|
Expertise Reversal Effect
The expertise reversal effect refers to the reversal of the effectiveness of instructional techniques on learners with differing levels of prior knowledge.Kalyuga, S. (2007). Expertise reversal effect and its implications for learner-tailored instruction. ''Educational Psychology Review'', 19, 509–539.Kalyuga, S., Rikers, R., Pass, F. (2012). Educational implications of expertise reversal effect in learning and performance of complex cognitive and sensorimotor skills. Educational Psychology Review, 24, 313-337. The primary recommendation that stems from the expertise reversal effect is that instructional design methods need to be adjusted as learners acquire more knowledge in a specific domain. Expertise is described as "the ability to perform fluently in a specific class of tasks." Instructional techniques that assist learners to create long term memory schema are more effective for novices or low-knowledge individuals, who approach a learning situation or task without these kno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Educational Psychology Review
''Educational Psychology Review'' is a peer reviewed academic journal on the topic of educational psychology started in 1989, published by Springer Science+Business Media. Between 1999 and 2014, its highest impact factor was 2.83 in 2013, with 2020 impact factor of 8.705 (journal rank is #1 and #2 in the Educational Psychology and Education category, respectively). Its editor in chief is Fred Paas (Erasmus University Rotterdam and University of Wollongong). It is considered one of the "big five" educational psychology journals (along with ''Cognition and Instruction'', ''Journal of Educational Psychology'', ''Educational Psychologist'', and ''Contemporary Educational Psychology ''Contemporary Educational Psychology'' is a peer-reviewed academic journal on the topic of educational psychology. Its editor-in-chief is Patricia Alexander (University of Maryland). The journal was first published in 1976 for disseminating re ...'').{{cite journal , last1=Mitchell , first1=Anita , la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schema (psychology)
In psychology and cognitive science, a schema (plural ''schemata'' or ''schemas'') describes a pattern of thought or behavior that organizes categories of information and the relationships among them. It can also be described as a mental structure of preconceived ideas, a framework representing some aspect of the world, or a system of organizing and perceiving new information, such as a mental schema or conceptual model. Schemata influence attention and the absorption of new knowledge: people are more likely to notice things that fit into their schema, while re-interpreting contradictions to the schema as exceptions or distorting them to fit. Schemata have a tendency to remain unchanged, even in the face of contradictory information. Schemata can help in understanding the world and the rapidly changing environment. People can organize new perceptions into schemata quickly as most situations do not require complex thought when using schema, since automatic thought is all that is r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Experts
An expert is somebody who has a broad and deep understanding and competence in terms of knowledge, skill and experience through practice and education in a particular field. Informally, an expert is someone widely recognized as a reliable source of technique or skill whose faculty for judging or deciding rightly, justly, or wisely is accorded authority and status by peers or the public in a specific well-distinguished domain. An expert, more generally, is a person with extensive knowledge or ability based on research, experience, or occupation and in a particular area of study. Experts are called in for advice on their respective subject, but they do not always agree on the particulars of a field of study. An expert can be believed, by virtue of credentials, training, education, profession, publication or experience, to have special knowledge of a subject beyond that of the average person, sufficient that others may officially (and legally) rely upon the individual's opinio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Educational Psychologist (academic Journal)
The ''Educational Psychologist'' is a quarterly peer-reviewed academic journal published by Routledge on behalf of Division 15 (Educational Psychology) of the American Psychological Association. It was established in 1963 and the current co-editors are Jeffrey A. Greene (University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill) and Lisa Linnenbrink-Garcia (Michigan State University). The journal publishes conceptual, theoretical and review articles (including meta-analyses), rather than empirical studies, on all aspects of educational psychology and learning in formal and informal educational environments. It is considered one of the "big five" educational psychology journals (along with ''Cognition and Instruction'', ''Journal of Educational Psychology'', ''Educational Psychology Review'', and ''Contemporary Educational Psychology''). According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a two-year impact factor of 8.209 and a five-year impact factor of 11.302 (as of June 2022), makin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Load
In cognitive psychology, cognitive load refers to the amount of working memory resources used. There are three types of cognitive load: ''intrinsic'' cognitive load is the effort associated with a specific topic; ''extraneous'' cognitive load refers to the way information or tasks are presented to a learner; and ''germane'' cognitive load refers to the work put into creating a permanent store of knowledge (a schema). Cognitive load theory was developed in the late 1980s out of a study of problem solving by John Sweller. Sweller argued that instructional design can be used to reduce cognitive load in learners. Much later, other researchers developed a way to measure perceived mental effort which is indicative of cognitive load. Task-invoked pupillary response is a reliable and sensitive measurement of cognitive load that is directly related to working memory. Information may only be stored in long term memory after first being attended to, and processed by, working memory. Workin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
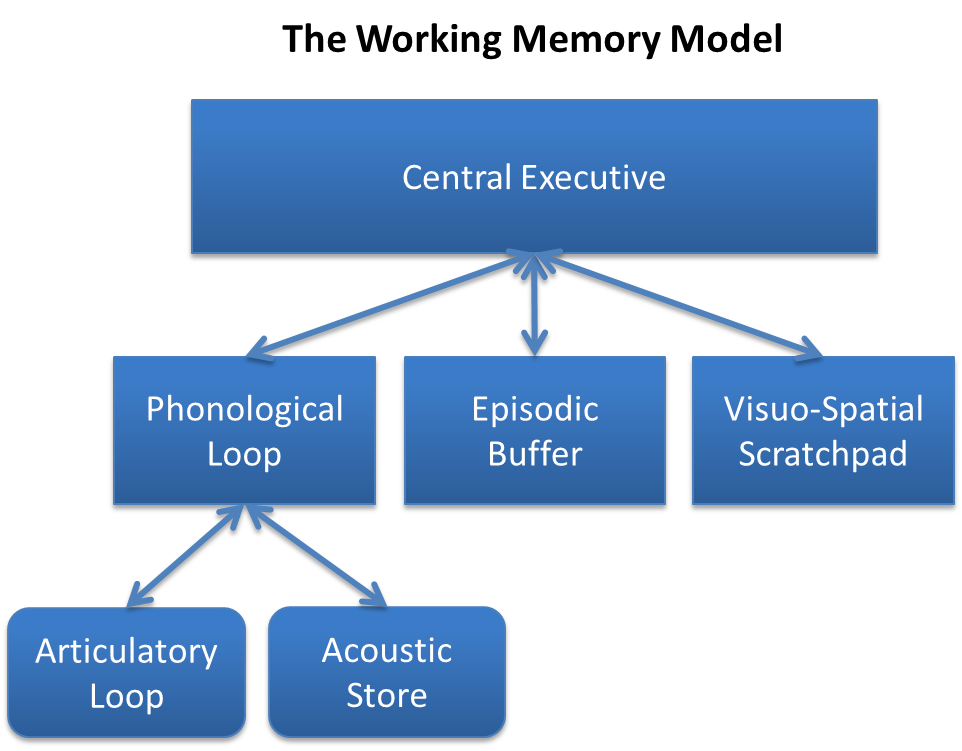
Working Memory
Working memory is a cognitive system with a limited capacity that can hold information temporarily. It is important for reasoning and the guidance of decision-making and behavior. Working memory is often used synonymously with short-term memory, but some theorists consider the two forms of memory distinct, assuming that working memory allows for the manipulation of stored information, whereas short-term memory only refers to the short-term storage of information. Working memory is a theoretical concept central to cognitive psychology, neuropsychology, and neuroscience. History The term "working memory" was coined by Miller, Galanter, and Pribram, and was used in the 1960s in the context of theories that likened the mind to a computer. In 1968, Atkinson and Shiffrin used the term to describe their "short-term store". What we now call working memory was formerly referred to variously as a "short-term store" or short-term memory, primary memory, immediate memory, operant memo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long-term Memory
Long-term memory (LTM) is the stage of the Atkinson–Shiffrin memory model in which informative knowledge is held indefinitely. It is defined in contrast to short-term and working memory, which persist for only about 18 to 30 seconds. Long-term memory is commonly labelled as explicit memory ( declarative), as well as episodic memory, semantic memory, autobiographical memory, and implicit memory (procedural memory). Dual-store memory model According to Miller, whose paper in 1956 popularized the theory of the "magic number seven", short-term memory is limited to a certain number of chunks of information, while long-term memory has a limitless store. Atkinson–Shiffrin memory model According to the dual store memory model proposed by Richard C. Atkinson and Richard Shiffrin in 1968, memories can reside in the short-term "buffer" for a limited time while they are simultaneously strengthening their associations in long-term memory. When items are first presented, they enter sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expertise Reversal Effect Diagram
An expert is somebody who has a broad and deep understanding and competence in terms of knowledge, skill and experience through practice and education in a particular field. Informally, an expert is someone widely recognized as a reliable source of technique or skill whose faculty for judging or deciding rightly, justly, or wisely is accorded authority and status by peers or the public in a specific well-distinguished domain. An expert, more generally, is a person with extensive knowledge or ability based on research, experience, or occupation and in a particular area of study. Experts are called in for advice on their respective subject, but they do not always agree on the particulars of a field of study. An expert can be believed, by virtue of credentials, training, education, profession, publication or experience, to have special knowledge of a subject beyond that of the average person, sufficient that others may officially (and legally) rely upon the individual's opinio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motivational
Motivation is the reason for which humans and other animals initiate, continue, or terminate a behavior at a given time. Motivational states are commonly understood as forces acting within the agent that create a disposition to engage in goal-directed behavior. It is often held that different mental states compete with each other and that only the strongest state determines behavior. This means that we can be motivated to do something without actually doing it. The paradigmatic mental state providing motivation is desire. But various other states, such as beliefs about what one ought to do or intentions, may also provide motivation. Motivation is derived from the word 'motive', which denotes a person's needs, desires, wants, or urges. It is the process of motivating individuals to take action in order to achieve a goal. The psychological elements fueling people's behavior in the context of job goals might include a desire for money. Various competing theories have been proposed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Split Attention Effect
The split-attention effect is a learning effect inherent within some poorly designed instructional materials. It is apparent when the same modality (e.g. visual) is used for various types of information within the same display. Users must split their attention between the materials, for example, an image and text, to understand the information being conveyed. The split-attention effect can occur physically through visual and auditory splits and temporally when time distances two pieces of information that should be connected. A visual example of split attention Consider the graphic below from Tarmizi and Sweller. They used these graphics to compare the learning that takes place given split attention conditions. Each is a possibility of how one might arrange graphical material within a lesson. Ward and Sweller advise instructional designers to be careful when they direct a learner's attention. In several studies and experiments, Sweller and his associates found that learners had diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |