|
Ethionamide
Ethionamide is an antibiotic used to treat tuberculosis. Specifically it is used, along with other antituberculosis medications, to treat active multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. It is no longer recommended for leprosy. It is taken by mouth. Ethionamide has a high rate of side effects. Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and loss of appetite. Serious side effects may include liver inflammation and depression. It should not be used in people with significant liver problems. Use in pregnancy is not recommended as safety is unclear. Ethionamide is in the thioamides family of medications. It is believed to work by interfering with the use of mycolic acid. Ethionamide was discovered in 1956 and approved for medical use in the United States in 1965. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Medical uses Ethionamide is used in combination with other antituberculosis agents as part of a second-line regimen for active tubercul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antituberculosis Medications
Tuberculosis management describes the techniques and procedures utilized for treating tuberculosis (TB). The medical standard for active TB is a short course treatment involving a combination of isoniazid, rifampicin (also known as Rifampin), pyrazinamide, and ethambutol for the first two months. During this initial period, Isoniazid is taken alongside pyridoxal phosphate to obviate peripheral neuropathy. Isoniazid is then taken coincident with rifampicin for the remaining four months of treatment. A patient is considered free of all living TB bacteria after six months. Latent tuberculosis or latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI) is treated with three to nine months of isoniazid alone. This long-term treatment often risks the development of hepatotoxicity. A combination of isoniazid plus rifampicin for a period of three to four months is shown to be an equally effective method for treating LTBI, while mitigating risks to hepatotoxicity. Treatment of LTBI is essential in preventin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multidrug-resistant Tuberculosis
Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) is a form of tuberculosis (TB) infection caused by bacteria that are resistant to treatment with at least two of the most powerful first-line anti-TB medications (drugs): isoniazid and rifampin. Some forms of TB are also resistant to second-line medications, and are called extensively drug-resistant TB ( XDR-TB). Tuberculosis is caused by infection with the bacterium '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis''. Almost one in four people in the world are infected with TB bacteria. Only when the bacteria become active do people become ill with TB. Bacteria become active as a result of anything that can reduce the person's immunity, such as HIV, advancing age, diabetes or other immunocompromising illnesses. TB can usually be treated with a course of four standard, or first-line, anti-TB drugs (i.e., isoniazid, rifampin, pyrazinamide and ethambutol). However, beginning with the first antibiotic treatment for TB in 1943, some strains of the TB ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Administration
Oral administration is a route of administration where a substance is taken through the mouth. Per os abbreviated to P.O. is sometimes used as a direction for medication to be taken orally. Many medications are taken orally because they are intended to have a systemic effect, reaching different parts of the body via the bloodstream, for example. Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes, such as injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients willing and able to swallow. Terminology ''Per os'' (; ''P.O.'') is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "through the mouth" or "by mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Plasma
Blood plasma is a light amber-colored liquid component of blood in which blood cells are absent, but contains proteins and other constituents of whole blood in suspension. It makes up about 55% of the body's total blood volume. It is the intravascular part of extracellular fluid (all body fluid outside cells). It is mostly water (up to 95% by volume), and contains important dissolved proteins (6–8%; e.g., serum albumins, globulins, and fibrinogen), glucose, clotting factors, electrolytes (, , , , , etc.), hormones, carbon dioxide (plasma being the main medium for excretory product transportation), and oxygen. It plays a vital role in an intravascular osmotic effect that keeps electrolyte concentration balanced and protects the body from infection and other blood-related disorders. Blood plasma is separated from the blood by spinning a vessel of fresh blood containing an anticoagulant in a centrifuge until the blood cells fall to the bottom of the tube. The blood plasm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspartate Transaminase
Aspartate transaminase (AST) or aspartate aminotransferase, also known as AspAT/ASAT/AAT or (serum) glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (GOT, SGOT), is a pyridoxal phosphate (PLP)-dependent transaminase enzyme () that was first described by Arthur Karmen and colleagues in 1954. AST catalyzes the reversible transfer of an α-amino group between aspartate and glutamate and, as such, is an important enzyme in amino acid metabolism. AST is found in the liver, heart, skeletal muscle, kidneys, brain, red blood cells and gall bladder. Serum AST level, serum ALT (alanine transaminase) level, and their ratio ( AST/ALT ratio) are commonly measured clinically as biomarkers for liver health. The tests are part of blood panels. The half-life of total AST in the circulation approximates 17 hours and, on average, 87 hours for ''mitochondrial'' AST. Aminotransferase is cleared by sinusoidal cells in the liver. Function Aspartate transaminase catalyzes the interconversion of aspartate and α-k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
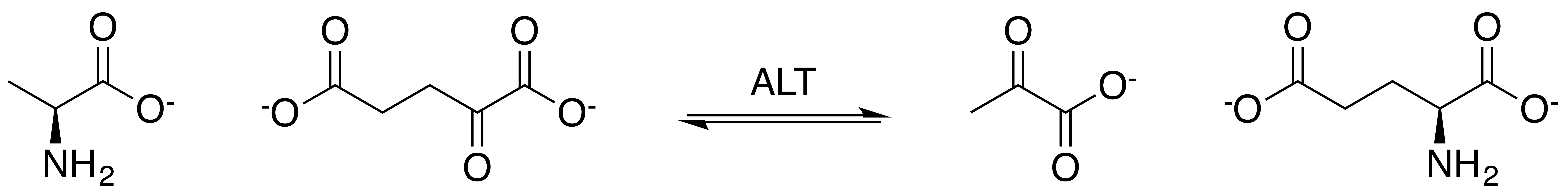
Alanine Aminotransferase
Alanine transaminase (ALT) is a transaminase enzyme (). It is also called alanine aminotransferase (ALT or ALAT) and was formerly called serum glutamate-pyruvate transaminase or serum glutamic-pyruvic transaminase (SGPT) and was first characterized in the mid-1950s by Arthur Karmen and colleagues. ALT is found in plasma and in various body tissues but is most common in the liver. It catalyzes the two parts of the alanine cycle. Serum ALT level, serum AST (aspartate transaminase) level, and their ratio ( AST/ALT ratio) are commonly measured clinically as biomarkers for liver health. The tests are part of blood panels. The half-life of ALT in the circulation approximates 47 hours. Aminotransferase is cleared by sinusoidal cells in the liver. Function ALT catalyzes the transfer of an amino group from L-alanine to α-ketoglutarate, the products of this reversible transamination reaction being pyruvate and L-glutamate. : L-alanine + α-ketoglutarate ⇌ pyruvate + L-gluta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isoniazid
Isoniazid, also known as isonicotinic acid hydrazide (INH), is an antibiotic used for the treatment of tuberculosis. For active tuberculosis it is often used together with rifampicin, pyrazinamide, and either streptomycin or ethambutol. For latent tuberculosis it is often used by itself. It may also be used for atypical types of mycobacteria, such as '' M. avium'', '' M. kansasii'', and ''M. xenopi''. It is usually taken by mouth but may be used by injection into muscle. Common side effects include increased blood levels of liver enzymes and numbness in the hands and feet. Serious side effects may include liver inflammation and acute liver failure. It is unclear if use during pregnancy is safe for the baby. Use during breastfeeding is likely safe. Pyridoxine may be given to reduce the risk of side effects. Isoniazid works in part by disrupting the formation of the bacteria's cell wall which results in cell death. Isoniazid was first made in 1952. It is on the World Heal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liver Function Tests
Liver function tests (LFTs or LFs), also referred to as a hepatic panel, are groups of blood tests that provide information about the state of a patient's liver. These tests include prothrombin time (PT/INR), activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT), albumin, bilirubin (direct and indirect), and others. The liver transaminases aspartate transaminase (AST or SGOT) and alanine transaminase (ALT or SGPT) are useful biomarkers of liver injury in a patient with some degree of intact liver function. Most liver diseases cause only mild symptoms initially, but these diseases must be detected early. Hepatic (liver) involvement in some diseases can be of crucial importance. This testing is performed on a patient's blood sample. Some tests are associated with functionality (e.g., albumin), some with cellular integrity (e.g., transaminase), and some with conditions linked to the biliary tract (gamma-glutamyl transferase and alkaline phosphatase). Because some of these tests do not m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liver Disease
Liver disease, or hepatic disease, is any of many diseases of the liver. If long-lasting it is termed chronic liver disease. Although the diseases differ in detail, liver diseases often have features in common. Signs and symptoms Some of the signs and symptoms of a liver disease are the following: * Jaundice * Confusion and altered consciousness caused by hepatic encephalopathy. * Thrombocytopenia and coagulopathy. * Risk of bleeding symptoms particularly taking place in gastrointestinal tract Liver diseases File:Ground glass hepatocytes high mag cropped 2.jpg, Ground glass hepatocytes File:Primary biliary cirrhosis intermed mag much cropping.jpg, Primary biliary cirrhosis File:Buddchiari2.PNG, Budd-chiari syndrome File:Non-alcoholic_fatty_liver_disease1.jpg, Micrograph of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease There are more than a hundred different liver diseases. Some of the most common are: * Fascioliasis, a parasitic infection of liver caused by a liver fluke of the genus ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatocyte
A hepatocyte is a cell of the main parenchymal tissue of the liver. Hepatocytes make up 80% of the liver's mass. These cells are involved in: * Protein synthesis * Protein storage * Transformation of carbohydrates * Synthesis of cholesterol, bile salts and phospholipids * Detoxification, modification, and excretion of exogenous and endogenous substances * Initiation of formation and secretion of bile Structure The typical hepatocyte is cubical with sides of 20-30 μm, (in comparison, a human hair has a diameter of 17 to 180 μm).The diameter of human hair ranges from 17 to 181 μm. The typical volume of a hepatocyte is 3.4 x 10−9 cm3. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum is abundant in hepatocytes, in contrast to most other cell types. Microanatomy Hepatocytes display an eosinophilic cytoplasm, reflecting numerous mitochondria, and basophilic stippling due to large amounts of smooth endoplasmic reticulum and free ribosomes. Brown lipofuscin granules are also obser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pregnancy Category
The pregnancy category of a medication is an assessment of the risk of fetal injury due to the pharmaceutical, if it is used as directed by the mother during pregnancy. It does ''not'' include any risks conferred by pharmaceutical agents or their metabolites in breast milk. Every drug has specific information listed in its product literature. The British National Formulary used to provide a table of drugs to be avoided or used with caution in pregnancy, and did so using a limited number of key phrases, but now Appendix 4 (which was the Pregnancy table) has been removed. Appendix 4 is now titled "Intravenous Additives". However, information that was previously available in the former Appendix 4 (pregnancy) and Appendix 5 (breast feeding) is now available in the individual drug monographs. United States American law requires that certain drugs and biological products must be labelled very specifically.Title 21, Part 201.57 (9)(i)of the Code of Federal Regulations lists specific requ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food And Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food safety, tobacco products, caffeine products, dietary supplements, Prescription drug, prescription and Over-the-counter drug, over-the-counter pharmaceutical drugs (medications), vaccines, biopharmaceuticals, blood transfusions, medical devices, electromagnetic radiation emitting devices (ERED), cosmetics, Animal feed, animal foods & feed and Veterinary medicine, veterinary products. The FDA's primary focus is enforcement of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C), but the agency also enforces other laws, notably Section 361 of the Public Health Service Act, as well as associated regulations. Much of this regulatory-enforcement work is not d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)