|
Entropy Encoding
In information theory, an entropy coding (or entropy encoding) is any lossless data compression method that attempts to approach the lower bound declared by Shannon's source coding theorem, which states that any lossless data compression method must have expected code length greater or equal to the entropy of the source. More precisely, the source coding theorem states that for any source distribution, the expected code length satisfies \mathbb E_ (d(x))\geq \mathbb E_ \log_b(P(x))/math>, where l is the number of symbols in a code word, d is the coding function, b is the number of symbols used to make output codes and P is the probability of the source symbol. An entropy coding attempts to approach this lower bound. Two of the most common entropy coding techniques are Huffman coding and arithmetic coding. If the approximate entropy characteristics of a data stream are known in advance (especially for signal compression), a simpler static code may be useful. These static codes in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Theory
Information theory is the scientific study of the quantification (science), quantification, computer data storage, storage, and telecommunication, communication of information. The field was originally established by the works of Harry Nyquist and Ralph Hartley, in the 1920s, and Claude Shannon in the 1940s. The field is at the intersection of probability theory, statistics, computer science, statistical mechanics, information engineering (field), information engineering, and electrical engineering. A key measure in information theory is information entropy, entropy. Entropy quantifies the amount of uncertainty involved in the value of a random variable or the outcome of a random process. For example, identifying the outcome of a fair coin flip (with two equally likely outcomes) provides less information (lower entropy) than specifying the outcome from a roll of a dice, die (with six equally likely outcomes). Some other important measures in information theory are mutual informat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asymmetric Numeral Systems
Asymmetric numeral systems (ANS)J. Duda, K. Tahboub, N. J. Gadil, E. J. Delp''The use of asymmetric numeral systems as an accurate replacement for Huffman coding'' Picture Coding Symposium, 2015.J. Duda''Asymmetric numeral systems: entropy coding combining speed of Huffman coding with compression rate of arithmetic coding'' arXiv:1311.2540, 2013. is a family of entropy encoding methods introduced by Jarosław (Jarek) Duda from Jagiellonian University, used in data compression since 2014 due to improved performance compared to previous methods. ANS combines the compression ratio of arithmetic coding (which uses a nearly accurate probability distribution), with a processing cost similar to that of Huffman coding. In the tabled ANS (tANS) variant, this is achieved by constructing a finite-state machine to operate on a large alphabet without using multiplication. Among others, ANS is used in the Facebook Zstandard compressor [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Wiegand
Thomas Wiegand (born 6 May 1970 in Wismar) is a German electrical engineer who substantially contributed to the creation of the H.264/AVC, H.265/HEVC, and H.266/VVC video coding standards. For H.264/AVC, Wiegand was one of the chairmen of the Joint Video Team (JVT) standardization committee that created the standard and was the chief editor of the standard itself. He was also a very active technical contributor to the H.264/AVC, H.265/HEVC, and H.266/VVC video coding standards. Wiegand also holds a chairmanship position in the ITU-T VCEG of ITU-T Study Group 16 and previously in ISO/IEC MPEG standardization organizations. In July 2006, the video coding work of the ITU-T jointly led by Gary J. Sullivan and Wiegand for the preceding six years was voted as the most influential area of the standardization work of the CCITT and ITU-T in their 50-year history. Since 2018, Wiegand has served as chair of the ITU/WHO Focus Group on Artificial Intelligence for Health (FG-AI4H). Sinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David MacKay (scientist)
Professor Sir David John Cameron MacKay (22 April 1967 – 14 April 2016) was a British physicist, mathematician, and academic. He was the Regius Professor of Engineering in the Department of Engineering at the University of Cambridge and from 2009 to 2014 was Chief Scientific Advisor to the UK Department of Energy and Climate Change (DECC). MacKay wrote the book ''Sustainable Energy – Without the Hot Air''. Education MacKay was educated at Newcastle High School and represented Britain in the International Physics Olympiad in Yugoslavia in 1985, receiving the first prize for experimental work. He continued his education at Trinity College, Cambridge, and received a Bachelor of Arts degree in Natural Sciences (Experimental and theoretical physics) in 1988. He went to the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) as a Fulbright Scholar, where his supervisor was John Hopfield. He was awarded a PhD in 1992. Career and research In January 1992 MacKay was appointed the Roya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
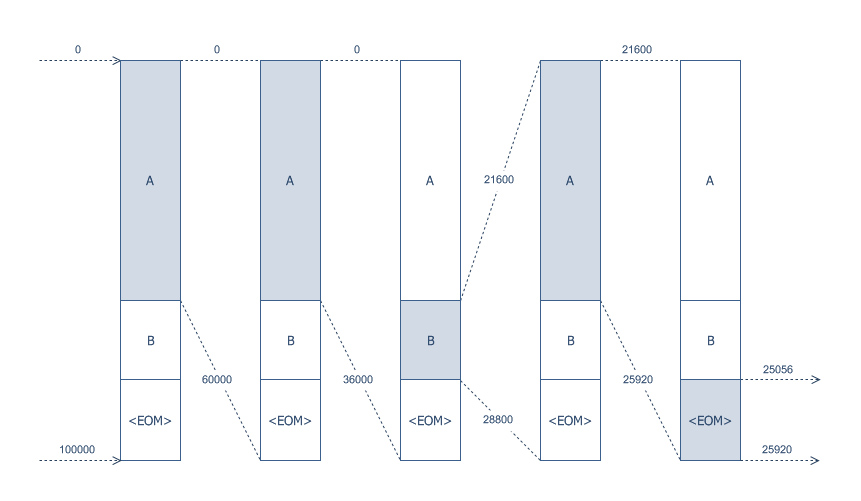
Range Coding
Range coding (or range encoding) is an entropy coding method defined by G. Nigel N. Martin in a 1979 paper,, 100000)) using the probability distribution . The encoder breaks down the range [0, 100000) into three subranges: A: [ 0, 60000) B: [ 60000, 80000) : [ 80000, 100000) Since our first symbol is an A, it reduces our initial range down to [0, 60000). The second symbol choice leaves us with three sub-ranges of this range. We show them following the already-encoded 'A': AA: [ 0, 36000) AB: [ 36000, 48000) A: [ 48000, 60000) With two symbols encoded, our range is now [0, 36000) and our third symbol leads to the following choices: AAA: [ 0, 21600) AAB: [ 21600, 28800) AA: [ 28800, 36000) This time it is the second of our three choices that represent the message we want to encode, and our range becomes [21600, 28800). It may look harder to determine our sub-ranges in this case, but it is actually not: we can mere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Context-adaptive Binary Arithmetic Coding
Context-adaptive binary arithmetic coding (CABAC) is a form of entropy encoding used in the H.264/MPEG-4 AVC and High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC) standards. It is a lossless compression technique, although the video coding standards in which it is used are typically for lossy compression applications. CABAC is notable for providing much better compression than most other entropy encoding algorithms used in video encoding, and it is one of the key elements that provides the H.264/AVC encoding scheme with better compression capability than its predecessors. In H.264/MPEG-4 AVC, CABAC is only supported in the Main and higher profiles (but not the extended profile) of the standard, as it requires a larger amount of processing to decode than the simpler scheme known as context-adaptive variable-length coding (CAVLC) that is used in the standard's Baseline profile. CABAC is also difficult to parallelize and vectorize, so other forms of parallelism (such as spatial region parallelis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asymmetric Numeral Systems
Asymmetric numeral systems (ANS)J. Duda, K. Tahboub, N. J. Gadil, E. J. Delp''The use of asymmetric numeral systems as an accurate replacement for Huffman coding'' Picture Coding Symposium, 2015.J. Duda''Asymmetric numeral systems: entropy coding combining speed of Huffman coding with compression rate of arithmetic coding'' arXiv:1311.2540, 2013. is a family of entropy encoding methods introduced by Jarosław (Jarek) Duda from Jagiellonian University, used in data compression since 2014 due to improved performance compared to previous methods. ANS combines the compression ratio of arithmetic coding (which uses a nearly accurate probability distribution), with a processing cost similar to that of Huffman coding. In the tabled ANS (tANS) variant, this is achieved by constructing a finite-state machine to operate on a large alphabet without using multiplication. Among others, ANS is used in the Facebook Zstandard compressor [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arithmetic Coding
Arithmetic coding (AC) is a form of entropy encoding used in lossless data compression. Normally, a string of characters is represented using a fixed number of bits per character, as in the ASCII code. When a string is converted to arithmetic encoding, frequently used characters will be stored with fewer bits and not-so-frequently occurring characters will be stored with more bits, resulting in fewer bits used in total. Arithmetic coding differs from other forms of entropy encoding, such as Huffman coding, in that rather than separating the input into component symbols and replacing each with a code, arithmetic coding encodes the entire message into a single number, an arbitrary-precision fraction ''q'', where . It represents the current information as a range, defined by two numbers. A recent family of entropy coders called asymmetric numeral systems allows for faster implementations thanks to directly operating on a single natural number representing the current information., b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistical Classification
In statistics, classification is the problem of identifying which of a set of categories (sub-populations) an observation (or observations) belongs to. Examples are assigning a given email to the "spam" or "non-spam" class, and assigning a diagnosis to a given patient based on observed characteristics of the patient (sex, blood pressure, presence or absence of certain symptoms, etc.). Often, the individual observations are analyzed into a set of quantifiable properties, known variously as explanatory variables or ''features''. These properties may variously be categorical (e.g. "A", "B", "AB" or "O", for blood type), ordinal (e.g. "large", "medium" or "small"), integer-valued (e.g. the number of occurrences of a particular word in an email) or real-valued (e.g. a measurement of blood pressure). Other classifiers work by comparing observations to previous observations by means of a similarity or distance function. An algorithm that implements classification, especially in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Stream
In connection-oriented communication, a data stream is the transmission of a sequence of digitally encoded coherent signals to convey information. Typically, the transmitted symbols are grouped into a series of packets. Data streaming has become ubiquitous. Anything transmitted over the Internet is transmitted as a data stream. Using a mobile phone to have a conversation transmits the sound as a data stream. Formal definition In a formal way, a data stream is any ordered pair ( s, \Delta ) where: # s is a sequence of tuples and # \Delta is a sequence of positive real time intervals. Content Data Stream contains different sets of data, that depend on the chosen data format. * Attributes – each attribute of the data stream represents a certain type of data, e.g. segment / data point ID, timestamp, geodata. * Timestamp attribute helps to identify when an event occurred. * Subject ID is an encoded-by-algorithm ID, that has been extracted out of a cookie. * Raw Data inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Similarity Measure
In statistics and related fields, a similarity measure or similarity function or similarity metric is a real-valued function that quantifies the similarity between two objects. Although no single definition of a similarity exists, usually such measures are in some sense the inverse of distance metrics: they take on large values for similar objects and either zero or a negative value for very dissimilar objects. Though, in more broad terms, a similarity function may also satisfy metric axioms. Cosine similarity is a commonly used similarity measure for real-valued vectors, used in (among other fields) information retrieval to score the similarity of documents in the vector space model. In machine learning, common kernel functions such as the RBF kernel can be viewed as similarity functions. Use in clustering In spectral clustering, a similarity, or affinity, measure is used to transform data to overcome difficulties related to lack of convexity in the shape of the data distribut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rice Coding
Golomb coding is a lossless data compression method using a family of data compression codes invented by Solomon W. Golomb in the 1960s. Alphabets following a geometric distribution will have a Golomb code as an optimal prefix code, making Golomb coding highly suitable for situations in which the occurrence of small values in the input stream is significantly more likely than large values. Rice coding Rice coding (invented by Robert F. Rice) denotes using a subset of the family of Golomb codes to produce a simpler (but possibly suboptimal) prefix code. Rice used this set of codes in an adaptive coding scheme; "Rice coding" can refer either to that adaptive scheme or to using that subset of Golomb codes. Whereas a Golomb code has a tunable parameter that can be any positive integer value, Rice codes are those in which the tunable parameter is a power of two. This makes Rice codes convenient for use on a computer since multiplication and division by 2 can be implemented more e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |