedly could not have evolved by successive small modifications from earlier less complex systems through natural selection, which would need all intermediate precursor systems to have been fully functional. Irreducible complexity has become central to the creationist concept of intelligent design, but the concept of irreducible complexity has been rejected by the scientific community,"We therefore find that Professor Behe's claim for irreducible complexity has been refuted in peer-reviewed research papers and has been rejected by the scientific community at large." 4:Whether ID Is Science, in E. Application of the Endorsement Test to the ID Policy, Ruling, Judge John E. Jones III, ''Kitzmiller v. Dover Area School District'' which regards intelligent design as pseudoscience. Irreducible complexity is one of two mai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complex Traits
Complex traits, also known as quantitative traits, are traits that do not behave according to simple Mendelian inheritance laws. More specifically, their inheritance cannot be explained by the genetic segregation of a single gene. Such traits show a continuous range of variation and are influenced by both environmental and genetic factors. Compared to strictly Mendelian traits, complex traits are far more common, and because they can be hugely polygenic, they are studied using statistical techniques such as QTL mapping rather than classical genetics methods. Examples of complex traits include height, circadian rhythms, enzyme kinetics, and many diseases including diabetes and Parkinson's disease. One major goal of genetic research today is to better understand the molecular mechanisms through which genetic variants act to influence complex traits. History When Mendel’s work on inheritance was rediscovered in 1900, scientists debated whether Mendel’s laws could account for t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
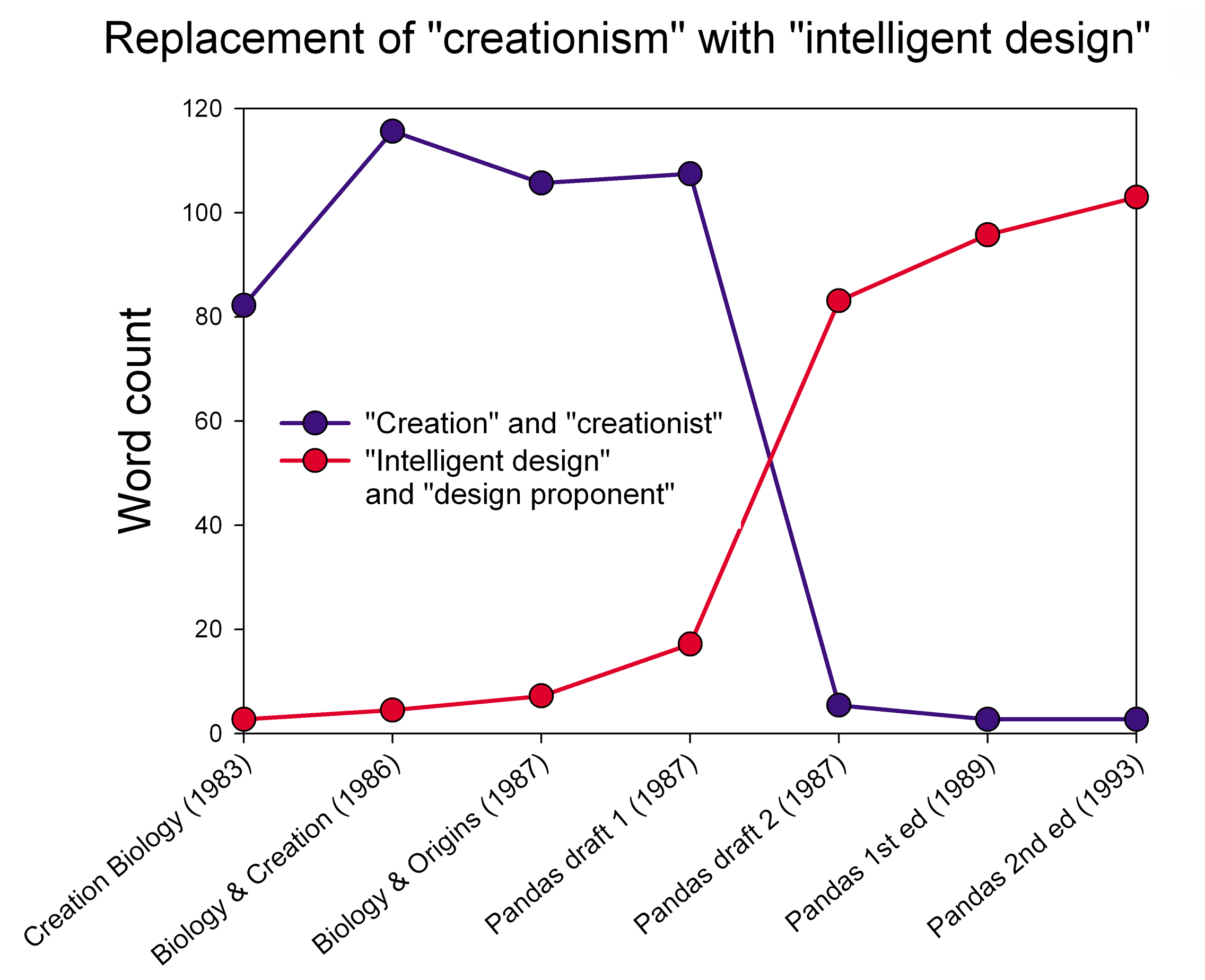
Intelligent Design
Intelligent design (ID) is a pseudoscientific argument for the existence of God, presented by its proponents as "an evidence-based scientific theory about life's origins". Numbers 2006, p. 373; " Dcaptured headlines for its bold attempt to rewrite the basic rules of science and its claim to have found indisputable evidence of a God-like being. Proponents, however, insisted it was 'not a religious-based idea, but instead an evidence-based scientific theory about life's origins – one that challenges strictly materialistic views of evolution.' Although the intellectual roots of the design argument go back centuries, its contemporary incarnation dates from the 1980s" Article available froUniversiteit Gent/ref> Proponents claim that "certain features of the universe and of living things are best explained by an intelligent cause, not an undirected process such as natural selection." * * ID is a form of creationism that lacks empirical support and offers no testable or tenable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Creationism
Creationism is the religious belief that nature, and aspects such as the universe, Earth, life, and humans, originated with supernatural acts of divine creation. Gunn 2004, p. 9, "The ''Concise Oxford Dictionary'' says that creationism is 'the belief that the universe and living organisms originated from specific acts of divine creation.'" In its broadest sense, creationism includes a continuum of religious views, Haarsma 2010, p. 168, "Some Christians, often called 'Young Earth creationists,' reject evolution in order to maintain a semi-literal interpretation of certain biblical passages. Other Christians, called 'progressive creationists,' accept the scientific evidence for some evolution over a long history of the earth, but also insist that God must have performed some miracles during that history to create new life-forms. Intelligent design, as it is promoted in North America is a form of progressive creation. Still other Christians, called theistic evolutionists' or 'ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extended Evolutionary Synthesis
The extended evolutionary synthesis consists of a set of theoretical concepts argued to be more comprehensive than the earlier modern synthesis of evolutionary biology that took place between 1918 and 1942. The extended evolutionary synthesis was called for in the 1950s by C. H. Waddington, argued for on the basis of punctuated equilibrium by Stephen Jay Gould and Niles Eldredge in the 1980s, and was reconceptualized in 2007 by Massimo Pigliucci and Gerd B. Müller. Notably, Dr. Müller concluded from this research that Natural Selection has no way of explaining speciation, saying: “selection has no innovative capacity...the generative and the ordering aspects of morphological evolution are thus absent from evolutionary theory.” The extended evolutionary synthesis revisits the relative importance of different factors at play, examining several assumptions of the earlier synthesis, and augmenting it with additional causative factors. It includes multilevel selection, transgene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Assimilation
Genetic assimilation is a process described by Conrad H. Waddington by which a phenotype originally produced in response to an environmental condition, such as exposure to a teratogen, later becomes genetically encoded via artificial selection or natural selection. Despite superficial appearances, this does not require the (Lamarckian) inheritance of acquired characters, although epigenetic inheritance could potentially influence the result. Waddington stated that genetic assimilation overcomes the barrier to selection imposed by what he called canalization of developmental pathways; he supposed that the organism's genetics evolved to ensure that development proceeded in a certain way regardless of normal environmental variations. The classic example of genetic assimilation was a pair of experiments in 1942 and 1953 by Waddington. He exposed ''Drosophila'' fruit fly embryos to ether, producing an extreme change in their phenotype: they developed a double thorax, resembling the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baldwin Effect
In evolutionary biology, the Baldwin effect, a phenotype-first theory of evolution, describes the effect of learned behaviour on evolution. James Mark Baldwin and others suggested during the eclipse of Darwinism in the late 19th century that an organism's ''ability to learn'' new behaviours (e.g. to acclimatise to a new stressor) will affect its reproductive success and will therefore have an effect on the genetic makeup of its species through natural selection. Though this process appears similar to Lamarckism, that view proposes that living things ''inherited'' their parents' acquired characteristics. The Baldwin effect has been independently proposed several times, and today it is generally recognized as part of the modern synthesis. "A New Factor in Evolution" The effect, then unnamed, was put forward in 1896 in a paper "A New Factor in Evolution" by the American psychologist James Mark Baldwin, with a second paper in 1897. The paper proposed a mechanism for specific selecti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |