|
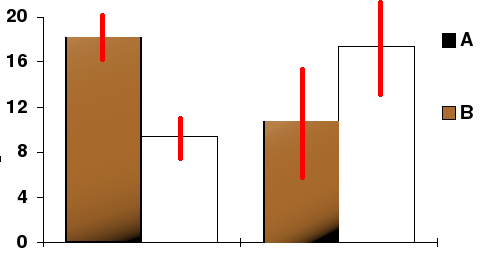
Error Bar
Error bars are graphical representations of the variability of data and used on graphs to indicate the error or uncertainty in a reported measurement. They give a general idea of how precise a measurement is, or conversely, how far from the reported value the true (error free) value might be. Error bars often represent one standard deviation of uncertainty, one standard error, or a particular confidence interval (e.g., a 95% interval). These quantities are not the same and so the measure selected should be stated explicitly in the graph or supporting text. Error bars can be used to compare visually two quantities if various other conditions hold. This can determine whether differences are statistically significant. Error bars can also suggest goodness of fit of a given function, i.e., how well the function describes the data. Scientific papers in the experimental sciences are expected to include error bars on all graphs, though the practice differs somewhat between sciences ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Error
An error (from the Latin ''error'', meaning "wandering") is an action which is inaccurate or incorrect. In some usages, an error is synonymous with a mistake. The etymology derives from the Latin term 'errare', meaning 'to stray'. In statistics, "error" refers to the difference between the value which has been computed and the correct value. An error could result in failure or in a deviation from the intended performance or behavior. Human behavior One reference differentiates between "error" and "mistake" as follows: In human behavior the norms or expectations for behavior or its consequences can be derived from the intention of the actor or from the expectations of other individuals or from a social grouping or from social norms. (See deviance.) Gaffes and faux pas can be labels for certain instances of this kind of error. More serious departures from social norms carry labels such as misbehavior and labels from the legal system, such as misdemeanor and crime. Departures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Errors And Residuals
In statistics and optimization, errors and residuals are two closely related and easily confused measures of the deviation of an observed value of an element of a statistical sample from its "true value" (not necessarily observable). The error of an observation is the deviation of the observed value from the true value of a quantity of interest (for example, a population mean). The residual is the difference between the observed value and the ''estimated'' value of the quantity of interest (for example, a sample mean). The distinction is most important in regression analysis, where the concepts are sometimes called the regression errors and regression residuals and where they lead to the concept of studentized residuals. In econometrics, "errors" are also called disturbances. Introduction Suppose there is a series of observations from a univariate distribution and we want to estimate the mean of that distribution (the so-called location model). In this case, the errors are th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Measurement Uncertainty
In metrology, measurement uncertainty is the expression of the statistical dispersion of the values attributed to a measured quantity. All measurements are subject to uncertainty and a measurement result is complete only when it is accompanied by a statement of the associated uncertainty, such as the standard deviation. By international agreement, this uncertainty has a probabilistic basis and reflects incomplete knowledge of the quantity value. It is a non-negative parameter. The measurement uncertainty is often taken as the standard deviation of a state-of-knowledge probability distribution over the possible values that could be attributed to a measured quantity. Relative uncertainty is the measurement uncertainty relative to the magnitude of a particular single choice for the value for the measured quantity, when this choice is nonzero. This particular single choice is usually called the measured value, which may be optimal in some well-defined sense (e.g., a mean, median, or m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Deviation
In statistics, the standard deviation is a measure of the amount of variation or dispersion of a set of values. A low standard deviation indicates that the values tend to be close to the mean (also called the expected value) of the set, while a high standard deviation indicates that the values are spread out over a wider range. Standard deviation may be abbreviated SD, and is most commonly represented in mathematical texts and equations by the lower case Greek letter σ (sigma), for the population standard deviation, or the Latin letter '' s'', for the sample standard deviation. The standard deviation of a random variable, sample, statistical population, data set, or probability distribution is the square root of its variance. It is algebraically simpler, though in practice less robust, than the average absolute deviation. A useful property of the standard deviation is that, unlike the variance, it is expressed in the same unit as the data. The standard deviation of a popu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Error
The standard error (SE) of a statistic (usually an estimate of a parameter) is the standard deviation of its sampling distribution or an estimate of that standard deviation. If the statistic is the sample mean, it is called the standard error of the mean (SEM). The sampling distribution of a mean is generated by repeated sampling from the same population and recording of the sample means obtained. This forms a distribution of different means, and this distribution has its own mean and variance. Mathematically, the variance of the sampling mean distribution obtained is equal to the variance of the population divided by the sample size. This is because as the sample size increases, sample means cluster more closely around the population mean. Therefore, the relationship between the standard error of the mean and the standard deviation is such that, for a given sample size, the standard error of the mean equals the standard deviation divided by the square root of the sample size. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
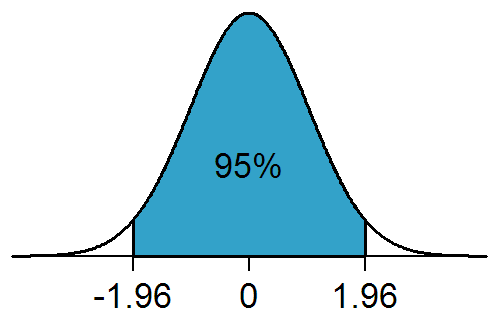
Confidence Interval
In frequentist statistics, a confidence interval (CI) is a range of estimates for an unknown parameter. A confidence interval is computed at a designated ''confidence level''; the 95% confidence level is most common, but other levels, such as 90% or 99%, are sometimes used. The confidence level represents the long-run proportion of corresponding CIs that contain the true value of the parameter. For example, out of all intervals computed at the 95% level, 95% of them should contain the parameter's true value. Factors affecting the width of the CI include the sample size, the variability in the sample, and the confidence level. All else being the same, a larger sample produces a narrower confidence interval, greater variability in the sample produces a wider confidence interval, and a higher confidence level produces a wider confidence interval. Definition Let be a random sample from a probability distribution with statistical parameter , which is a quantity to be estimate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistically Significant
In statistical hypothesis testing, a result has statistical significance when it is very unlikely to have occurred given the null hypothesis (simply by chance alone). More precisely, a study's defined significance level, denoted by \alpha, is the probability of the study rejecting the null hypothesis, given that the null hypothesis is true; and the p-value, ''p''-value of a result, ''p'', is the probability of obtaining a result at least as extreme, given that the null hypothesis is true. The result is statistically significant, by the standards of the study, when p \le \alpha. The significance level for a study is chosen before data collection, and is typically set to 5% or much lower—depending on the field of study. In any experiment or Observational study, observation that involves drawing a Sampling (statistics), sample from a Statistical population, population, there is always the possibility that an observed effect would have occurred due to sampling error alone. But if the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goodness Of Fit
The goodness of fit of a statistical model describes how well it fits a set of observations. Measures of goodness of fit typically summarize the discrepancy between observed values and the values expected under the model in question. Such measures can be used in statistical hypothesis testing, e.g. to test for normality of residuals, to test whether two samples are drawn from identical distributions (see Kolmogorov–Smirnov test), or whether outcome frequencies follow a specified distribution (see Pearson's chi-square test). In the analysis of variance, one of the components into which the variance is partitioned may be a lack-of-fit sum of squares. Fit of distributions In assessing whether a given distribution is suited to a data-set, the following tests and their underlying measures of fit can be used: * Bayesian information criterion *Kolmogorov–Smirnov test *Cramér–von Mises criterion *Anderson–Darling test * Shapiro–Wilk test *Chi-squared test *Akaike informat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Style Guide
A style guide or manual of style is a set of standards for the writing, formatting, and design of documents. It is often called a style sheet, although that term also has multiple other meanings. The standards can be applied either for general use, or be required usage for an individual publication, a particular organization, or a specific field. A style guide establishes standard style requirements to improve communication by ensuring consistency both within a document, and across multiple documents. Because practices vary, a style guide may set out standards to be used in areas such as punctuation, capitalization, citing sources, formatting of numbers and dates, table appearance and other areas. The style guide may require certain best practices in writing style, usage, language composition, visual composition, orthography, and typography. For academic and technical documents, a guide may also enforce the best practice in ethics (such as authorship, research ethics, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Manipulation Interface
In computer science, human–computer interaction, and interaction design, direct manipulation is an approach to interfaces which involves continuous representation of objects of interest together with rapid, reversible, and incremental actions and feedback. As opposed to other interaction styles, for example, the command language, the intention of direct manipulation is to allow a user to manipulate objects presented to them, using actions that correspond at least loosely to manipulation of physical objects. An example of direct manipulation is resizing a graphical shape, such as a rectangle, by dragging its corners or edges with a mouse. Having real-world metaphors for objects and actions can make it easier for a user to learn and use an interface (some might say that the interface is more natural or intuitive), and rapid, incremental feedback allows a user to make fewer errors and complete tasks in less time, because they can see the results of an action before completing the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plus–minus Sign
The plus–minus sign, , is a mathematical symbol with multiple meanings. *In mathematics, it generally indicates a choice of exactly two possible values, one of which is obtained through addition and the other through subtraction. *In experimental sciences, the sign commonly indicates the confidence interval or uncertainty bounding a range of possible errors in a measurement, often the standard deviation or standard error. The sign may also represent an inclusive range of values that a reading might have. *In medicine, it means "with or without". *In engineering, the sign indicates the tolerance, which is the range of values that are considered to be acceptable, safe, or which comply with some standard or with a contract. *In botany, it is used in morphological descriptions to notate "more or less". *In chemistry, the sign is used to indicate a racemic mixture. *In chess, the sign indicates a clear advantage for the white player; the complementary minus-or-plus sign, , indicate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |