|
Face Gear
A crown gear (also known as a face gear or a contrate gear) is a gear which has teeth that project at right angles to the face of the wheel. In particular, a crown gear is a type of bevel gear where the pitch cone angle is 90 degrees. A pitch cone of any other angle is simply called a bevel gear. Crown gears normally mesh with other bevel gears, or sometimes spur gears, a typical use being a crown gear and pinion system which allows a rotary motion to be shifted 90 degrees. See also * Crown circle * Bevel gear ** Spiral bevel gear A spiral bevel gear is a bevel gear with helical teeth. The main application of this is in a vehicle differential, where the direction of drive from the drive shaft must be turned 90 degrees to drive the wheels. The helical design produces less ... References Gears {{Mech-engineering-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crown Gear
A crown gear (also known as a face gear or a contrate gear) is a gear which has teeth that project at right angles to the face of the wheel. In particular, a crown gear is a type of bevel gear where the pitch cone angle is 90 degrees. A pitch cone of any other angle is simply called a bevel gear. Crown gears normally mesh with other bevel gears, or sometimes spur gears, a typical use being a crown gear and pinion system which allows a rotary motion to be shifted 90 degrees. See also * Crown circle * Bevel gear ** Spiral bevel gear A spiral bevel gear is a bevel gear with helical teeth. The main application of this is in a vehicle differential, where the direction of drive from the drive shaft must be turned 90 degrees to drive the wheels. The helical design produces less ... References Gears {{Mech-engineering-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
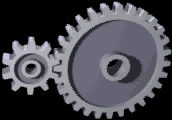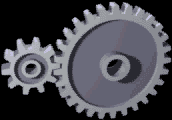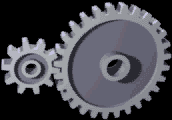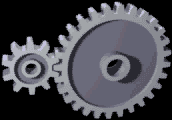
Gear
A gear is a rotating circular machine part having cut teeth or, in the case of a cogwheel or gearwheel, inserted teeth (called ''cogs''), which mesh with another (compatible) toothed part to transmit (convert) torque and speed. The basic principle behind the operation of gears is analogous to the basic principle of levers. A gear may also be known informally as a cog. Geared devices can change the speed, torque, and direction of a power source. Gears of different sizes produce a change in torque, creating a mechanical advantage, through their ''gear ratio'', and thus may be considered a simple machine. The rotational speeds, and the torques, of two meshing gears differ in proportion to their diameters. The teeth on the two meshing gears all have the same shape. Two or more meshing gears, working in a sequence, are called a gear train or a '' transmission''. The gears in a transmission are analogous to the wheels in a crossed, belt pulley system. An advantage of gears is tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bevel Gear
Bevel gears are gears where the axes of the two shafts intersect and the tooth-bearing faces of the gears themselves are conically shaped. Bevel gears are most often mounted on shafts that are 90 degrees apart, but can be designed to work at other angles as well. The pitch surface of bevel gears is a cone, known as a pitch cone. Bevel gears transfer the energy from linear to vertical power, making it very useful in machines widely used in mechanical settings. Introduction Two important concepts in gearing are pitch surface and pitch angle. The pitch surface of a gear is the imaginary toothless surface that you would have by averaging out the peaks and valleys of the individual teeth. The pitch surface of an ordinary gear is the shape of a cylinder. The pitch angle of a gear is the angle between the face of the pitch surface and the axis. The most familiar kinds of bevel gears have pitch angles of less than 90 degrees and therefore are cone-shaped. This type of bevel gear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pitch Cone
This page lists the standard US nomenclature used in the description of mechanical gear construction and function, together with definitions of the terms. The terminology was established by the American Gear Manufacturers Association (AGMA), under accreditation from the American National Standards Institute (ANSI). Addendum The addendum is the height by which a tooth of a gear projects beyond (outside for external, or inside for internal) the standard pitch circle or pitch line; also, the radial distance between the pitch diameter and the outside diameter. Addendum angle Addendum angle in a bevel gear, is the angle between face cone and pitch cone. Addendum circle The addendum circle coincides with the tops of the teeth of a gear and is concentric with the standard (reference) pitch circle and radially distant from it by the amount of the addendum. For external gears, the addendum circle lies on the outside cylinder while on internal gears the addendum circle lies on th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Press
Industrial Press, Inc., is a privately held corporation headquartered in South Norwalk, Connecticut. Its primary areas of business are publishing technical books for engineering, technology, and manufacturing. The company was founded in New York City in 1883, and moved to Connecticut in 2013. Industrial Press's flagship title is the ''Machinery's Handbook ''Machinery's Handbook'' ''for machine shop and drafting-room; a reference book on machine design and shop practice for the mechanical engineer, draftsman, toolmaker, and machinist'' (the full title of the 1st edition) is a classic reference ...''. It is a reference for mechanical and manufacturing engineers, designers, draftsmen, toolmakers, and machinists. External links * Book publishing companies based in Connecticut Companies based in Norwalk, Connecticut Publishing companies based in New York City Publishing companies established in 1880 1880 establishments in New York (state) Privately held companies base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spur Gear
Spur gears or straight-cut gears are the simplest type of gear. They consist of a cylinder or disk with teeth projecting radially. Viewing the gear at 90 degrees from the shaft length (side on) the tooth faces are straight and aligned parallel to the axis of rotation. Looking down the length of the shaft, a tooth's cross section is usually not triangular. Instead of being straight (as in a triangle) the sides of the cross section have a curved form (usually involute and less commonly cycloidal) to achieve a constant drive ratio. Spur gears mesh together correctly only if fitted to parallel shafts. No axial thrust is created by the tooth loads. Spur gears are excellent at moderate speeds but tend to be noisy at high speeds. Spur gear can be classified into two pressure angles, 20° being the current industry standard and 14½° being the former (often found in older equipment). Spur gear teeth are manufactured as either involute In mathematics, an involute (also known as an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinion
A pinion is a round gear—usually the smaller of two meshed gears—used in several applications, including drivetrain and rack and pinion systems. Applications Drivetrain Drivetrains usually feature a gear known as the pinion, which may vary in different systems, including * the typically smaller gear in a gear drive train (although in the first commercially successful steam locomotive—the ''Salamanca''—the ''pinion'' was rather large). In many cases, such as remote controlled toys, the pinion is also the drive gear for a reduction in speed, since electric motors operate at higher speed and lower torque than desirable at the wheels. However the reverse is true in watches, where gear trains commence with a high-torque, low-speed spring and terminate in the fast-and-weak escapement. * the smaller gear that drives in a 90-degree angle towards a crown gear in a differential drive. * the small front sprocket on a chain driven motorcycle. *the clutch bell gear when pair ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Gear Nomenclature
This page lists the standard US nomenclature used in the description of mechanical gear construction and function, together with definitions of the terms. The terminology was established by the American Gear Manufacturers Association (AGMA), under accreditation from the American National Standards Institute (ANSI). Addendum The addendum is the height by which a tooth of a gear projects beyond (outside for external, or inside for internal) the standard pitch circle or pitch line; also, the radial distance between the pitch diameter and the outside diameter. Addendum angle Addendum angle in a bevel gear, is the angle between face cone and pitch cone. Addendum circle The addendum circle coincides with the tops of the teeth of a gear and is concentric with the standard (reference) pitch circle and radially distant from it by the amount of the addendum. For external gears, the addendum circle lies on the outside cylinder while on internal gears the addendum circle lies on th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bevel Gear
Bevel gears are gears where the axes of the two shafts intersect and the tooth-bearing faces of the gears themselves are conically shaped. Bevel gears are most often mounted on shafts that are 90 degrees apart, but can be designed to work at other angles as well. The pitch surface of bevel gears is a cone, known as a pitch cone. Bevel gears transfer the energy from linear to vertical power, making it very useful in machines widely used in mechanical settings. Introduction Two important concepts in gearing are pitch surface and pitch angle. The pitch surface of a gear is the imaginary toothless surface that you would have by averaging out the peaks and valleys of the individual teeth. The pitch surface of an ordinary gear is the shape of a cylinder. The pitch angle of a gear is the angle between the face of the pitch surface and the axis. The most familiar kinds of bevel gears have pitch angles of less than 90 degrees and therefore are cone-shaped. This type of bevel gear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiral Bevel Gear
A spiral bevel gear is a bevel gear with helical teeth. The main application of this is in a vehicle differential, where the direction of drive from the drive shaft must be turned 90 degrees to drive the wheels. The helical design produces less vibration and noise than conventional straight-cut or spur-cut gear with straight teeth. A spiral bevel gear set should always be replaced in pairs i.e. both the left hand and right hand gears should be replaced together since the gears are manufactured and lapped in pairs. Handedness A right hand spiral bevel gear is one in which the outer half of a tooth is inclined in the clockwise direction from the axial plane through the midpoint of the tooth as viewed by an observer looking at the face of the gear. A left hand spiral bevel gear is one in which the outer half of a tooth is inclined in the counterclockwise direction from the axial plane through the midpoint of the tooth as viewed by an observer looking at the face of the gear. No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |