|
Evolutionary Biology
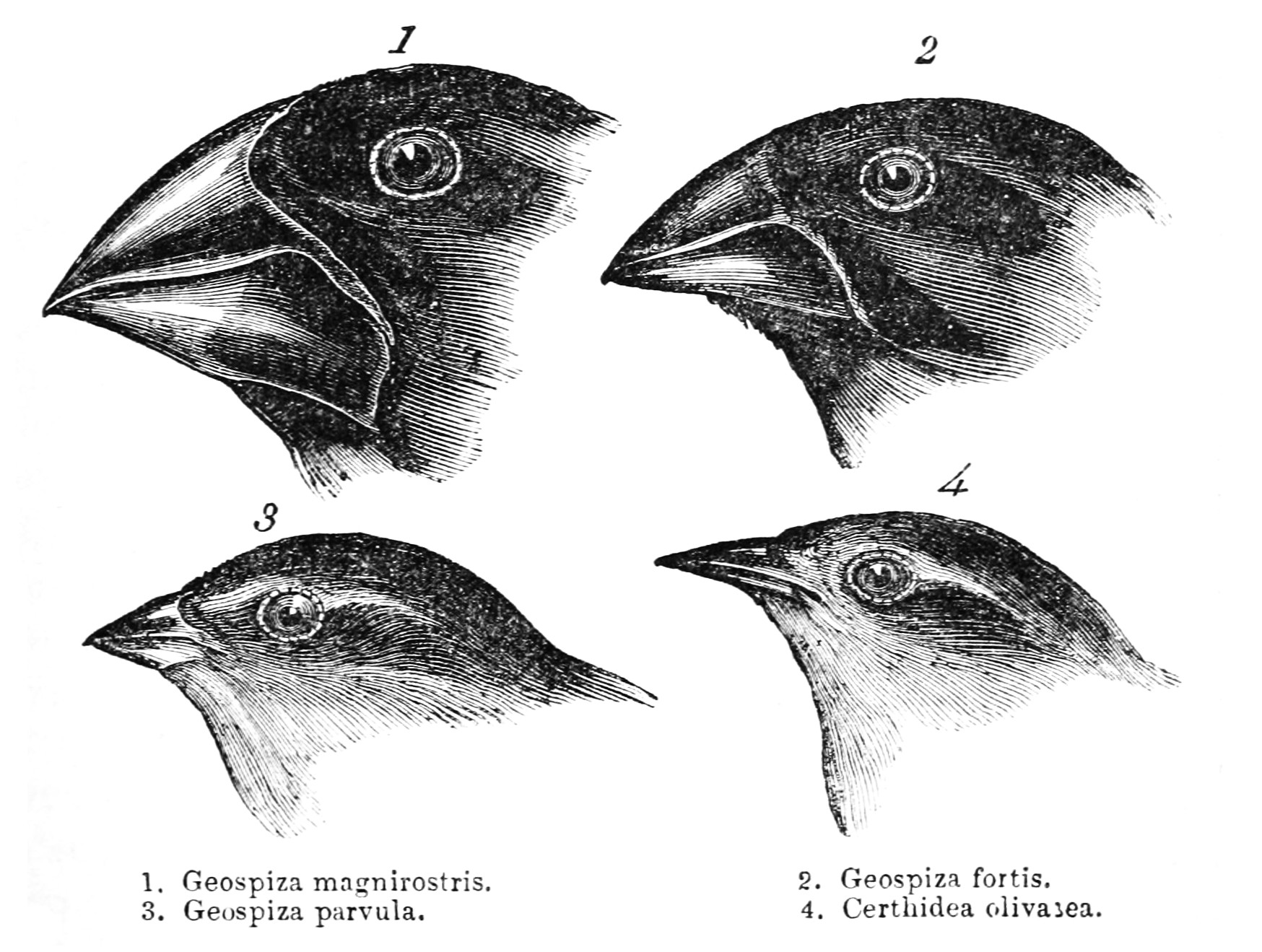
Evolutionary biology is the subfield of biology that studies the evolutionary processes (natural selection, common descent, speciation) that produced the diversity of life on Earth. It is also defined as the study of the history of life forms on Earth. Evolution is based on the theory that all species are related and they gradually change over time. In a population, the genetic variations affect the physical characteristics i.e. phenotypes of an organism. These changes in the phenotypes will be an advantage to some organisms, which will then be passed onto their offspring. Some examples of evolution in species over many generations are the Peppered Moth and Flightless birds. In the 1930s, the discipline of evolutionary biology emerged through what Julian Huxley called the modern synthesis of understanding, from previously unrelated fields of biological research, such as genetics and ecology, systematics, and paleontology. The importance of studying Evolutionary biology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systematics
Biological systematics is the study of the diversification of living forms, both past and present, and the relationships among living things through time. Relationships are visualized as evolutionary trees (synonyms: cladograms, phylogenetic trees, phylogenies). Phylogenies have two components: branching order (showing group relationships) and branch length (showing amount of evolution). Phylogenetic trees of species and higher taxa are used to study the evolution of traits (e.g., anatomical or molecular characteristics) and the distribution of organisms ( biogeography). Systematics, in other words, is used to understand the evolutionary history of life on Earth. The word systematics is derived from the Latin word ''systema,'' which means systematic arrangement of organisms. Carl Linnaeus used 'Systema Naturae' as the title of his book. Branches and applications In the study of biological systematics, researchers use the different branches to further understand the relations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Population Biology
The term population biology has been used with different meanings. In 1971 Edward O. Wilson ''et al''. used the term in the sense of applying mathematical models to population genetics, community ecology, and population dynamics. Alan Hastings used the term in 1997 as the title of his book on the mathematics used in population dynamics. The name was also used for a course given at UC Davis in the late 2010s, which describes it as an interdisciplinary field combining the areas of ecology and evolutionary biology. The course includes mathematics, statistics, ecology, genetics, and systematics Biological systematics is the study of the diversification of living forms, both past and present, and the relationships among living things through time. Relationships are visualized as evolutionary trees (synonyms: cladograms, phylogenetic t .... Numerous types of organisms are studied. The journal '' Theoretical Population Biology'' is published. See also References External li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Biology
Cell biology (also cellular biology or cytology) is a branch of biology that studies the structure, function, and behavior of cells. All living organisms are made of cells. A cell is the basic unit of life that is responsible for the living and functioning of organisms. Cell biology is the study of structural and functional units of cells. Cell biology encompasses both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and has many subtopics which may include the study of cell metabolism, cell communication, cell cycle, biochemistry, and cell composition. The study of cells is performed using several microscopy techniques, cell culture, and cell fractionation. These have allowed for and are currently being used for discoveries and research pertaining to how cells function, ultimately giving insight into understanding larger organisms. Knowing the components of cells and how cells work is fundamental to all biological sciences while also being essential for research in biomedical fields ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Biology
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecular basis of biological activity in and between cells, including biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactions. The study of chemical and physical structure of biological macromolecules is known as molecular biology. Molecular biology was first described as an approach focused on the underpinnings of biological phenomena - uncovering the structures of biological molecules as well as their interactions, and how these interactions explain observations of classical biology. In 1945 the term molecular biology was used by physicist William Astbury. In 1953 Francis Crick, James Watson, Rosalind Franklin, and colleagues, working at Medical Research Council unit, Cavendish laboratory, Cambridge (now the MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology), made a double helix model of DNA which changed the entire research scenario. They proposed the DNA structure based on previous research done by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Organisation
Biological organisation is the hierarchy of complex biological structures and systems that define life using a reductionistic approach. The traditional hierarchy, as detailed below, extends from atoms to biospheres. The higher levels of this scheme are often referred to as an ecological organisation concept, or as the field, hierarchical ecology. Each level in the hierarchy represents an increase in organisational complexity, with each "object" being primarily composed of the previous level's basic unit. The basic principle behind the organisation is the concept of ''emergence''—the properties and functions found at a hierarchical level are not present and irrelevant at the lower levels. The biological organisation of life is a fundamental premise for numerous areas of scientific research, particularly in the medical sciences. Without this necessary degree of organisation, it would be much more difficult—and likely impossible—to apply the study of the effects of va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Developmental Biology
Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop. Developmental biology also encompasses the biology of regeneration, asexual reproduction, metamorphosis, and the growth and differentiation of stem cells in the adult organism. Perspectives The main processes involved in the embryonic development of animals are: tissue patterning (via regional specification and patterned cell differentiation); tissue growth; and tissue morphogenesis. * Regional specification refers to the processes that create the spatial patterns in a ball or sheet of initially similar cells. This generally involves the action of cytoplasmic determinants, located within parts of the fertilized egg, and of inductive signals emitted from signaling centers in the embryo. The early stages of regional specification do not generate functional differentiated cells, but cell populations committed to developing to a specific region or part of the organism. These are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embryogenesis
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sperm cell. The resulting fusion of these two cells produces a single-celled zygote that undergoes many cell divisions that produce cells known as blastomeres. The blastomeres are arranged as a solid ball that when reaching a certain size, called a morula, takes in fluid to create a cavity called a blastocoel. The structure is then termed a blastula, or a blastocyst in mammals. The mammalian blastocyst hatches before implantating into the endometrial lining of the womb. Once implanted the embryo will continue its development through the next stages of gastrulation, neurulation, and organogenesis. Gastrulation is the formation of the three germ layers that will form all of the different parts of the body. Neurulation forms the ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
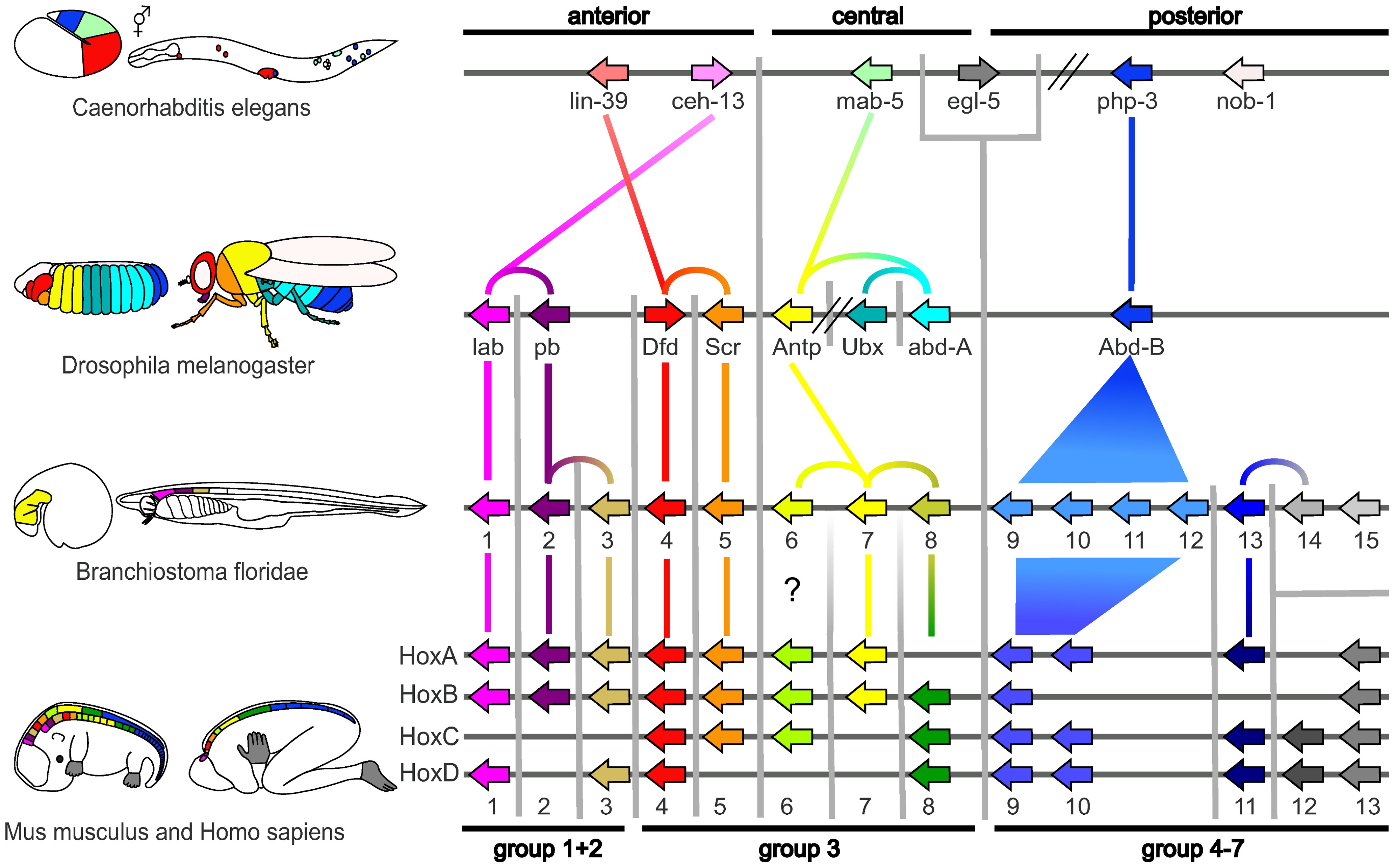
Evolutionary Developmental Biology
Evolutionary developmental biology (informally, evo-devo) is a field of biological research that compares the developmental processes of different organisms to infer how developmental processes evolved. The field grew from 19th-century beginnings, where embryology faced a mystery: zoologists did not know how embryonic development was controlled at the molecular level. Charles Darwin noted that having similar embryos implied common ancestry, but little progress was made until the 1970s. Then, recombinant DNA technology at last brought embryology together with molecular genetics. A key early discovery was of homeotic genes that regulate development in a wide range of eukaryotes. The field is composed of multiple core evolutionary concepts. One is deep homology, the finding that dissimilar organs such as the eyes of insects, vertebrates and cephalopod molluscs, long thought to have evolved separately, are controlled by similar genes such as ''pax-6'', from the evo-devo gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biogeography
Biogeography is the study of the distribution of species and ecosystems in geographic space and through geological time. Organisms and biological communities often vary in a regular fashion along geographic gradients of latitude, elevation, isolation and habitat area.Brown University, "Biogeography." Accessed February 24, 2014. . Phytogeography is the branch of biogeography that studies the distribution of plants. Zoogeography is the branch that studies distribution of animals. Mycogeography is the branch that studies distribution of fungi, such as mushrooms. Knowledge of spatial variation in the numbers and types of organisms is as vital to us today as it was to our early human ancestors, as we adapt to heterogeneous but geographically predictable environments. Biogeography is an integrative field of inquiry that unites concepts and information from ecology, evolutionary biology, taxonomy, geology, physical geography, palaeontology, and climatology.Dansereau, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Drift
Genetic drift, also known as allelic drift or the Wright effect, is the change in the frequency of an existing gene variant (allele) in a population due to random chance. Genetic drift may cause gene variants to disappear completely and thereby reduce genetic variation. It can also cause initially rare alleles to become much more frequent and even fixed. When few copies of an allele exist, the effect of genetic drift is more notable, and when many copies exist, the effect is less notable. In the middle of the 20th century, vigorous debates occurred over the relative importance of natural selection versus neutral processes, including genetic drift. Ronald Fisher, who explained natural selection using Mendelian genetics, held the view that genetic drift plays at most a minor role in evolution, and this remained the dominant view for several decades. In 1968, population geneticist Motoo Kimura rekindled the debate with his neutral theory of molecular evolution, which claims ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexual Selection
Sexual selection is a mode of natural selection in which members of one biological sex choose mates of the other sex to mate with (intersexual selection), and compete with members of the same sex for access to members of the opposite sex (intrasexual selection). These two forms of selection mean that some individuals have greater reproductive success than others within a population, for example because they are more attractive or prefer more attractive partners to produce offspring. Successful males benefit from frequent mating and monopolizing access to one or more fertile females. Females can maximise the return on the energy they invest in reproduction by selecting and mating with the best males. The concept was first articulated by Charles Darwin who wrote of a "second agency" other than natural selection, in which competition between mate candidates could lead to speciation. The theory was given a mathematical basis by Ronald Fisher in the early 20th century. Sexual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |